UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
|
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016
or
|
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 1-13395
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Delaware |
|
56-2010790 |
|
(State or other jurisdiction of |
|
(I.R.S. Employer |
|
incorporation or organization) |
|
Identification No.) |
|
4401 Colwick Road |
|
|
|
Charlotte, North Carolina |
|
28211 |
|
(Address of principal executive offices) |
|
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (704) 566-2400
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Title of each class |
|
Name of each exchange on which registered |
|
Class A common stock, $0.01 par value |
|
New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer ☒ |
Accelerated filer ☐ |
|
Non-accelerated filer ☐ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Smaller reporting company ☐ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). ☐ Yes ☒ No
The aggregate market value of the voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $554.9 million based upon the closing sales price of the registrant’s Class A common stock on June 30, 2016 of $17.11 per share.
As of February 21, 2017, there were 32,855,850 shares of Class A common stock, par value $0.01 per share, and 12,029,375 shares of Class B common stock, par value $0.01 per share, outstanding.
Documents incorporated by reference. Portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held April 18, 2017 are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
UNCERTAINTY OF FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS AND INFORMATION
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains, and written or oral statements made from time to time by us or by our authorized officers may contain, “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements address our future objectives, plans and goals, as well as our intent, beliefs and current expectations regarding future operating performance, results and events, and can generally be identified by words such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “believe,” “expect,” “estimate,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “plan,” “foresee” and other similar words or phrases.
These forward-looking statements are based on our current estimates and assumptions and involve various risks and uncertainties. As a result, you are cautioned that these forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance, and that actual results could differ materially from those projected in these forward-looking statements. Factors which may cause actual results to differ materially from our projections include those risks described in “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and elsewhere in this report, as well as:
|
|
• |
the number of new and used vehicles sold in the United States as compared to our expectations and the expectations of the market; |
|
|
• |
our ability to generate sufficient cash flows or obtain additional financing to fund our EchoPark® expansion, our One Sonic-One Experience initiative, capital expenditures, our share repurchase program, dividends on our common stock, acquisitions and general operating activities; |
|
|
• |
our business and growth strategies, including, but not limited to, our EchoPark® initiative and our One Sonic-One Experience initiative; |
|
|
• |
the reputation and financial condition of vehicle manufacturers whose brands we represent, the financial incentives vehicle manufacturers offer and their ability to design, manufacture, deliver and market their vehicles successfully; |
|
|
• |
our relationships with manufacturers, which may affect our ability to obtain desirable new vehicle models in inventory or complete additional acquisitions; |
|
|
• |
adverse resolution of one or more significant legal proceedings against us or our dealerships or EchoPark® stores; |
|
|
• |
changes in laws and regulations governing the operation of automobile franchises, accounting standards, taxation requirements and environmental laws; |
|
|
• |
general economic conditions in the markets in which we operate, including fluctuations in interest rates, employment levels, the level of consumer spending and consumer credit availability; |
|
|
• |
high competition in the automotive retailing industry, which not only creates pricing pressures on the products and services we offer, but also on businesses we may seek to acquire; |
|
|
• |
our ability to successfully integrate potential future acquisitions; and |
|
|
• |
the rate and timing of overall economic recovery or decline. |
These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this report or when made, and we undertake no obligation to revise or update these statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances, except as required under the federal securities laws and the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2016
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
|
|
|
PAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1. |
|
|
1 |
|
|
Item 1A. |
|
|
9 |
|
|
Item 1B. |
|
|
23 |
|
|
Item 2. |
|
|
23 |
|
|
Item 3. |
|
|
23 |
|
|
Item 4. |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5. |
|
|
24 |
|
|
Item 6. |
|
|
25 |
|
|
Item 7. |
|
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
|
27 |
|
Item 7A. |
|
|
61 |
|
|
Item 8. |
|
|
62 |
|
|
Item 9. |
|
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
|
62 |
|
Item 9A. |
|
|
62 |
|
|
Item 9B. |
|
|
63 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 10. |
|
|
64 |
|
|
Item 11. |
|
|
64 |
|
|
Item 12. |
|
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
|
64 |
|
Item 13. |
|
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
|
64 |
|
Item 14. |
|
|
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 15. |
|
|
65 |
|
|
Item 16. |
|
|
71 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
72 |
|||
|
|
73 |
|||
|
|
||||
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
Sonic Automotive, Inc. was incorporated in Delaware in 1997. We are one of the largest automotive retailers in the United States (as measured by total revenue). As of December 31, 2016, we operated 116 franchises in 13 states (representing 25 different brands of cars and light trucks) and 18 collision repair centers. For management and operational reporting purposes, we group certain franchises together that share management and inventory (principally used vehicles) into “stores.” As of December 31, 2016, we operated 107 franchised dealership stores and five EchoPark® stores.
Our franchised dealerships provide comprehensive services, including (1) sales of both new and used cars and light trucks; (2) sales of replacement parts and performance of vehicle maintenance, manufacturer warranty repairs, and paint and collision repair services (collectively, “Fixed Operations”); and (3) arrangement of extended warranties, service contracts, financing, insurance and other aftermarket products (collectively, “F&I”) for our customers.
EchoPark® provides the same services (excluding new vehicle sales and manufacturer warranty repairs) in unique stand-alone specialty retail locations. Our EchoPark® business operates independently from our franchised new and used dealership sales operations. Sales operations in our first EchoPark® market in Denver, Colorado began in the fourth quarter of 2014. As of December 31, 2016, we had five EchoPark® stores in operation, and we expect to open another store in Colorado in the first half of 2017. During the second quarter of 2016, we announced that we have begun the process of expanding EchoPark® operations into additional markets in North Carolina, South Carolina and Texas with operations in these markets expected to begin in 2017 and 2018. We believe that our EchoPark® business will provide long-term benefits to us, our stockholders and guests. However, in the short term, this initiative may negatively impact our overall operating results as we allocate management and capital resources to this business.
References to “Sonic,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” and “our” used throughout this Annual Report on Form 10-K refer to Sonic Automotive, Inc. and its subsidiaries.
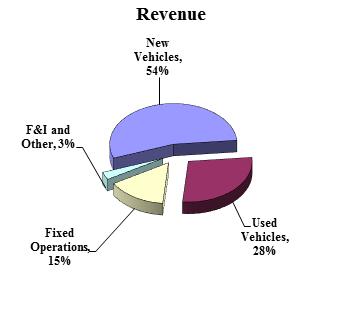
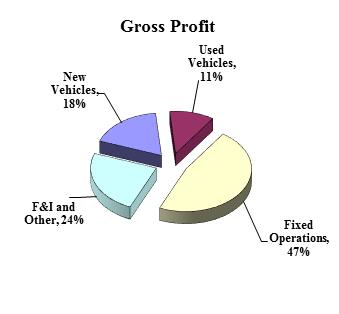
The following charts depict the multiple sources of continuing operations revenue and gross profit for the year ended December 31, 2016:


1
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
As of December 31, 2016, we operated in the following states:
|
Market |
|
Number of Franchises |
|
|
Percent of 2016 Total Revenue |
|
||
|
California |
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
30.3 |
% |
|
Texas |
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
25.0 |
% |
|
Tennessee |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
7.3 |
% |
|
Florida |
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
6.1 |
% |
|
Alabama |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
5.3 |
% |
|
Colorado |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
4.7 |
% |
|
Georgia |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
3.5 |
% |
|
North Carolina |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
3.2 |
% |
|
Virginia |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2.9 |
% |
|
Ohio |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
2.7 |
% |
|
Maryland |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
2.7 |
% |
|
South Carolina |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
2.4 |
% |
|
Nevada |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
2.1 |
% |
|
Disposed franchises and holding companies |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
0.5 |
% |
|
Total Franchised Dealerships |
|
|
116 |
|
|
|
98.7 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EchoPark® - Colorado |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
1.3 |
% |
|
Total |
|
|
121 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
% |
In the future, we may purchase dealerships and open new stores that we believe will enrich our portfolio and divest dealerships or close stores that we believe will not yield acceptable returns over the long term. The automotive retailing industry remains highly fragmented, and we believe that further consolidation may occur. We believe that attractive acquisition opportunities continue to exist for dealership groups with the capital and experience to identify, acquire and professionally manage dealerships. Our ability to complete acquisitions and open new stores in the future will depend on many factors, including the availability of financing and the existence of any contractual provisions that may restrict our acquisition activity.
See “Item 7 Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations – Liquidity and Capital Resources,” for a discussion of our plans for the use of capital generated from operations.
Operating Segments
As of December 31, 2016, we had two operating segments: Franchised Dealerships and EchoPark®. The Franchised Dealerships segment is comprised of retail automotive franchises that sell new vehicles and buy and sell used vehicles, sell replacement parts, perform vehicle repair and maintenance services, and arrange finance and insurance products. The EchoPark® segment is comprised of stand-alone specialty retail locations that provide customers an opportunity to search, buy, service, finance and sell pre-owned vehicles.
For the year ended December 31, 2016, EchoPark® revenue represented approximately 1.3% of total revenue. See Note 14, “Segment Information,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for additional financial information regarding our two operating segments.
Unless otherwise noted, the following discussion of our business is presented on a consolidated basis.
Business Strategy
Execute our Stand-Alone Pre-Owned Store Initiative. We have augmented our manufacturer-franchised dealership operations with our EchoPark® stand-alone pre-owned specialty retail locations. Our EchoPark® business operates independently from our franchised new and used dealership sales operations and offers customers an exciting shopping and buying experience. Sales operations for our EchoPark® initiative began in Denver, Colorado in the fourth quarter of 2014. As of December 31, 2016, we had five EchoPark® stores in operation, and expect to open an additional EchoPark® store in Colorado in the first half of 2017.
Execute our Customer Experience Initiative. Our One Sonic-One Experience (“OSOE”) initiative includes several new processes and proprietary technologies from inventory management, electronic desking and pricing tools to a fully developed “customer-centric” Customer Relationship Management tool. We believe that the development of these processes and technologies
2
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
will allow us to better serve our customers across our entire platform of stores. Our goal is to allow our guests to control the buying process and move at their pace so that once the vehicle has been selected our team can utilize these processes and technologies to allow our guests to complete a new or pre-owned vehicle sales transaction in less than an hour. During the latter half of 2014 and throughout 2015, we rolled out the OSOE initiative at our dealerships in Charlotte, North Carolina. In 2016, we introduced the technology component of the initiative to 14 additional stores in our Alabama, Tennessee and California markets.
Achieve High Levels of Customer Satisfaction. We focus on maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction. Our personalized sales process is designed to satisfy customers by providing high-quality vehicles and service in a positive, “consumer friendly” buying environment. Several manufacturers offer specific financial incentives on a per vehicle basis if certain Customer Satisfaction Index (“CSI”) levels (which vary by manufacturer) are achieved by a dealership. In addition, all manufacturers consider CSI scores in approving acquisitions or awarding new dealership open points. In order to keep dealership and executive management focused on customer satisfaction, we include CSI results as a component of our incentive-based compensation programs for certain groups of associates.
Invest in Dealership Properties. Historically, we have operated our dealerships primarily on property financed through long-term operating leases. As these leases mature, or as we have an opportunity to purchase the underlying real estate prior to renewal, we take actions to own more of our dealership properties when the effect is financially or operationally favorable to us. We remain opportunistic in purchasing existing properties or relocating dealership operations to owned real estate where the returns are favorable. We believe owning our properties will, over the long term, strengthen our balance sheet and reduce our overall cost of operating and financing our facilities.
Improve Capital Structure. As we generate cash through operations, we will opportunistically repurchase our Class A common stock in open-market or structured transactions.
Maximize Asset Returns Through Process Execution. We have developed standardized operating processes that are documented in operating playbooks for our dealerships. Through the continued implementation of our operating playbooks, we believe organic growth opportunities exist by offering a more favorable buying experience to our customers and creating efficiencies in our business processes. We believe the development, refinement and implementation of these operating processes will enhance the customer experience, make us more competitive in the markets we serve and drive profit growth across each of our revenue streams.
Maintain Diverse Revenue Streams. We have multiple revenue streams. In addition to new vehicle sales, our revenue sources include used vehicle sales, which we believe are less sensitive to economic cycles and seasonal influences that exist with new vehicle sales. Our Fixed Operations sales carry a higher gross margin than new and used vehicle sales and, in the past, have not been as economically sensitive as new vehicle sales. We also offer customers assistance in obtaining financing and a range of automobile related warranty, aftermarket and insurance products.
Manage Portfolio. Our long-term growth and acquisition strategy is focused on large metropolitan markets, predominantly in the Southeast, Southwest, Midwest and California. We seek to add like-branded dealerships to our portfolio that exist in regions in which we already operate; however, we may look outside of our existing geographic footprint when considering the location of new EchoPark® stores. A majority of our franchised dealerships are either luxury or mid-line import brands. For the year ended December 31, 2016, approximately 88.1% of our total new vehicle revenue was generated by luxury and mid-line import dealerships, which usually have higher operating margins, more stable Fixed Operations departments, lower associate turnover and lower inventory levels.
3
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
The following table depicts the breakdown of our new vehicle revenues from continuing operations by brand:
|
|
|
Percentage of New Vehicle Revenue |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
Brand |
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Luxury: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BMW |
|
|
20.2 |
% |
|
|
21.7 |
% |
|
|
21.8 |
% |
|
Mercedes |
|
|
10.6 |
% |
|
|
9.7 |
% |
|
|
9.6 |
% |
|
Lexus |
|
|
5.9 |
% |
|
|
5.6 |
% |
|
|
5.2 |
% |
|
Audi |
|
|
5.3 |
% |
|
|
4.8 |
% |
|
|
5.0 |
% |
|
Land Rover |
|
|
3.3 |
% |
|
|
4.0 |
% |
|
|
2.8 |
% |
|
Cadillac |
|
|
3.3 |
% |
|
|
3.2 |
% |
|
|
4.1 |
% |
|
Porsche |
|
|
2.3 |
% |
|
|
2.5 |
% |
|
|
2.4 |
% |
|
MINI |
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
|
1.9 |
% |
|
|
2.1 |
% |
|
Other luxury (1) |
|
|
3.0 |
% |
|
|
3.1 |
% |
|
|
3.1 |
% |
|
Total Luxury |
|
|
55.5 |
% |
|
|
56.5 |
% |
|
|
56.1 |
% |
|
Mid-line Import: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Honda |
|
|
16.8 |
% |
|
|
15.5 |
% |
|
|
14.9 |
% |
|
Toyota |
|
|
11.4 |
% |
|
|
11.1 |
% |
|
|
10.4 |
% |
|
Volkswagen |
|
|
1.5 |
% |
|
|
1.7 |
% |
|
|
1.9 |
% |
|
Hyundai |
|
|
1.2 |
% |
|
|
1.4 |
% |
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
Other imports (2) |
|
|
1.7 |
% |
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
|
2.3 |
% |
|
Total Mid-line Import |
|
|
32.6 |
% |
|
|
31.3 |
% |
|
|
31.1 |
% |
|
Domestic: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ford |
|
|
6.8 |
% |
|
|
6.8 |
% |
|
|
7.3 |
% |
|
General Motors (3) |
|
|
5.1 |
% |
|
|
5.4 |
% |
|
|
5.5 |
% |
|
Total Domestic |
|
|
11.9 |
% |
|
|
12.2 |
% |
|
|
12.8 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
100.0 |
% |
|
|
100.0 |
% |
|
|
100.0 |
% |
(1) Includes Volvo, Acura, Infiniti, Jaguar and Smart.
(2) Includes Nissan, Kia, Scion and Subaru.
(3) Includes Buick, Chevrolet and GMC.
Expand our eCommerce Capabilities. Automotive customers have become increasingly more comfortable using technology to research their vehicle buying alternatives and communicate with dealership personnel. The internet presents a marketing, advertising and automotive sales channel that we will continue to utilize to drive value for our dealerships and enhance the customer experience. Our technology platforms give us the ability to leverage technology to efficiently integrate systems, customize our dealership websites and use our data to improve the effectiveness of our advertising and interaction with our customers. These platforms also allow us to market all of our products and services to a national audience and, at the same time, support the local market penetration of our individual dealerships.
Train, Develop and Retain Associates. We believe our associates are the cornerstone of our business and crucial to our financial success. Our goal is to develop our associates and foster an environment where our associates can contribute and grow with the Company. Associate satisfaction is very important to us, and we believe a high level of associate satisfaction reduces associate turnover and enhances our customers’ experience at our dealerships by pairing our customers with well-trained associates. We believe that our comprehensive training of all employees provides us with a competitive advantage over other dealership groups.
Increase Sales of Higher-Margin Products and Services. We continue to pursue opportunities to increase our sales of higher-margin products and services by expanding the following:
Finance, Insurance and Other Aftermarket Products. Each sale of a new or used vehicle gives us an opportunity to provide our customers with financing and insurance options and earn financing fees and insurance commissions. We also offer our customers the opportunity to purchase extended warranties, service contracts and other aftermarket products. We currently offer a wide range of non-recourse financing, leasing, other aftermarket products, extended warranties, service contracts and insurance
4
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
products to our customers. We emphasize menu-selling techniques and other best practices to increase our sales of F&I products at our dealerships.
Parts, Service and Collision Repair. Each of our franchised dealerships offers a fully integrated service and parts department. Manufacturers permit warranty work to be performed only at franchised dealerships such as ours. As a result, our franchised dealerships are uniquely qualified and positioned to perform work covered by manufacturer warranties on increasingly complex vehicles. We believe we can continue to grow our profitable parts and service business over the long term by increasing service capacity, investing in sophisticated equipment and well-trained technicians, using variable rate pricing structures, focusing on customer service and efficiently managing our parts inventory. In addition, we believe our emphasis on selling extended service contracts associated with new and used vehicle retail sales will drive further service and parts business in our dealerships as we increase the potential to retain current customers beyond the term of the standard manufacturer warranty period.
Certified Pre-Owned Vehicles. Various manufacturers provide franchised dealers the opportunity to sell certified pre-owned (“CPO”) vehicles. This certification process extends the standard manufacturer warranty on the CPO vehicle, which we believe increases our potential to retain the pre-owned purchaser as a future parts and service customer. Since CPO warranty work can only be performed at franchised dealerships, we believe CPO warranty work adds additional stability and will increase our Fixed Operations business.
Relationships with Manufacturers
Each of our dealerships operates under a separate franchise or dealer agreement that governs the relationship between the dealership and the manufacturer. Each franchise or dealer agreement specifies the location of the dealership for the sale of vehicles and for the performance of certain approved services in a specified market area. The designation of such areas generally does not guarantee exclusivity within a specified territory. In addition, most manufacturers allocate vehicles on a “turn and earn” basis that rewards high unit sales volume. A franchise or dealer agreement incentivizes the dealer to meet specified standards regarding showrooms, facilities and equipment for servicing vehicles, inventories, minimum net working capital, personnel training and other aspects of the business. Each franchise or dealer agreement also gives the related manufacturer the right to approve the dealer operator and any material change in management or ownership of the dealership. Each manufacturer may terminate a franchise or dealer agreement under certain circumstances, such as a change in control of the dealership without manufacturer approval, the impairment of the reputation or financial condition of the dealership, the death, removal or withdrawal of the dealer operator, the conviction of the dealership or the dealership’s owner or dealer operator of certain crimes, the failure to adequately operate the dealership or maintain new vehicle financing arrangements, insolvency or bankruptcy of the dealership or a material breach of other provisions of the applicable franchise or dealer agreement.
Many automobile manufacturers have developed and implemented policies regarding public ownership of dealerships, which include the ability to force the sale of their respective franchises:
|
|
• |
upon a change in control of our company or a material change in the composition of our Board of Directors; |
|
|
• |
if an automobile manufacturer or distributor acquires more than 5% of the voting power of our securities; and |
|
|
• |
if an individual or entity (other than an automobile manufacturer or distributor) acquires more than 20% of the voting power of our securities, and the manufacturer disapproves of such individual’s or entity’s ownership interest. |
To the extent that new or amended manufacturer policies restrict the number of dealerships that may be owned by a dealership group or the transferability of our common stock, such policies could have a material adverse effect on us. We believe that we will be able to renew at expiration all of our existing franchise and dealer agreements.
Many states have placed limitations upon manufacturers’ and distributors’ ability to sell new motor vehicles directly to customers in their respective states in an effort to protect dealers from practices they believe constitute unfair competition. In general, these statutes make it unlawful for a manufacturer or distributor to compete with a new motor vehicle dealer in the same brand operating under an agreement or franchise from the manufacturer or distributor in the relevant market area. Certain states, including Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina and Virginia, limit the amount of time that a manufacturer or distributor may temporarily operate a dealership.
In addition, all of the states in which our dealerships currently do business require manufacturers or distributors to show “good cause” for terminating or failing to renew a dealer’s franchise or dealer agreement. Further, each of the states provides some method for dealers to challenge manufacturer attempts to establish dealerships of the same brand in their relevant market area.
5
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
Competition
The retail automotive industry is highly competitive. Depending on the geographic market, we compete both with dealers offering the same brands and product lines as ours and dealers offering other manufacturers’ vehicles. We also compete for vehicle sales with auto brokers, leasing companies and services offered on the internet that provide customer referrals to other dealerships or who broker vehicle sales between customers and other dealerships. We compete with small, local dealerships and with large multi-franchise and pre-owned automotive dealership groups.
We believe that the principal competitive factors in vehicle sales are the customer experience provided, the location of dealerships, the marketing campaigns conducted by manufacturers, the ability of dealerships to offer an attractive selection of the most popular vehicles and the quality of services and pricing (including manufacturer rebates and other special offers). In particular, pricing has become more important as a result of price-savvy customers using sources available on the internet to determine current market retail prices. Other competitive factors include customer preference for makes of automobiles and coverage under manufacturer warranties.
In addition to competition for vehicle sales, we also compete with other auto dealers, service stores, auto parts retailers and independent mechanics in providing parts and service. We believe that the principal competitive factors in parts and service sales are price, the use of factory-approved replacement parts, factory-trained technicians, the familiarity with a manufacturer’s makes and models and the quality of customer service. A number of regional and national chains offer selected parts and services at prices that may be lower than our prices.
In arranging or providing financing for our customers’ vehicle purchases, we compete with a broad range of financial institutions. In addition, financial institutions are now offering F&I products through the internet. We believe the principal competitive factors in providing financing are convenience, interest rates and contract terms.
Our success depends, in part, on national and regional automobile-buying trends, local and regional economic factors and other regional competitive pressures. Conditions and competitive pressures affecting the markets in which we operate, such as price-cutting by dealers in these areas, or in any new markets we enter, could adversely affect us, even though the retail automobile industry as a whole might not be affected.
Governmental Regulations and Environmental Matters
Numerous federal and state regulations govern our business of marketing, selling, financing and servicing automobiles. We are also subject to laws and regulations relating to business corporations.
Under the laws of the states in which we currently operate as well as the laws of other states into which we may expand, we must obtain a license in order to establish, operate or relocate a dealership or operate an automotive repair service. These laws also regulate our conduct of business, including our sales, operating, advertising, financing and employment practices, including federal and state wage-hour, anti-discrimination and other employment practices laws.
Our financing activities with customers are subject to federal truth-in-lending, consumer privacy, consumer leasing and equal credit opportunity regulations as well as state and local motor vehicle finance laws, installment finance laws, usury laws and other installment sales laws. Some states regulate finance fees that may be paid as a result of vehicle sales.
Federal, state and local environmental regulations, including regulations governing air and water quality, the clean-up of contaminated property and the use, storage, handling, recycling and disposal of gasoline, oil and other materials, also apply to us and our dealership properties.
As with automobile dealerships generally, and service, parts and body shop operations in particular, our business involves the use, storage, handling and contracting for recycling or disposal of hazardous or toxic substances or wastes and other environmentally sensitive materials. Our business also involves the past and current operation and/or removal of above ground and underground storage tanks containing such substances, wastes or materials. Accordingly, we are subject to regulation by federal, state and local authorities that establish health and environmental quality standards, provide for liability related to those standards and provide penalties for violations of those standards. We are also subject to laws, ordinances and regulations governing remediation of contamination at facilities we own or operate or to which we send hazardous or toxic substances or wastes and other environmentally sensitive materials for treatment, recycling or disposal.
We do not have any known material environmental liabilities, and we believe that compliance with environmental laws and regulations will not, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition
6
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
and cash flows. However, soil and groundwater contamination is known to exist at certain properties owned and used by us. Further, environmental laws and regulations are complex and subject to frequent change. In addition, in connection with our past or future acquisitions, it is possible that we will assume or become subject to new or unforeseen environmental costs or liabilities, some of which may be material.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
Our executive officers as of the date of this Form 10-K, are as follows:
|
Name |
|
Age |
|
|
Position(s) with Sonic |
|
|
O. Bruton Smith |
|
|
89 |
|
|
Executive Chairman and Director |
|
B. Scott Smith |
|
|
49 |
|
|
Chief Executive Officer, President and Director |
|
David Bruton Smith |
|
|
42 |
|
|
Vice Chairman and Director |
|
Heath R. Byrd |
|
|
50 |
|
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
|
Jeff Dyke |
|
|
49 |
|
|
Executive Vice President of Operations |
O. Bruton Smith is the Founder of Sonic and has served as Sonic’s Executive Chairman since July 2015. Prior to his appointment as Executive Chairman, Mr. Smith had served as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the Company since its organization in January 1997. Mr. Smith has also served as a director of Sonic since its organization in January 1997. Mr. Smith is also a director of many of Sonic’s subsidiaries. Mr. Smith has worked in the retail automobile industry since 1966. Mr. Smith is also the Executive Chairman and a director of Speedway Motorsports, Inc. (“SMI”), which is controlled by Mr. Smith and his family. SMI is a public company whose shares are traded on the New York Stock Exchange (the “NYSE”). Among other things, SMI owns and operates the following Speedways: Atlanta Motor Speedway, Bristol Motor Speedway, Charlotte Motor Speedway, Kentucky Speedway, Las Vegas Motor Speedway, New Hampshire Motor Speedway, Sonoma Raceway and Texas Motor Speedway. He is also a director of most of SMI’s operating subsidiaries.
B. Scott Smith is the Co-Founder of Sonic. He is also Chief Executive Officer, President and a director of Sonic. Prior to his appointment as Chief Executive Officer in July 2015, Mr. Smith had served as President and Chief Strategic Officer of Sonic since March 2007. Prior to that, Mr. Smith served as Sonic’s Vice Chairman and Chief Strategic Officer from October 2002 to March 2007 and President and Chief Operating Officer from April 1997 to October 2002. Mr. Smith has been a director of Sonic since its organization in January 1997. Mr. Smith also serves as a director and executive officer of many of Sonic’s subsidiaries. Mr. Smith, who is the son of O. Bruton Smith and the brother of David Bruton Smith, has been an executive officer of Town & Country Ford since 1993, and was a minority owner of both Town & Country Ford and Fort Mill Ford before Sonic’s acquisition of those dealerships in 1997. Mr. Smith became the General Manager of Town & Country Ford in November 1992 where he remained until his appointment as President and Chief Operating Officer of Sonic in April 1997. Mr. Smith has over 27 years of experience in the automobile dealership industry.
David Bruton Smith was appointed to the office of Vice Chairman in March 2013. He has served as Executive Vice President and a director of Sonic since October 2008 and has served in Sonic’s organization since 1998. Prior to being named a director and Executive Vice President in 2008, Mr. Smith served as Sonic’s Senior Vice President of Corporate Development. Mr. Smith served as Sonic’s Vice President of Corporate Strategy from October 2005 to March 2007, and also served prior to that time as Dealer Operator and General Manager of several Sonic dealerships. He is the son of Mr. O. Bruton Smith and the brother of Mr. B. Scott Smith.
Heath R. Byrd has served as Sonic’s Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer since April 2013. Mr. Byrd was previously a Vice President and Sonic’s Chief Information Officer from December 2007 to March 2013, and has served our organization since 2007. Prior to joining Sonic, Mr. Byrd served in a variety of management positions at HR America, Inc., a workforce management firm that provided customized human resource and workforce development through co-sourcing arrangements, including as a director, as President and Chief Operating Officer and as Chief Financial Officer and Chief Information Officer. Prior to HR America, Mr. Byrd served as a Manager in the Management Consulting Division of Ernst & Young LLP.
Jeff Dyke has served as Sonic’s Executive Vice President of Operations since October 2008 and is responsible for direct oversight for all of Sonic’s retail automotive operations. From March 2007 to October 2008, Mr. Dyke served as our Division Chief Operating Officer – Southeast Division, where he oversaw retail automotive operations for the states of Alabama, Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee and Texas. Mr. Dyke first joined Sonic in October 2005 as our Vice President of Retail Strategy, a position that he held until April 2006, when he was promoted to Division Vice President – Eastern Division, a position he held from April 2006 to March 2007. Prior to joining Sonic, Mr. Dyke worked in the automotive retail industry at AutoNation, Inc. from 1996 to 2005, where he held several positions in divisional, regional and dealership management with that company.
7
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
Employees
As of December 31, 2016, we employed approximately 9,800 associates. We believe that our relationships with our associates are good. Approximately 275 of our associates, primarily service technicians in our nothern California markets, are represented by a labor union. Although only a small percentage of our associates is represented by a labor union, we may be affected by labor strikes, work slowdowns and walkouts at automobile manufacturers’ manufacturing facilities.
Company Information
Our website is located at www.sonicautomotive.com. Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and all amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), as well as proxy statements and other information we file with, or furnish to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) are available free of charge on our website. We make these documents available as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically transmit them to the SEC. Except as otherwise stated in these documents, the information contained on our website or available by hyperlink from our website is not incorporated into this Annual Report on Form 10-K or other documents we transmit to the SEC.
8
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
Our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows, prospects and the prevailing market price and performance of our Class A common stock may be adversely affected by a number of factors, including the material risks noted below. Our stockholders and prospective investors should consider these risks, uncertainties and other factors prior to making an investment decision.
Risks Related to Our Sources of Financing and Liquidity
Our significant indebtedness could materially adversely affect our financial health, limit our ability to finance future acquisitions, expansion plans and capital expenditures and prevent us from fulfilling our financial obligations.
As of December 31, 2016, our total outstanding indebtedness was approximately $2.4 billion, which includes floor plan notes payable, long-term debt and short-term debt.
We have up to $250.0 million of maximum borrowing availability under a syndicated revolving credit facility (the “2016 Revolving Credit Facility”) and up to $1.0 billion of maximum borrowing availability for combined syndicated new and used vehicle inventory floor plan financing (the “2016 Floor Plan Facilities”). We refer to the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility and the 2016 Floor Plan Facilities collectively as our “2016 Credit Facilities.” Based on balances as of December 31, 2016, we had approximately $207.0 million available for additional borrowings under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility based on the borrowing base calculation, which is affected by numerous factors including eligible asset balances. We are able to borrow under our 2016 Revolving Credit Facility only if, at the time of the borrowing, we have met all representations and warranties and are in compliance with all financial and other covenants contained therein. We also have capacity to finance new and used vehicle inventory purchases under floor plan agreements with various manufacturer-affiliated finance companies and other lending institutions (the “Silo Floor Plan Facilities”) as well as our 2016 Floor Plan Facilities. In addition, the indentures relating to our 5.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 (the “5.0% Notes”), our 7.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2022 (the “7.0% Notes”) and our other debt instruments allow us to incur additional indebtedness, including secured indebtedness, as long as we comply with the terms thereunder.
In addition, the majority of our dealership properties are leased under long-term operating lease arrangements that commonly have initial terms of fifteen to twenty years with renewal options generally ranging from five to ten years. These operating leases require compliance with financial and operating covenants similar to those under our 2016 Credit Facilities, and monthly payments of rent that may fluctuate based on interest rates and local consumer price indices. The total future minimum lease payments related to these operating leases and certain equipment leases are significant and are disclosed in Note 12, “Commitments and Contingencies,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Our failure to comply with certain covenants in these agreements or indentures could materially adversely affect our ability to access our borrowing capacity, subject us to acceleration of our outstanding debt, result in a cross default on other indebtedness and could have a material adverse effect on our ability to continue our business.
An acceleration of our obligation to repay all or a substantial portion of our outstanding indebtedness or lease obligations would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our 2016 Credit Facilities, the indentures governing the 5.0% Notes and the 7.0% Notes and many of our operating leases contain numerous financial and operating covenants. A breach of any of these covenants could result in a default under the applicable agreement or indenture. In addition, a default under one agreement or indenture could result in a default and acceleration of our repayment obligations under the other agreements or indentures, including the indentures governing our outstanding 5.0% Notes and 7.0% Notes. If a cross default were to occur, we may not be able to pay our debts or borrow sufficient funds to refinance them. Even if new financing were available, it may not be on terms acceptable to us. If a default were to occur, we may be unable to adequately finance our operations and the value of our common stock would be materially adversely affected because of acceleration and cross-default provisions. As a result of this risk, we could be forced to take actions that we otherwise would not take, or not take actions that we otherwise might take, in order to comply with the covenants in these agreements and indentures.
9
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
Our ability to make interest and principal payments when due to holders of our debt securities depends upon our future performance and our receipt of sufficient funds from our subsidiaries.
Our ability to meet our debt obligations and other expenses will depend on our future performance, which will be affected by financial, business, domestic and foreign economic conditions, the regulatory environment and other factors, many of which we are unable to control. Substantially all of our consolidated assets are held by our subsidiaries and substantially all of our consolidated cash flow and net income are generated by our subsidiaries. Accordingly, our cash flow and ability to service debt depend to a substantial degree on the results of operations of our subsidiaries and upon the ability of our subsidiaries to provide us with cash. We may receive cash from our subsidiaries in the form of dividends, loans or distributions. We may use this cash to service our debt obligations or for working capital. Our subsidiaries are separate and distinct legal entities and have no obligation, contingent or otherwise, to distribute cash to us or to make funds available to service debt.
If our cash flow is not sufficient to service our debt as it becomes due, we may be required to refinance the debt, sell assets or sell shares of our common stock on terms that we do not find attractive. Further, our failure to comply with the financial and other restrictive covenants relating to the 2016 Credit Facilities and the indentures pertaining to our outstanding notes could result in a default under these agreements and indentures that would prevent us from borrowing under the 2016 Credit Facilities, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. If a default and acceleration of repayment were to occur, we may be unable to adequately finance our operations and the value of our Class A common stock could be materially adversely affected.
We have financed the purchase of certain dealership properties with mortgage notes that require balloon payments at the end of the notes’ terms.
Many of our mortgage notes’ principal and interest payments are based on an amortization period longer than the actual terms (maturity dates) of the notes. We will be required to repay or refinance the remaining principal balances for certain of our mortgages with balloon payments at the notes’ maturity dates, which range from 2017 to 2033. The amounts to be repaid or refinanced at the maturity dates could be significant. We may not have sufficient liquidity to make such payments at the notes’ maturity dates. In the event we do not have sufficient liquidity to completely repay the remaining principal balances at maturity, we may not be able to refinance the notes at interest rates that are acceptable to us, or depending on market conditions, refinance the notes at all. Our inability to repay or refinance these notes could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We depend on the performance of subleases to offset costs related to certain of our lease agreements.
In many cases, when we sell a dealership, the buyer of the dealership will sublease the dealership property from us, but we are not released from the underlying lease obligation to the primary landlord. We rely on the sublease income from the buyer to offset the expense incurred related to our obligation to pay the primary landlord. We also rely on the buyer to maintain the property in accordance with the terms of the sublease (which in most cases mirror the terms of the lease we have with the primary landlord). Although we assess the financial condition of a buyer at the time we sell the dealership, and seek to obtain guarantees of the buyer’s sublease obligation from the stockholders or affiliates of the buyer, the financial condition of the buyer and/or the sublease guarantors may deteriorate over time. In the event the buyer does not perform under the terms of the sublease agreement (due to the buyer’s financial condition or other factors), we may not be able to recover amounts owed to us under the terms of the sublease agreement or the related guarantees. Our operating results, financial condition and cash flows may be materially adversely affected if sublessees do not perform their obligations under the terms of the sublease agreements.
Our use of hedging transactions could limit our financial gains or result in financial losses.
To reduce our exposure to fluctuations in cash flow due to interest rate fluctuations, we have entered into, and in the future expect to enter into, certain derivative instruments (or hedging agreements). No hedging activity can completely insulate us from the risks associated with changes in interest rates. As of December 31, 2016, we had interest rate swap agreements to effectively convert a portion of our LIBOR-based variable rate debt to a fixed rate. See the heading “Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities” under Note 6, “Long-Term Debt,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements. We intend to hedge as much of the interest rate risk as management determines is in our best interests given the cost of such hedging transactions.
Our hedging transactions expose us to certain risks and financial losses, including, among other things:
|
|
• |
counterparty credit risk; |
|
|
• |
available interest rate hedging may not correspond directly with the interest rate risk for which we seek protection; |
10
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
|
|
• |
the duration or the amount of the hedge may not match the duration or the amount of the related liability; |
|
|
• |
the value of derivatives used for hedging may be adjusted from time to time in accordance with accounting rules to reflect changes in fair value, downward adjustments, or “mark-to-market losses,” which would affect our stockholders’ equity; and |
|
|
• |
all of our hedging instruments contain terms and conditions with which we are required to meet. In the event those terms and conditions are not met, we may be required to settle the instruments prior to the instruments’ maturity with cash payments which could significantly affect our liquidity. |
A failure on our part to effectively hedge against interest rate changes may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be able to satisfy our debt obligations upon the occurrence of a change of control.
Upon the occurrence of a change of control, as defined in the 5.0% Notes and the 7.0% Notes, holders of these instruments will have the right to require us to purchase all or any part of such holders’ notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any. The events that constitute a change of control under these indentures may also constitute a default under our 2016 Credit Facilities. Any future debt instruments that we may incur may contain similar provisions regarding repurchases in the event of a change of control triggering event. There can be no assurance that we would have sufficient resources available to satisfy all of our obligations under these debt instruments in the event of a change of control. In the event we were unable to satisfy these obligations, it could have a material adverse impact on our business and our stockholders.
Risks Related to Our Relationships with Vehicle Manufacturers
Our operations may be adversely affected if one or more of our manufacturer franchise or dealer agreements is terminated or not renewed.
Each of our dealerships operates under a separate franchise or dealer agreement with the applicable automobile manufacturer. Without a franchise or dealer agreement, we cannot obtain new vehicles from a manufacturer or advertise as an authorized factory service center. As a result, we are significantly dependent on our relationships with the manufacturers.
Moreover, manufacturers exercise a great degree of control over the operations of our dealerships through the franchise and dealer agreements. The franchise and dealer agreements govern, among other things, our ability to purchase vehicles from the manufacturer and to sell vehicles to customers. Each of our franchise or dealer agreements provides for termination or non-renewal for a variety of causes, including certain changes in the financial condition of the dealerships and any unapproved change of ownership or management. Manufacturers may also have a right of first refusal if we seek to sell dealerships.
We cannot guarantee that any of our existing franchise and dealer agreements will be renewed or that the terms and conditions of such renewals will be favorable to us. Actions taken by manufacturers to exploit their superior bargaining position in negotiating the terms of franchise and dealer agreements or renewals of these agreements or otherwise could also have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Our failure to meet a manufacturer’s customer satisfaction, financial and sales performance and facility requirements may adversely affect our profitability and our ability to acquire new dealerships.
A manufacturer may condition its allotment of vehicles, participation in bonus programs, or acquisition of additional franchises upon our compliance with its brand and facility standards. These standards may require investments in technology and facilities that we otherwise would not make. This may put us in a competitive disadvantage with other competing dealerships and may ultimately result in our decision to sell a franchise when we believe it may be difficult to recover the cost of the required investment to reach the manufacturer’s brand and facility standards.
11
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
In addition, many manufacturers attempt to measure customers’ satisfaction with their sales and warranty service experiences through manufacturer-determined CSI scores. The components of CSI vary by manufacturer and are modified periodically. Franchise and dealer agreements may also impose financial and sales performance standards. Under our agreements with certain manufacturers, a dealership’s CSI scores and financial and sales performance standards may be considered as factors in evaluating applications for additional dealership acquisitions. From time to time, some of our dealerships have had difficulty meeting various manufacturers’ CSI requirements or performance standards. We cannot assure you that our dealerships will be able to comply with these requirements or performance standards in the future. A manufacturer may refuse to consent to an acquisition of one of its franchises if it determines our dealerships do not comply with its CSI requirements or performance standards, which could impair the execution of our acquisition strategy. In addition, we receive incentive payments from the manufacturers based, in part, on CSI scores, which could be materially adversely affected if our CSI scores decline.
If state dealer laws are repealed or weakened, our dealerships will be more susceptible to termination, non-renewal or renegotiation of their franchise and dealer agreements.
State dealer laws generally provide that a manufacturer may not terminate or refuse to renew a franchise or dealer agreement unless it has first provided the dealer with written notice setting forth good cause and stating the grounds for termination or non-renewal. Some state dealer laws allow dealers to file protests or petitions or attempt to comply with the manufacturer’s criteria within the notice period to avoid the termination or non-renewal. Manufacturers’ lobbying efforts (including those of Tesla) may lead to the repeal or revision of state dealer laws. If dealer laws are repealed or weakened in the states in which we operate, manufacturers may be able to terminate our franchises without providing advance notice, an opportunity to cure or a showing of good cause. Without the protection of state dealer laws, it may also be more difficult for our dealerships to renew their franchise or dealer agreements upon expiration.
The ability of a manufacturer to grant additional franchises is based on several factors which are not within our control. If manufacturers grant new franchises in areas near or within our existing markets, this could significantly impact our revenues and/or profitability. In addition, current state dealer laws generally restrict the ability of automobile manufacturers to enter the retail market and sell directly to consumers. However, if manufacturers obtain the ability to directly retail vehicles and do so in our markets, such competition could have a material adverse effect on us.
Our sales volume and profit margin on each sale may be materially adversely affected if manufacturers discontinue or change their incentive programs.
Our dealerships depend on the manufacturers for certain sales incentives, warranties and other programs that are intended to promote and support dealership new vehicle sales. Manufacturers routinely modify their incentive programs in response to changing market conditions. Some of the key incentive programs include:
|
|
• |
customer rebates or below market financing on new and used vehicles; |
|
|
• |
employee pricing; |
|
|
• |
dealer incentives on new vehicles; |
|
|
• |
manufacturer floor plan interest and advertising assistance; |
|
|
• |
warranties on new and used vehicles; and |
|
|
• |
sponsorship of certified pre-owned vehicle sales by authorized new vehicle dealers. |
Manufacturers frequently offer incentives to potential customers. A reduction or discontinuation of a manufacturer’s incentive programs may materially adversely impact vehicle demand and affect our results of operations.
Our sales volume may be materially adversely affected if manufacturer captives change their customer financing programs or are unable to provide floor plan financing.
One of the primary finance sources used by consumers in connection with the purchase of a new or used vehicle is the manufacturer captive finance companies. These captive finance companies rely, to a certain extent, on the public debt markets to provide the capital necessary to support their financing programs. In addition, the captive finance companies will occasionally change their loan underwriting criteria to alter the risk profile of their loan portfolio. A limitation or reduction of available consumer financing for these or other reasons could affect consumers’ ability to purchase a vehicle and, thus, could have a material adverse effect on our sales volume.
12
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
Our parts and service sales volume and margins are dependent on manufacturer warranty programs.
Franchised automotive retailers perform factory authorized service work and sell original replacement parts on vehicles covered by warranties issued by the automotive manufacturer. Dealerships which perform work covered by a manufacturer warranty are reimbursed at rates established by the manufacturer. For the year ended December 31, 2016, approximately 17.1% of our parts, service and collision repair revenue was for work covered by manufacturer warranties. To the extent a manufacturer reduces the labor rates or markup of replacement parts for such warranty work, our parts and service sales volume and margins could be adversely affected.
Adverse conditions affecting one or more key manufacturers or lenders may negatively impact our results of operations.
Our results of operations depend on the products, services, and financing and incentive programs offered by major automobile manufacturers, and could be negatively impacted by any significant changes to these manufacturers’ financial condition, marketing strategy, vehicle design, publicity concerning a particular manufacturer or vehicle model, production capabilities, management, reputation and labor relations.
Events such as labor strikes or other disruptions in production, including those caused by natural disasters, that may adversely affect a manufacturer may also adversely affect us. In particular, labor strikes at a manufacturer that continue for a substantial period of time could have a material adverse effect on our business. Similarly, the delivery of vehicles from manufacturers at a time later than scheduled, which may occur during critical periods of new product introductions, could limit sales of those vehicles during those periods. This has been experienced at some of our dealerships from time to time. Adverse conditions affecting these and other important aspects of manufacturers’ operations and public relations may adversely affect our ability to sell their automobiles and, as a result, significantly and detrimentally affect our business and results of operations.
Moreover, our business could be materially adversely impacted by the bankruptcy of a major vehicle manufacturer or related lender. For example:
|
|
• |
a manufacturer in bankruptcy could attempt to terminate all or certain of our franchises, in which case we may not receive adequate compensation for our franchises; |
|
|
• |
consumer demand for such manufacturer’s products could be substantially reduced; |
|
|
• |
a lender in bankruptcy could attempt to terminate our floor plan financing and demand repayment of any amounts outstanding; |
|
|
• |
we may be unable to arrange financing for our customers for their vehicle purchases and leases through such lender, in which case we would be required to seek financing with alternate financing sources, which may be difficult to obtain on similar terms, if at all; |
|
|
• |
we may be unable to collect some or all of our significant receivables that are due from such manufacturer or lender, and we may be subject to preference claims relating to payments made by such manufacturer or lender prior to bankruptcy; and |
|
|
• |
such manufacturer may be relieved of its indemnification obligations with respect to product liability claims. |
Additionally, any such bankruptcy may result in us being required to incur impairment charges with respect to the inventory, fixed assets and intangible assets related to certain dealerships, which could adversely impact our results of operations, financial condition and our ability to remain in compliance with the financial ratios contained in our debt agreements.
Manufacturer stock ownership restrictions may impair our ability to maintain or renew franchise or dealer agreements or issue additional equity.
Some of our franchise and dealer agreements prohibit transfers of any ownership interests of a dealership and, in some cases, its parent, without prior approval of the applicable manufacturer. Our existing franchise and dealer agreements could be terminated if a person or entity acquires a substantial ownership interest in us or acquires voting power above certain levels without the applicable manufacturer’s approval. While the holders of our Class B common stock currently maintain voting control of Sonic, their future investment decisions as well as those of holders of our Class A common stock are generally outside of our control and could result in the termination or non-renewal of existing franchise or dealer agreements or impair our ability to negotiate new franchise or dealer agreements for dealerships we acquire in the future. In addition, if we cannot obtain any requisite approvals on a timely basis, we may not be able to issue additional equity or otherwise raise capital on terms acceptable to us. These restrictions may also prevent or deter a prospective acquirer from acquiring control of us.
13
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
We depend on manufacturers to supply us with sufficient numbers of popular new models.
Manufacturers typically allocate their vehicles among dealerships based on the sales history of each dealership. Supplies of popular new vehicles may be limited by the applicable manufacturer’s production capabilities. Popular new vehicles that are in limited supply typically produce the highest profit margins. We depend on manufacturers to provide us with a desirable mix of popular new vehicles. Our operating results may be materially adversely affected if we do not obtain a sufficient supply of these vehicles on a timely basis.
A decline in the quality of vehicles we sell, or consumers’ perception of the quality of those vehicles, may adversely affect our business.
Our business is highly dependent on consumer demand and preferences. Events such as manufacturer recalls, negative publicity or legal proceedings related to these events may have a negative impact on the products we sell. If such events are significant, the profitability of our dealerships related to those manufacturers could be adversely affected and we could experience a material adverse effect on our overall results of operations, financial position and cash flows.
For instance, negative publicity and legal proceedings related to events such as the well-known Volkswagen/Audi emissions issue may have a negative impact on the products we sell and the profitability of our dealerships related to those manufacturers could be adversely affected. Depending on the ultimate outcome of the Volkswagen/Audi emissions issue and whether or not other manufacturers have implemented similar technologies, the resulting impact could result in a material adverse effect on our overall results of operations, financial position and cash flows. As of December 31, 2016, we operated five Volkswagen and five Audi franchised dealerships. During the year ended December 31, 2016, these dealerships generated revenues of approximately $647.3 million, representing approximately 6.7% of our total revenues.
In the event that consumer or other related lawsuits are filed against our Volkswagen and Audi dealerships related to this issue, we believe that our dealerships are entitled to indemnification and assumption of defense from Volkswagen Group of America, Inc. related to such claims.
Risks Related to Our Growth Strategy
Our investment in new business strategies, services and technologies is inherently risky, and could disrupt our ongoing business or have a material adverse effect on our overall business and results of operations.
We have invested and expect to continue to invest in new business strategies, services and technologies, including our EchoPark® stores and our OSOE initiative. Such endeavors may involve significant risks and uncertainties, including allocating management resources away from current operations, insufficient revenues to offset expenses associated with these new investments, inadequate return of capital on our investments and unidentified issues not discovered in our due diligence of such strategies and offerings. Because these ventures are inherently risky, no assurance can be given that such strategies and offerings will be successful and will not have a material adverse effect on our reputation, financial condition and operating results.
Our ability to make acquisitions, execute our stand-alone pre-owned store initiative and grow organically may be restricted by the terms and limits of the 2016 Credit Facilities.
The amount of capital available to us is limited to the liquidity available under our 2016 Credit Facilities and capital generated through operating activities. Pursuant to the 2016 Credit Facilities, we are restricted from making dealership acquisitions in any fiscal year if the aggregate cost of all such acquisitions is in excess of certain amounts, without the written consent of the required lenders (as that term is defined in the 2016 Credit Facilities). Our pace and scale of growing our stand-alone pre-owned store initiative may be limited in the event other sources of capital are unavailable. These restrictions may limit our growth strategy.
We may not be able to capitalize on future real estate and dealership acquisition opportunities because our ability to obtain capital to fund these acquisitions is limited.
We intend to finance future real estate and dealership acquisitions with cash generated from operations, through issuances of our stock or debt securities and through borrowings under credit arrangements. We may not be able to obtain additional financing by issuing stock or debt securities due to the market price of our Class A common stock, overall market conditions or covenants under our 2016 Credit Facilities that restrict our ability to issue additional indebtedness, or the need for manufacturer consent to the issuance of equity securities. Using cash to complete acquisitions could substantially limit our operating or financial flexibility.
In addition, we are dependent to a significant extent on our ability to finance our new and certain of our used vehicle inventory under the 2016 Floor Plan Facilities or the Silo Floor Plan Facilities (“floor plan financing”). Floor plan financing arrangements allow
14
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
us to borrow money to buy a particular new vehicle from the manufacturer or a used vehicle on trade-in or at auction and pay off the loan when we sell that particular vehicle. We must obtain floor plan financing or obtain consents to assume existing floor plan financing in connection with our acquisition of dealerships. In the event that we are unable to obtain such financing, our ability to complete dealership acquisitions could be limited.
Substantially all the assets of our dealerships are pledged to secure the indebtedness under our Silo Floor Plan Facilities and the 2016 Credit Facilities. These pledges may impede our ability to borrow from other sources. Moreover, because certain lending institutions are either owned by or affiliated with an automobile manufacturer, any deterioration of our relationship with the particular manufacturer-affiliated finance subsidiary could adversely affect our relationship with the affiliated manufacturer, and vice-versa.
Manufacturers’ restrictions on acquisitions could limit our future growth.
We are required to obtain the approval of the applicable manufacturer before we can acquire an additional franchise of that manufacturer. In determining whether to approve an acquisition, manufacturers may consider many factors such as our financial condition and CSI scores.
Certain manufacturers also limit the number of its dealerships that we may own, our national market share of that manufacturer’s sales of new vehicles or the number of dealerships we may own in a particular geographic area. In addition, under an applicable franchise or dealer agreement or under state law, a manufacturer may have a right of first refusal to acquire a dealership that we seek to acquire.
A manufacturer may condition approval of an acquisition on the implementation of material changes in our operations or extraordinary corporate transactions, facilities improvements or other capital expenditures. If we are unable or unwilling to comply with these conditions, we may be required to sell the assets of that manufacturer’s dealerships or terminate our franchise or dealer agreement. We cannot assure you that manufacturers will approve future acquisitions or do so on a timely basis, which could impair the execution of our acquisition strategy.
Failure to effectively integrate acquired dealerships with our existing operations could adversely affect our future operating results.
Our future operating results depend on our ability to integrate the operations of acquired dealerships with our existing operations. In particular, we need to integrate our management information systems, procedures and organizational structures, which can be difficult. Our growth strategy has focused on the pursuit of strategic acquisitions or brand development that either expand or complement our business.
We cannot assure you that we will effectively and profitably integrate the operations of these dealerships without substantial costs, delays or operational or financial problems, due to:
|
|
• |
the difficulties of managing operations located in geographic areas where we have not previously operated; |
|
|
• |
the management time and attention required to integrate and manage newly acquired dealerships; |
|
|
• |
the difficulties of assimilating and retaining employees; |
|
|
• |
the challenges of keeping customers; and |
|
|
• |
the challenge of retaining or attracting appropriate dealership management personnel. |
These factors could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We may not adequately anticipate all of the demands that growth through acquisitions or brand development will impose.
We face risks growing through acquisitions or expansion. These risks include, but are not limited to:
|
|
• |
incurring significantly higher capital expenditures and operating expenses; |
|
|
• |
failing to assimilate the operations and personnel of acquired dealerships; |
|
|
• |
entering new markets with which we are unfamiliar; |
|
|
• |
potential undiscovered liabilities and operational difficulties at acquired dealerships; |
15
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
|
|
• |
disrupting our ongoing business; |
|
|
• |
diverting our management resources; |
|
|
• |
failing to maintain uniform standards, controls and policies; |
|
|
• |
impairing relationships with employees, manufacturers and customers as a result of changes in management; |
|
|
• |
increased expenses for accounting and computer systems, as well as integration difficulties; |
|
|
• |
failure to obtain a manufacturer’s consent to the acquisition of one or more of its franchises or renew the franchise or dealer agreement on terms acceptable to us; and |
|
|
• |
incorrectly valuing entities to be acquired or assessing markets entered. |
We may not adequately anticipate all of the demands that growth will impose on our business.
We may not be able to execute our growth strategy without the costs escalating.
We have grown our business primarily through acquisitions in the past. We may not be able to consummate any future acquisitions at acceptable prices and terms or identify suitable candidates. In addition, increased competition for acquisition candidates could result in fewer acquisition opportunities for us and higher acquisition prices. The magnitude, timing, pricing and nature of future acquisitions or growth opportunities will depend upon various factors, including:
|
|
• |
the availability of suitable acquisition candidates; |
|
|
• |
competition with other dealer groups or institutional investors for suitable acquisitions; |
|
|
• |
the negotiation of acceptable terms with the seller and with the manufacturer; |
|
|
• |
our financial capabilities and ability to obtain financing on acceptable terms; |
|
|
• |
our stock price; and |
|
|
• |
the availability of skilled employees to manage the acquired companies. |
We may not be able to determine the actual financial condition of dealerships we acquire until after we complete the acquisition and take control of the dealerships.
The operating and financial condition of acquired businesses cannot be determined accurately until we assume control. Although we conduct what we believe to be a prudent level of investigation regarding the operating and financial condition of the businesses we purchase, in light of the circumstances of each transaction, an unavoidable level of risk remains regarding the actual operating condition of these businesses. Similarly, many of the dealerships we acquire, including some of our largest acquisitions, do not have financial statements audited or prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. We may not have an accurate understanding of the historical financial condition and performance of our acquired entities. Until we actually assume control of business assets and their operations, we may not be able to ascertain the actual value or understand the potential liabilities of the acquired entities and their operations.
Risks Related to the Automotive Retail Industry
Our facilities and operations are subject to extensive governmental laws and regulations. If we are found to be in violation of or subject to liabilities under any of these laws or regulations, or if new laws or regulations are enacted that adversely affect our operations, business, operating results, financial condition, cash flows and prospects could suffer.
The automotive retail industry, including our facilities and operations, is subject to a wide range of federal, state, and local laws and regulations, such as those relating to motor vehicle sales, retail installment sales, leasing, sales of finance, insurance and vehicle protection products, licensing, consumer protection, consumer privacy, employment practices, escheatment, anti-money laundering, environmental, vehicle emissions and fuel economy, and health and safety. With respect to motor vehicle sales, retail installment sales, leasing, and sales of finance, insurance and vehicle protection products at our stores, we are subject to various laws and regulations, the violation of which could subject us to consumer class action or other lawsuits or governmental investigations and adverse publicity, in addition to administrative, civil or criminal sanctions. With respect to employment practices, we are subject to various laws and regulations, including complex federal, state, and local wage and hour and anti-discrimination laws. We are also subject to lawsuits and governmental investigations alleging violations of these laws and regulations, including purported class action lawsuits, which could result in significant liability, fines and penalties. The violation of other laws and regulations to which we are
16
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
subject also can result in administrative, civil or criminal sanctions against us, which may include a cease and desist order against the subject operations or even revocation or suspension of our license to operate the subject business, as well as significant liability, fines and penalties. We currently devote significant resources to comply with applicable federal, state and local regulation of health, safety, environmental, zoning and land use regulations, and we may need to spend additional time, effort and money to keep our operations and existing or acquired facilities in compliance. In addition, we may be subject to broad liabilities arising out of contamination at our currently and formerly owned or operated facilities, at locations to which hazardous substances were transported from such facilities, and at such locations related to entities formerly affiliated with us. Although for some such liabilities we believe we are entitled to indemnification from other entities, we cannot assure you that such entities will view their obligations as we do or will be able to satisfy them. Failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations may have an adverse effect on our operations, business, operating results, financial condition, cash flows and prospects.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”), which was signed into law on July 21, 2010, established the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (the “CFPB”), a new independent federal agency funded by the U.S. Federal Reserve with broad regulatory powers and limited oversight from the U.S. Congress. Although automotive dealers are generally excluded, the Dodd-Frank Act has led to additional, indirect regulation of automotive dealers, in particular, their sale and marketing of finance and insurance products, through its regulation of automotive finance companies and other financial institutions. In March 2013, the CFPB issued supervisory guidance highlighting its concern that the practice of automotive dealers being compensated for arranging customer financing through discretionary markup of wholesale rates offered by financial institutions (“dealer markup”) results in a significant risk of pricing disparity in violation of The Equal Credit Opportunity Act (the “ECOA”). The CFPB recommended that financial institutions under its jurisdiction take steps to ensure compliance with the ECOA, which may include imposing controls on dealer markup, monitoring and addressing the effects of dealer markup policies, and eliminating dealer discretion to markup buy rates and fairly compensating dealers using a different mechanism that does not result in disparate impact to certain groups of consumers. In addition, we believe that the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, which was signed into law on March 23, 2010, has increased and will continue to increase our annual employee health care costs that we fund, and has also increased our cost of compliance and compliance risk related to offering health care benefits.
Furthermore, we expect that new laws and regulations, particularly at the federal level, in other areas such as a proposed “border adjustment tax” on imported goods, may be enacted, which could also materially adversely impact our business. The labor policy of the prior administration led to increased unionization efforts for U.S. companies, which could lead to higher labor costs for our company, disrupt our store operations, and adversely affect our results of operations.
Climate change legislation or regulations restricting emission of greenhouse gases could result in increased operating costs and reduced demand for the vehicles we sell.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has adopted rules under existing provisions of the federal Clean Air Act that require a reduction in emissions of greenhouse gases from motor vehicles, require certain construction and operating permit reviews for greenhouse gas emissions from certain large stationary sources, and require monitoring and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions from specified sources on an annual basis. The adoption of any laws or regulations requiring significant increases in fuel economy requirements or new federal or state restrictions on emissions of greenhouse gases from our operations or on vehicles and automotive fuels in the United States could adversely affect demand for those vehicles and require us to incur costs to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases associated with our operations.
Increasing competition among automotive retailers and the use of the internet reduces our profit margins on vehicle sales and related businesses.
Automobile retailing is a highly competitive business. Our competitors include publicly and privately owned dealerships, some of which are larger and have greater financial and marketing resources than we do. Many of our competitors sell the same or similar makes of new and used vehicles that we offer in our markets at competitive prices. We do not have any cost advantage in purchasing new vehicles from manufacturers due to economies of scale or otherwise. We typically rely on advertising, merchandising, sales expertise, customer service reputation and dealership location to sell new vehicles. Our revenues and profitability could be materially adversely affected if laws permit manufacturers to enter the retail market directly.
Our F&I business and other related businesses, which have higher margins than sales of new and used vehicles, are subject to strong competition from various financial institutions and other third parties.
Moreover, customers are using the internet to compare pricing for vehicles and related F&I services, which may further reduce margins for new and used vehicles and profits for related F&I services. If internet new vehicle sales are allowed to be conducted without the involvement of franchised dealers, our business could be materially adversely affected. In addition, other dealership
17
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
groups have aligned themselves with services offered on the internet or are investing heavily in the development of their own internet capabilities, which could materially adversely affect our business.
Our franchise and dealer agreements do not grant us the exclusive right to sell a manufacturer’s product within a given geographic area. Our revenues or profitability could be materially adversely affected if any of our manufacturers award franchises to others in the same markets where we operate or if existing franchised dealers increase their market share in our markets.
We may face increasingly significant competition as we strive to gain market share through acquisitions or otherwise. Our operating margins may decline over time as we expand into markets where we do not have a leading position.
The effect of companies entering into the automotive space may affect our ability to grow or maintain the business over the long-term.
Large and well-capitalized technology companies have begun to enter into the automotive space in recent years. Companies such as Google, Apple, Tesla, Uber and Lyft may challenge the existing automotive manufacturing, transportation and retail models. Tesla has been challenging state dealer franchise laws in many states with mixed results, but its business model has been accepted by many consumers. Although Tesla’s participation in the competitive landscape has had minimal impact on the overall retail automotive space thus far, these other large technology companies may continue to change consumers’ view on how automobiles should be manufactured, equipped, used and retailed in the future. Because these companies have the ability to connect with each individual consumer easily through their technology platforms, we may ultimately be at a competitive disadvantage in marketing, financing, selling and servicing vehicles.
Our dealers depend upon new vehicle sales and, therefore, their success depends in large part upon customer demand for the particular vehicles they carry.
The success of our dealerships depends in large part on the overall success of the vehicle lines they carry. New vehicle sales generate the majority of our total revenue and lead to sales of higher-margin products and services such as finance, insurance, vehicle protection products and other aftermarket products, and parts and service operations. Our new vehicle sales operations are comprised primarily of luxury and mid-line import brands, which exposes us to manufacturer concentration risks. Although our parts and service operations and used vehicle sales may serve to offset some of this risk, changes in automobile manufacturers’ vehicle models and customer demand for particular vehicles may have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our business will be harmed if overall consumer demand suffers from a severe or sustained downturn.
Our business is heavily dependent on consumer demand and preferences. Retail vehicle sales are cyclical and historically have experienced periodic downturns characterized by oversupply and weak demand. These cycles are often dependent on economic conditions, consumer confidence, the level of discretionary personal income and credit availability. Deterioration in any of these conditions may have a material adverse effect on our retail business, particularly sales of new and used automobiles.
In addition, severe or sustained changes in gasoline prices may lead to a shift in consumer buying patterns. Availability of preferred models may not exist in sufficient quantities to satisfy consumer demand and allow our stores to meet sales expectations.
A decline of available financing in the lending market may adversely affect our vehicle sales volume.
A significant portion of vehicle buyers, particularly in the used car market, finance their purchases of automobiles. Sub-prime lenders have historically provided financing for consumers who, for a variety of reasons including poor credit histories and lack of down payment, do not have access to more traditional finance sources. In the event lenders tighten their credit standards or there is a decline in the availability of credit in the lending market, the ability of these consumers to purchase vehicles could be limited, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, revenues and profitability.
Our business may be adversely affected by import product restrictions and foreign trade risks that may impair our ability to sell foreign vehicles profitably.
A significant portion of our new vehicle business involves the sale of vehicles, parts or vehicles composed of parts that are manufactured outside the United States. As a result, our operations are subject to risks of importing merchandise, including fluctuations in the relative values of currencies, import duties or tariffs, exchange controls, trade restrictions, work stoppages and general political and socio-economic conditions in other countries. The United States or the countries from which our products are imported may, from time to time, impose new quotas, duties, tariffs or other restrictions, or adjust presently prevailing quotas, duties or tariffs, which may affect our operations and our ability to purchase imported vehicles and/or parts at reasonable prices.
18
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
Natural disasters and adverse weather events can disrupt our business.
Our dealerships are concentrated in states and regions in the United States, including California, Colorado, Florida and Texas, in which actual or threatened natural disasters and severe weather events (such as hail storms, floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, fires and landslides) may disrupt our store operations, which may adversely impact our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. In addition to business interruption, the automotive retailing business is subject to substantial risk of property loss due to the significant concentration of property values at store locations. Although we have substantial insurance, subject to certain deductibles, limitations and exclusions, we may be exposed to uninsured or underinsured losses that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
In addition, the automotive manufacturing supply chain spans the globe. As such, supply chain disruptions resulting from natural disasters and adverse weather events may affect the flow of inventory or parts to us or our manufacturing partners. Such disruptions could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Security breaches and other disruptions could compromise our information and expose us to liability, which would cause our business and reputation to suffer.
We have invested in internal and external business applications to execute our strategy of employing technology to benefit our business. In the ordinary course of business, we collect and store sensitive data, including intellectual property, our proprietary business information and that of our customers, suppliers and business partners, and personally identifiable information of our customers and employees. Although we have attempted to mitigate the cyber-security risk of both our internal and outsourced functions by implementing various cyber-security controls, we remain subject to cyber-security risks.
These cyber-security risks include:
|
|
• |
vulnerability to cyber-attack of our internal or externally hosted business applications; |
|
|
• |
interruption of service or access to systems may affect our ability to deliver vehicles or complete transactions with customers; |
|
|
• |
unauthorized access or theft of customer or employee personal confidential information, including financial information, or strategically sensitive data; |
|
|
• |
disruption of communications (both internally and externally) that may affect the quality of information used to make informed business decisions; and |
|
|
• |
damage to our reputation as a result of a breach in security that could affect the financial security of our customers. |
Moreover, significant technology-related business functions of ours are outsourced, including:
|
|
• |
payroll and human resources management systems, including expense reimbursement management; |
|
|
• |
customer relationship management, ecommerce hosting and marketing campaign management; |
|
|
• |
dealer management, inventory management and financial reporting systems; |
|
|
• |
consumer credit application management, fund transfers/ACH/online banking; and |
|
|
• |
IP telephony and WAN/LAN administration (switch & router configuration). |
Despite our security measures, our information technology and infrastructure may be vulnerable to attacks by hackers or breaches due to employee error, malfeasance or other disruptions. Any such breach could compromise our networks and the information stored there could be accessed, publicly disclosed, lost or stolen. Any such access, disclosure or other loss of information could result in legal claims or proceedings, liability under laws that protect the privacy of personal information, regulatory penalties, damage our reputation, and cause a loss of confidence in our services, which could materially adversely affect our competitive position, results of operations and financial condition.
General Risks Related to Investing in Our Securities
Concentration of voting power and anti-takeover provisions of our charter, our bylaws, Delaware law and our franchise and dealer agreements may reduce the likelihood of a potential change of control from a third party. At the same time, such voting power concentration also could increase the likelihood of a change of control notwithstanding other factors.
19
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
Our common stock is divided into two classes with different voting rights. This dual class stock ownership allows the present holders of the Class B common stock to control us. Holders of Class A common stock have one vote per share on all matters. Holders of Class B common stock have 10 votes per share on all matters, except that they have only one vote per share on any transaction proposed or approved by the Board of Directors or a Class B common stockholder or otherwise benefiting the Class B common stockholders constituting a:
|
|
• |
“going private” transaction; |
|
|
• |
disposition of substantially all of our assets; |
|
|
• |
transfer resulting in a change in the nature of our business; or |
|
|
• |
merger or consolidation in which current holders of common stock would own less than 50% of the common stock following such transaction. |
The holders of Class B common stock (which include Mr. O. Bruton Smith, Sonic’s Executive Chairman and Director, his family members and entities they control) currently hold less than a majority of our outstanding common stock, but a majority of our voting power. As a result, the holders of Class B common stock may be able to control fundamental corporate matters and transactions, subject to the above limitations. The concentration of voting power may also discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of us from a third party even if the action was favored by holders of Class A common stock. In addition, a sale or transfer of shares by one or more of the holders of Class B common stock could result in a change of control or put downward pressure on the market price of our Class A common stock. The perception among the public that these sales or transfers will occur could also contribute to a decline in the market price of our Class A common stock.
Our charter and bylaws make it more difficult for our stockholders to take corporate actions at stockholders’ meetings. In addition, stock options, restricted stock and restricted stock units granted under the Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2004 Stock Incentive Plan or the Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan and other obligations become immediately exercisable or automatically vest upon a change in control. Delaware law also makes it difficult for stockholders who have recently acquired a large interest in a company to consummate a business combination transaction with the company against its directors’ wishes. Finally, restrictions imposed by our franchise and dealer agreements may impede or prevent any potential takeover bid. Our franchise and dealer agreements allow the manufacturers the right to terminate the agreements upon a change of control of our company and impose restrictions upon the transferability of any significant percentage of our stock to any one person or entity that may be unqualified, as defined by the manufacturer, to own one of its dealerships. The inability of a person or entity to qualify with one or more of our manufacturers may prevent or seriously impede a potential takeover bid. In addition, there may be provisions of our lending arrangements that create an event of default upon a change in control. These agreements, corporate governance documents and laws may have the effect of discouraging, delaying or preventing a change in control or preventing stockholders from realizing a premium on the sale of their shares if we were acquired.
The outcome of legal and administrative proceedings we are or may become involved in could have a material adverse effect on our future business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows or prospects.
We are involved, and expect to continue to be involved, in numerous legal and administrative proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including regulatory investigations and private civil actions brought by plaintiffs purporting to represent a potential class or for which a class has been certified.
Although we vigorously defend ourselves in all legal and administrative proceedings, the outcomes of pending and future proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including litigation with customers, employment-related lawsuits, contractual disputes, class actions, purported class actions and actions brought by governmental authorities, cannot be predicted with certainty. An unfavorable resolution of one or more of these matters could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows or prospects.
Our business may be adversely affected by claims alleging violations of laws and regulations in our advertising, sales and finance and insurance activities.
Our business is highly regulated. In the past several years, private plaintiffs and state attorneys general have increased their scrutiny of advertising, sales and finance and insurance activities in the sale and leasing of motor vehicles. The conduct of our business is subject to numerous federal, state and local laws and regulations regarding unfair, deceptive and/or fraudulent trade practices (including advertising, marketing, sales, insurance, repair and promotion practices), truth-in-lending, consumer leasing, fair credit practices, equal credit opportunity, privacy, insurance, motor vehicle finance, installment finance, closed-end credit, usury and other installment sales. Claims arising out of actual or alleged violations of law may be asserted against us or any of our dealers by
20
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
individuals, either individually or through class actions, or by governmental entities in civil or criminal investigations and proceedings. Such actions may expose us to substantial monetary damages and legal defense costs, injunctive relief and criminal and civil fines and penalties, including suspension or revocation of our licenses and franchise or dealer agreements to conduct dealership operations.
Our business may be adversely affected by unfavorable conditions in our local markets, even if those conditions are not prominent nationally.
Our performance is subject to local economic, competitive, weather and other conditions prevailing in geographic areas where we operate. We may not be able to expand geographically and any geographic expansion may not adequately insulate us from the adverse effects of local or regional economic conditions. In addition, due to the provisions and terms contained in our operating lease agreements, we may not be able to relocate a dealership operation to a more favorable location without incurring significant costs or penalties.
The loss of key personnel and limited management and personnel resources could adversely affect our operations and growth.
Our success depends to a significant degree upon the continued contributions of our management team, particularly our senior management, and service and sales personnel. Additionally, franchise or dealer agreements may require the prior approval of the applicable manufacturer before any change is made in dealership general managers. We do not have employment agreements with most members of our senior management team, our dealership managers and other key dealership personnel. Consequently, the loss of the services of one or more of these key employees could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
In addition, as we expand, we may need to hire additional managers. The market for qualified employees in the industry and in the regions in which we operate, particularly for general managers and sales and service personnel, is highly competitive and may subject us to increased labor costs during periods of low unemployment. The loss of the services of key employees or the inability to attract additional qualified managers could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. In addition, the lack of qualified management or employees employed by potential acquisition candidates may limit our ability to consummate future acquisitions.
Potential conflicts of interest between us and our officers or directors could adversely affect our future performance.
Mr. O. Bruton Smith serves as the Executive Chairman of SMI. Accordingly, we compete with SMI for the management time of Mr. Smith.
We have in the past and will likely in the future enter into transactions with Mr. Smith, entities controlled by Mr. Smith and his family or our other affiliates. We believe that all of our existing arrangements with affiliates are as favorable to us as if the arrangements were negotiated between unaffiliated parties, although the majority of these transactions have neither been verified by third parties in that regard nor are likely to be so verified in the future. Potential conflicts of interest could arise in the future between us and our officers or directors in the enforcement, amendment or termination of arrangements existing between them.
We may be subject to substantial withdrawal liability assessments in the future related to a multiemployer pension plan to which certain of our dealerships make contributions pursuant to collective bargaining agreements.
Six of our dealership subsidiaries in northern California currently make fixed-dollar contributions to the Automotive Industries Pension Plan (the “AI Pension Plan”) pursuant to collective bargaining agreements between our subsidiaries and the International Association of Machinists (the “IAM”) and the International Brotherhood of Teamsters (the “IBT”). The AI Pension Plan is a “multiemployer plan” as defined under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended, and our six dealership subsidiaries are among approximately 149 employers that are obligated to make contributions to the AI Pension Plan pursuant to collective bargaining agreements with the IAM, the IBT and other unions. In March 2008, the AI Pension Plan’s actuary, in accordance with the requirements of the federal Pension Protection Act of 2006, issued a certification that the AI Pension Plan was in critical status effective with the plan year commencing January 1, 2008. In conjunction with the AI Pension Plan’s critical status, the Board of Trustees of the AI Pension Plan implemented a requirement on all participating employers to increase employer contributions to the AI Pension Plan for a seven-year period commencing in 2013. According to publicly available information, in September 2016, the AI Pension Plan made a formal application for approval of suspension of benefits with the U.S. Treasury Department, which, if approved by the Treasury Department, would implement a benefit reduction effective July 1, 2017 for participants in the AI Pension Plan. The filing included an Actuarial Certification of Plan Status as of January 1, 2016 that the AI Pension Plan previously filed with the U.S. Internal Revenue Service on March 30, 2016, which reported that the AI Pension Plan was in critical and declining status as of January 1, 2016 and further notified that the AI Pension Plan is making the scheduled progress in meeting the requirements of the plan’s previously-adopted Rehabilitation Plan. The September 2016 filing with the Treasury Department also included an Actuarial Certification of Plan Solvency as of July 1, 2016 with the actuarial firm’s projection that the proposed suspensions of benefits are reasonably estimated to enable the AI Pension Plan to avoid insolvency assuming the proposed
21
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
RISK FACTORS
suspensions of benefits continue indefinitely and the benefit accrual reduction becomes effective upon the proposed July 1, 2017 suspension effective date. Under applicable federal law, any employer contributing to a multiemployer pension plan that completely ceases participating in the plan while the plan is underfunded is subject to payment of such employer’s assessed share of the aggregate unfunded vested benefits of the plan. In certain circumstances, an employer can be assessed withdrawal liability for a partial withdrawal from a multiemployer pension plan. If any of these adverse events were to occur in the future, it could result in a substantial withdrawal liability assessment that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Tax positions may exist related to our tax filings that could be challenged by governmental agencies and result in higher income tax expenses and affect our overall liquidity if we are unable to successfully defend these tax positions.
The California Franchise Tax Board examined our 2006 – 2008 California combined tax returns and challenged the “Method of Filing” of Sonic Automotive, Inc., Sonic Financial Corporation, SPR, LLC (i.e., Speedway Motorsports, Inc.), Oil-Chem Research Corporation (a privately held entity) and Sold, Inc. (a privately held entity) and asserted that all these companies should be filing one combined California tax return. In conjunction with this challenge, the State of California issued an assessment for each of the three years totaling $7.4 million. During 2012 and 2013, we responded on behalf of Sonic Automotive, Inc. and noted that we disagreed with the adjustments, amounts, facts, legal analysis and conclusion listed in the State’s assessment. We believe the State of California’s argument does not have merit and we will vigorously fight this through both the State’s administrative levels and through judicial means. However, if we are unsuccessful in our defense, it could result in a substantial tax charge that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
A change in historical experience and/or assumptions used to estimate reserves could have a material impact on our earnings.
As described in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations – Use of Estimates and Critical Accounting Policies,” management relies on estimates in various areas of accounting and financial reporting. For example, our estimates for finance, insurance and service contracts and insurance reserves are based on historical experience and assumptions. Differences between actual results and our historical experiences and/or our assumptions could have a material impact on our earnings in the period of the change and in periods subsequent to the change.
Our internal control over financial reporting may not be effective.
If we fail to maintain the adequacy of our internal controls, including any failure to implement or difficulty in implementing required new or improved controls, our business and results of operations could be harmed, the results of operations we report could be subject to adjustments, we could incur remediation costs, we could fail to be able to provide reasonable assurance as to our financial results or the effectiveness of our internal controls, or fail to meet our reporting obligations under SEC regulations and the terms of our debt agreements on a timely basis and there could be a material adverse effect on the price of our Class A common stock.
Impairment of our goodwill could have a material adverse impact on our earnings.
Pursuant to applicable accounting pronouncements, we evaluate goodwill for impairment annually or more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. We describe the process for testing goodwill more thoroughly in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Use of Estimates and Critical Accounting Policies.” If we determine that the amount of our goodwill is impaired at any point in time, we are required to reduce goodwill on our balance sheet. If goodwill is impaired based on a future impairment test, we will be required to record a significant non-cash impairment charge that may also have a material adverse effect on our results of operations for the period in which the impairment of goodwill occurs. As of December 31, 2016, our balance sheet reflected a carrying amount of approximately $472.4 million in goodwill.
22
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None.
Our principal executive offices are located at a property owned by us at 4401 Colwick Road, Charlotte, North Carolina 28211, and our telephone number at that location is (704) 566-2400.
Our dealerships are generally located along major U.S. or interstate highways. One of the principal factors we consider in evaluating a potential acquisition is its location. We prefer to acquire dealerships or build dealership facilities located along major thoroughfares, which can be easily visited by prospective customers.
We lease the majority of the properties utilized by our dealership operations from affiliates of Capital Automotive REIT and other individuals and entities. Under the terms of our franchise and dealer agreements, each of our dealerships must maintain an appropriate appearance and design of its dealership facility and is restricted in its ability to relocate. The properties utilized by our dealership operations that are owned by us or one of our subsidiaries are pledged as security for our 2016 Credit Facilities or mortgage financing arrangements. We believe that our facilities are adequate for our current needs.
We are involved, and expect to continue to be involved, in numerous legal and administrative proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including regulatory investigations and private civil actions brought by plaintiffs purporting to represent a potential class or for which a class has been certified. Although we vigorously defend ourselves in all legal and administrative proceedings, the outcomes of pending and future proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including litigation with customers, employment-related lawsuits, contractual disputes, class actions, purported class actions and actions brought by governmental authorities, cannot be predicted with certainty. Similarly, except as reflected in reserves we have provided for in other accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets, we are currently unable to estimate a range of reasonably possible loss, or a range of reasonably possible loss in excess of the amount accrued, for pending proceedings. An unfavorable resolution of one or more of these matters could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows or prospects. Included in other accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities at December 31, 2016 was approximately $0.3 million and $0.2 million, respectively, in reserves that we were holding for pending proceedings.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
23
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Our Class A common stock is currently traded on the NYSE under the symbol “SAH.” Our Class B common stock is not traded on a public market.
As of February 21, 2017, there were 32,855,850 shares of our Class A common stock and 12,029,375 shares of our Class B common stock outstanding. As of February 21, 2017, there were 83 record holders of the Class A common stock and four record holders of the Class B common stock. The closing stock price for the Class A common stock on February 21, 2017 was $25.95.
Our Board of Directors approved four quarterly cash dividends on all outstanding shares of common stock totaling approximately $0.20 per share during the year ended December 31, 2016 and $0.11 and $0.10 per share during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Subsequent to December 31, 2016, our Board of Directors approved a cash dividend on all outstanding shares of common stock of $0.05 per share for stockholders of record on March 15, 2017 to be paid on April 14, 2017. The declaration and payment of any future dividend is subject to the business judgment of our Board of Directors, taking into consideration our historic and projected results of operations, financial condition, cash flows, capital requirements, covenant compliance, share repurchases, current economic environment and other factors considered by our Board of Directors to be relevant. These factors are considered each quarter and will be scrutinized as our Board of Directors determines our future dividend policy. There is no guarantee that additional dividends will be declared and paid at any time in the future. See Note 6, “Long-Term Debt,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements and “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations – Liquidity and Capital Resources” for additional discussion of dividends and for a description of restrictions on the payment of dividends.
The following table sets forth the high and low closing sales prices for our Class A common stock for each calendar quarter during the periods indicated as reported by the NYSE Composite Tape and the dividends declared during such periods:
|
|
|
Market Price |
|
|
Cash Dividend |
|
||||||
|
|
|
High |
|
|
Low |
|
|
Declared |
|
|||
|
2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fourth Quarter |
|
$ |
24.00 |
|
|
$ |
16.90 |
|
|
$ |
0.050 |
|
|
Third Quarter |
|
$ |
19.19 |
|
|
$ |
16.68 |
|
|
$ |
0.050 |
|
|
Second Quarter |
|
$ |
19.04 |
|
|
$ |
16.15 |
|
|
$ |
0.050 |
|
|
First Quarter |
|
$ |
22.35 |
|
|
$ |
15.91 |
|
|
$ |
0.050 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fourth Quarter |
|
$ |
25.30 |
|
|
$ |
20.73 |
|
|
$ |
0.038 |
|
|
Third Quarter |
|
$ |
24.78 |
|
|
$ |
20.35 |
|
|
$ |
0.025 |
|
|
Second Quarter |
|
$ |
25.37 |
|
|
$ |
23.25 |
|
|
$ |
0.025 |
|
|
First Quarter |
|
$ |
26.74 |
|
|
$ |
23.16 |
|
|
$ |
0.025 |
|
24
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table sets forth information about the shares of Class A common stock we repurchased during the three months ended December 31, 2016:
|
|
|
Total Number of Shares Purchased |
|
|
Average Price Paid per Share |
|
|
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs (1) |
|
|
Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per share data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
October 2016 |
|
|
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
$ |
47,518 |
|
|
November 2016 |
|
|
147 |
|
|
$ |
16.90 |
|
|
|
147 |
|
|
$ |
45,033 |
|
|
December 2016 |
|
|
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
$ |
45,033 |
|
|
Total |
|
|
147 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
147 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)On January 20, 2016, we announced that our Board of Directors had increased the dollar amount authorized for us to repurchase shares of our Class A common stock pursuant to our previously announced share repurchase program. Our share repurchase program does not have an expiration date and current remaining availability under the program is as follows:
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|
January 2016 authorization |
|
|
$ |
100,000 |
|
|||||||||||
|
Total active program repurchases prior to December 31, 2016 |
|
|
|
(54,967 |
) |
|||||||||||
|
Current remaining availability as of December 31, 2016 |
|
|
$ |
45,033 |
|
|||||||||||
Subsequent to December 31, 2016, our Board of Directors authorized an additional $100.0 million to repurchase shares of our Class A common stock, increasing our remaining repurchase authorization to approximately $145.0 million before including the effect of any share repurchases subsequent to December 31, 2016.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
This selected consolidated financial data should be read in conjunction with “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
25
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
We have accounted for all of our dealership acquisitions using the purchase method of accounting and, as a result, we do not include in our consolidated financial statements the results of operations of these dealerships prior to the date we acquired them. Our selected consolidated financial data reflects the results of operations and financial positions of each of our dealerships acquired prior to December 31, 2016. As a result of the effects of our acquisitions and other potential factors in the future, the historical consolidated financial information described in the selected consolidated financial data is not necessarily indicative of the results of our operations and financial position in the future or the results of our operations and financial position that would have resulted had such acquisitions occurred at the beginning of the periods presented in the selected consolidated financial data.
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
(In millions, except per share data) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Income Statement Data (1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total revenues |
|
$ |
9,731.8 |
|
|
$ |
9,624.3 |
|
|
$ |
9,197.1 |
|
|
$ |
8,843.2 |
|
|
$ |
8,365.5 |
|
|
Impairment charges |
|
$ |
8.1 |
|
|
$ |
18.0 |
|
|
$ |
6.6 |
|
|
$ |
9.9 |
|
|
$ |
0.4 |
|
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations before taxes |
|
$ |
155.2 |
|
|
$ |
145.2 |
|
|
$ |
161.7 |
|
|
$ |
129.0 |
|
|
$ |
141.2 |
|
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations |
|
$ |
94.5 |
|
|
$ |
88.1 |
|
|
$ |
98.6 |
|
|
$ |
84.7 |
|
|
$ |
91.3 |
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
2.07 |
|
|
$ |
1.74 |
|
|
$ |
1.89 |
|
|
$ |
1.60 |
|
|
$ |
1.68 |
|
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
2.06 |
|
|
$ |
1.73 |
|
|
$ |
1.87 |
|
|
$ |
1.59 |
|
|
$ |
1.56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance Sheet Data (1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
3,639.3 |
|
|
$ |
3,562.4 |
|
|
$ |
3,168.3 |
|
|
$ |
3,036.8 |
|
|
$ |
2,762.7 |
|
|
Current maturities of long-term debt |
|
$ |
43.0 |
|
|
$ |
33.4 |
|
|
$ |
30.8 |
|
|
$ |
18.2 |
|
|
$ |
18.6 |
|
|
Total long-term debt |
|
$ |
882.7 |
|
|
$ |
814.6 |
|
|
$ |
758.5 |
|
|
$ |
734.0 |
|
|
$ |
615.4 |
|
|
Total long-term liabilities (including long-term debt) |
|
$ |
1,020.3 |
|
|
$ |
952.1 |
|
|
$ |
885.3 |
|
|
$ |
846.9 |
|
|
$ |
730.6 |
|
|
Cash dividends declared per common share |
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
$ |
0.11 |
|
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1) As discussed in “Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Liquidity and Capital Resources” and Notes 2, 5 and 6 to the accompanying consolidated financial statements, impairment charges, business combinations and dispositions and debt refinancings have had a material impact on our reported historical consolidated financial information. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
26
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
The following discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The financial and statistical data contained in the following discussion for all periods presented reflects our December 31, 2016 classification of dealerships between continuing and discontinued operations in accordance with “Presentation of Financial Statements” in the Accounting Standards Codification (the “ASC”).
Except to the extent that differences among operating segments are material to an understanding of our business taken as a whole, we present the discussion in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations on a consolidated basis.
Unless otherwise noted, all discussion of increases or decreases are compared to the same prior year period, as applicable. The following discussion of new vehicles, used vehicles, wholesale vehicles, parts, service and collision repair and finance, insurance and other are on a same store basis, except where otherwise noted. All continuing operations stores are included within the same store group in the first full month following the first anniversary of the store’s opening or acquisition. During the year ended December 31, 2016, we acquired three stand-alone used vehicle stores, opened two new manufacturer-awarded open point franchised dealerships and opened two new EchoPark® stores, which are included in reported figures for 2016, but are excluded from same store reporting for all periods. During the year ended December 31, 2015, we opened one EchoPark® store, which is included in reported figures for all periods and same store reporting for 2016 compared to 2015, but is excluded from same store reporting for 2015 compared to 2014. During the year ended December 31, 2014, we acquired one mid-line import franchise and two luxury franchises, which are included in both reported figures and same store reporting for all periods. During the year ended December 31, 2014, we opened two EchoPark® stores, which are included in reported figures for all periods and same store reporting for 2016 compared to 2015, but are excluded from same store reporting for 2015 compared to 2014.
We did not dispose of any dealership franchises during the year ended December 31, 2016 and we had no franchises held for sale as of December 31, 2016. We disposed of four franchises during the year ended December 31, 2015. We disposed of nine dealership franchises during the year ended December 31, 2014. The results of operations of these disposed stores are included in continuing operations on the accompanying consolidated statements of income for all periods presented. We elected to adopt and apply the guidance of Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2014-08 beginning with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2014. Dealership franchises disposed of subsequent to March 31, 2014 have not been reclassified to discontinued operations since they did not meet the criteria in ASU 2014-08. See Note 2, “Business Acquisitions and Dispositions,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for tabular disclosure of the effects of disposed stores that remain in continuing operations.
Overview
We are one of the largest automotive retailers in the United States (as measured by total revenue). As of December 31, 2016, we operated 116 franchises in 13 states (representing 25 different brands of cars and light trucks) and 18 collision repair centers. For management and operational reporting purposes, we group certain franchises together that share management and inventory (principally used vehicles) into “stores.” As of December 31, 2016, we operated 107 franchised dealership stores and five EchoPark® stores.
As a result of the way we manage our business, as of December 31, 2016, we had two operating segments: Franchised Dealerships and EchoPark®. Our franchised dealerships provide comprehensive services, including (1) sales of both new and used cars and light trucks; (2) sales of replacement parts and performance of vehicle maintenance, manufacturer warranty repairs, and paint and collision repair services (collectively, “Fixed Operations”); and (3) arrangement of extended warranties, service contracts, financing, insurance and other aftermarket products (collectively, “F&I”) for our customers. EchoPark® provides the same services (excluding new vehicles sales and manufacturer warranty repairs) in unique stand-alone specialty retail locations. Our EchoPark® business operates independently from our franchised new and used dealership sales operations and offers customers an exciting shopping and buying experience. Sales operations in our first EchoPark® market in Denver, Colorado began in the fourth quarter of 2014. As of December 31, 2016, we had five EchoPark® stores in operation, and we expect to open another store in Colorado in the first half of 2017. During the second quarter of 2016, we announced that we have begun the process of expanding EchoPark® operations into additional markets in North Carolina, South Carolina and Texas with operations in these markets expected to begin in 2017 and 2018. We believe that our EchoPark® business will provide long-term benefits to us, our stockholders and guests. However, in the short term, this initiative may negatively impact our overall operating results as we allocate management and capital resources to this business.
27
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
In the fourth quarter of 2013, we announced a new customer experience initiative known as “One Sonic-One Experience” (“OSOE”). This initiative includes several new processes and proprietary technologies from inventory management, electronic desking and pricing tools to a fully developed “customer-centric” Customer Relationship Management tool. We believe that the development of these processes and technologies will allow us to better serve our customers across our entire platform of stores. Our goal is to allow our guests to control the buying process and move at their pace so that once the vehicle has been selected our team can utilize these processes and technologies to allow our guests to complete a new or pre-owned vehicle sales transaction in less than an hour. During the latter half of 2014 and throughout 2015, we rolled out the OSOE initiative at our dealerships in Charlotte, North Carolina. During 2016, we introduced the technology component of the initiative to 14 additional stores in our Alabama, Tennessee and California markets. Additional market implementations will continue upon completion of migration activities and required market/brand specific technology modifications. We believe that our OSOE initiative will provide long-term benefits to us, our stockholders and guests. However, in the short term, this initiative may negatively impact our overall operating results as we allocate management and capital resources to this initiative.
Executive Summary
The U.S. retail automotive industry’s new vehicle unit sales volume increased 0.6% to 17.5 million vehicles in 2016, from 17.4 million vehicles in 2015, according to Bloomberg Financial Markets, via Stephens Inc. For 2017, analysts’ average industry expectation for the new vehicle seasonally adjusted annual rate of sales (“SAAR”) is approximately 17.4 million to 17.5 million vehicles, flat compared to the industry volume level in 2016. We estimate the 2017 new vehicle SAAR will be between 17.0 million and 17.5 million vehicles. Changes in consumer confidence, availability of consumer financing or changes in the financial stability of the automotive manufacturers could cause actual 2017 new vehicle SAAR to vary from expectations. Many factors such as brand and geographic concentrations have caused our past results to differ from the industry’s overall trend, as well as the industry sales mix between retail and fleet new vehicle sales volume. Our current operational goal focuses on growing our retail new vehicle sales, as opposed to fleet new vehicle sales, and, as a result, we believe it is appropriate to compare our retail new vehicle unit sales volume to the retail SAAR (which excludes fleet new vehicle sales). According to PIN from J.D. Power, retail new vehicle unit sales volume decreased 0.7% to 14.1 million vehicles in 2016, from 14.2 million vehicles in 2015.
Our same store retail new vehicle revenue was flat during 2016 in spite of a 2.3% decrease in retail new vehicle unit volume. Retail new vehicle gross profit decreased 2.8% on lower retail new vehicle unit volume and lower retail new vehicle gross profit per unit, which decreased $11 per unit, or 0.6%, to $1,936 per unit. We believe that lower gross margins on retail new vehicles are a result of downward pressure on pricing due to the availability of pricing information to consumers, increased competition for sales between similar branded dealerships and higher overall inventory levels. We anticipate that this trend may continue into 2017 and continue to impact new vehicle gross margins.
Our same store used vehicle unit volume increased 2.0% during 2016, driving a 0.9% increase in used vehicle revenue. Used vehicle gross profit decreased 3.0%, driven by a decrease in used vehicle gross profit per unit of $69 per unit, or 4.9%, to $1,331 per unit. Our same store wholesale vehicle gross loss increased approximately $0.1 million, or 1.3%, during 2016, driven by a 16.5% increase in wholesale unit volume. Our used vehicle inventories were elevated during much of 2016, due to a significant number of vehicles held in inventory as a result of open safety recalls on certain models where the manufacturer instructed dealers not to sell the particular model until the recall work was performed. These “stop-sale” vehicles increased our inventory on-hand and associated floor plan interest expense and negatively affected our retail used vehicle unit volume and gross profit per unit and may continue to negatively affect our dealerships’ results of operations until warranty replacement parts become available or as additional models and model years become included in these safety recalls. As of December 31, 2016, we had approximately 600 “stop-sale” used vehicles in our inventory, which increased our used vehicle days’ supply by approximately two days. We focus on maintaining used vehicle inventory days’ supply in the 30- to 35-day range in order to limit our exposure to market pricing volatility. Adjusted for “stop-sale” vehicles, our used vehicle inventory days’ supply was approximately 34 days as of December 31, 2016.
Our same store Fixed Operations revenue increased 4.3% during 2016, driving a 2.2% increase in Fixed Operations gross profit impacted by a 100 basis point decrease in the Fixed Operations gross margin rate. Our same store customer pay, warranty and internal, sublet and other gross profit increased on higher activity levels in our service bays and increased used vehicle reconditioning volume during 2016, offset partially by a decrease in our wholesale parts business. Although vehicle sales and sales of associated finance, insurance and other aftermarket products are cyclical and are affected by many factors, including overall economic conditions, consumer confidence, levels of discretionary personal income, interest rates and available credit, our parts, service and collision repair services are not closely tied to vehicle sales and are not as dependent upon near-term sales volume. However, significant changes to the level of manufacturer recall and warranty activity could negatively impact our Fixed Operations results in the future.
28
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Our same store F&I revenue increased 4.7% during 2016, driven by a 5.1% increase in F&I gross profit per retail unit, which increased $65 per unit to $1,346 per unit, offsetting the effect of flat combined retail new and used vehicle unit sales volume. We believe that our proprietary software applications, playbook processes and customer-centric selling approach drove increases in gross profit per F&I contract and penetration rates (the number of F&I products sold per vehicle) across our finance contract and service contract product lines. We believe we will continue to improve in this area as we refine our processes, train our associates and continue to sell high levels of retail new and used vehicles at our stores.
Results of Operations
The following table summarizes the percentages of total revenues represented by certain items reflected in our consolidated statements of income:
|
|
|
Percentage of Total Revenues |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New vehicles |
|
|
53.8 |
% |
|
|
54.7 |
% |
|
|
55.7 |
% |
|
Used vehicles |
|
|
26.0 |
% |
|
|
26.1 |
% |
|
|
25.1 |
% |
|
Wholesale vehicles |
|
|
2.2 |
% |
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
|
1.8 |
% |
|
Parts, service and collision repair |
|
|
14.5 |
% |
|
|
14.2 |
% |
|
|
14.1 |
% |
|
Finance, insurance and other, net |
|
|
3.5 |
% |
|
|
3.4 |
% |
|
|
3.3 |
% |
|
Total revenues |
|
|
100.0 |
% |
|
|
100.0 |
% |
|
|
100.0 |
% |
|
Cost of sales |
|
|
85.3 |
% |
|
|
85.3 |
% |
|
|
85.1 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
|
14.7 |
% |
|
|
14.7 |
% |
|
|
14.9 |
% |
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
11.4 |
% |
|
|
11.5 |
% |
|
|
11.6 |
% |
|
Impairment charges |
|
|
0.1 |
% |
|
|
0.2 |
% |
|
|
0.1 |
% |
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
0.8 |
% |
|
|
0.7 |
% |
|
|
0.7 |
% |
|
Operating income (loss) |
|
|
2.4 |
% |
|
|
2.3 |
% |
|
|
2.5 |
% |
|
Interest expense, floor plan |
|
|
0.3 |
% |
|
|
0.2 |
% |
|
|
0.2 |
% |
|
Interest expense, other, net |
|
|
0.5 |
% |
|
|
0.6 |
% |
|
|
0.6 |
% |
|
Other (income) expense, net |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
|
|
(0.1 |
%) |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations before taxes |
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
|
1.5 |
% |
|
|
1.8 |
% |
|
Provision for income taxes for continuing operations - (benefit) expense |
|
|
0.6 |
% |
|
|
0.6 |
% |
|
|
0.7 |
% |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations |
|
|
1.0 |
% |
|
|
0.9 |
% |
|
|
1.1 |
% |
New Vehicles
New vehicle revenues include the sale of new vehicles to retail customers (“retail new vehicles”), as well as the sale of fleet vehicles. New vehicle revenues and gross profit can be influenced by manufacturer incentives to consumers, which vary from cash-back incentives to low interest rate financing, among other things. New vehicle revenues and gross profit are also dependent on vehicle manufacturers providing adequate inventory allocations to our dealerships to meet customer demands and the availability of consumer credit. The automobile manufacturing industry is cyclical and historically has experienced periodic downturns characterized by oversupply and weak demand. As an automotive retailer, we seek to mitigate the effects of this cyclicality by maintaining a diverse brand mix of dealerships. Our brand diversity allows us to offer a broad range of products at a wide range of prices from lower priced, or economy vehicles, to luxury vehicles.
The U.S. retail automotive industry’s new vehicle unit sales volume below reflects all brands marketed or sold in the United States. This industry sales volume includes brands we do not sell and markets in which we do not operate, therefore our new vehicle sales volume may not trend directly in line with industry sales volume. We believe that retail unit sales volume is a more meaningful metric for comparing our new vehicles sales volume to the industry due to our minimal fleet vehicle business.
29
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
(In millions of vehicles) |
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
% Change |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||||
|
U.S. industry volume - Retail (1) |
|
|
14.1 |
|
|
|
14.2 |
|
|
|
(0.7 |
%) |
|
|
14.2 |
|
|
|
13.6 |
|
|
|
4.4 |
% |
|
U.S. industry volume - Fleet |
|
|
3.4 |
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
|
|
6.3 |
% |
|
|
3.2 |
|
|
|
2.8 |
|
|
|
14.3 |
% |
|
U.S. industry volume - Total (2) |
|
|
17.5 |
|
|
|
17.4 |
|
|
|
0.6 |
% |
|
|
17.4 |
|
|
|
16.4 |
|
|
|
6.1 |
% |
|
(1) |
Source: PIN from J.D. Power |
|
(2) |
Source: Bloomberg Financial Markets, via Stephens Inc. |
According to public sources, average industry volume expectations for the year ending December 31, 2017 are approximately 17.4 million to 17.5 million vehicles, which would be virtually flat compared to the industry volume for the year ended December 31, 2016.
The following tables provide a reconciliation of same store basis and reported basis for total new vehicles (retail and fleet sales):
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands, except unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total new vehicle revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
5,214,210 |
|
|
$ |
5,221,517 |
|
|
$ |
(7,307 |
) |
|
|
(0.1 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
20,295 |
|
|
|
43,884 |
|
|
|
(23,589 |
) |
|
|
(53.8 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
5,234,505 |
|
|
$ |
5,265,401 |
|
|
$ |
(30,896 |
) |
|
|
(0.6 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total new vehicle gross profit: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
259,403 |
|
|
$ |
266,632 |
|
|
$ |
(7,229 |
) |
|
|
(2.7 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
1,191 |
|
|
|
1,297 |
|
|
|
(106 |
) |
|
|
(8.2 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
260,594 |
|
|
$ |
267,929 |
|
|
$ |
(7,335 |
) |
|
|
(2.7 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total new vehicle units: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
135,605 |
|
|
|
138,901 |
|
|
|
(3,296 |
) |
|
|
(2.4 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
398 |
|
|
|
1,100 |
|
|
|
(702 |
) |
|
|
(63.8 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
|
136,003 |
|
|
|
140,001 |
|
|
|
(3,998 |
) |
|
|
(2.9 |
%) |
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands, except unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total new vehicle revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
5,187,076 |
|
|
$ |
4,965,615 |
|
|
$ |
221,461 |
|
|
|
4.5 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
78,325 |
|
|
|
158,414 |
|
|
|
(80,089 |
) |
|
|
(50.6 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
5,265,401 |
|
|
$ |
5,124,029 |
|
|
$ |
141,372 |
|
|
|
2.8 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total new vehicle gross profit: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
264,124 |
|
|
$ |
280,264 |
|
|
$ |
(16,140 |
) |
|
|
(5.8 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
3,805 |
|
|
|
8,362 |
|
|
|
(4,557 |
) |
|
|
(54.5 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
267,929 |
|
|
$ |
288,626 |
|
|
$ |
(20,697 |
) |
|
|
(7.2 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total new vehicle units: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
137,884 |
|
|
|
134,062 |
|
|
|
3,822 |
|
|
|
2.9 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
2,117 |
|
|
|
4,355 |
|
|
|
(2,238 |
) |
|
|
(51.4 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
|
140,001 |
|
|
|
138,417 |
|
|
|
1,584 |
|
|
|
1.1 |
% |
30
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Our reported new vehicle results (including fleet) are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reported new vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
5,234,505 |
|
|
$ |
5,265,401 |
|
|
$ |
(30,896 |
) |
|
|
(0.6 |
%) |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
260,594 |
|
|
$ |
267,929 |
|
|
$ |
(7,335 |
) |
|
|
(2.7 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
136,003 |
|
|
|
140,001 |
|
|
|
(3,998 |
) |
|
|
(2.9 |
%) |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
38,488 |
|
|
$ |
37,610 |
|
|
$ |
878 |
|
|
|
2.3 |
% |
|
Gross profit per unit |
|
$ |
1,916 |
|
|
$ |
1,914 |
|
|
$ |
2 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
% |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
5.0 |
% |
|
|
5.1 |
% |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reported new vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
5,265,401 |
|
|
$ |
5,124,029 |
|
|
$ |
141,372 |
|
|
|
2.8 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
267,929 |
|
|
$ |
288,626 |
|
|
$ |
(20,697 |
) |
|
|
(7.2 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
140,001 |
|
|
|
138,417 |
|
|
|
1,584 |
|
|
|
1.1 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
37,610 |
|
|
$ |
37,019 |
|
|
$ |
591 |
|
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
Gross profit per unit |
|
$ |
1,914 |
|
|
$ |
2,085 |
|
|
$ |
(171 |
) |
|
|
(8.2 |
%) |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
5.1 |
% |
|
|
5.6 |
% |
|
|
(50 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
Our same store new vehicle results (including fleet) are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Same store new vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
5,214,210 |
|
|
$ |
5,221,517 |
|
|
$ |
(7,307 |
) |
|
|
(0.1 |
%) |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
259,403 |
|
|
$ |
266,632 |
|
|
$ |
(7,229 |
) |
|
|
(2.7 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
135,605 |
|
|
|
138,901 |
|
|
|
(3,296 |
) |
|
|
(2.4 |
%) |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
38,451 |
|
|
$ |
37,592 |
|
|
$ |
859 |
|
|
|
2.3 |
% |
|
Gross profit per unit |
|
$ |
1,913 |
|
|
$ |
1,920 |
|
|
$ |
(7 |
) |
|
|
(0.4 |
%) |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
5.0 |
% |
|
|
5.1 |
% |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Same store new vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
5,187,076 |
|
|
$ |
4,965,615 |
|
|
$ |
221,461 |
|
|
|
4.5 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
264,124 |
|
|
$ |
280,264 |
|
|
$ |
(16,140 |
) |
|
|
(5.8 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
137,884 |
|
|
|
134,062 |
|
|
|
3,822 |
|
|
|
2.9 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
37,619 |
|
|
$ |
37,040 |
|
|
$ |
579 |
|
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
Gross profit per unit |
|
$ |
1,916 |
|
|
$ |
2,091 |
|
|
$ |
(175 |
) |
|
|
(8.4 |
%) |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
5.1 |
% |
|
|
5.6 |
% |
|
|
(50 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
31
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
During the year ended December 31, 2016, we believe our retail new vehicle unit sales volume was negatively affected by “stop-sale” vehicles held in inventory as a result of open safety recalls on certain models where the manufacturer instructed dealers not to sell the particular model until the recall work was performed. These “stop-sale” vehicles increased our inventory on-hand and associated floor plan interest expense and may continue to negatively affect our dealerships’ results of operations until warranty replacement parts become available or as additional models and model years are included in these safety recalls. As of December 31, 2016, we had approximately 400 “stop-sale” new vehicles in our inventory, which increased our new vehicle days’ supply by approximately one day.
2016 Compared to 2015
Excluding fleet sales, our retail new vehicle revenue was flat and our retail new vehicle unit sales volume decreased 2.3% driven primarily by decreases in retail new vehicle unit sales volume at our BMW, Toyota, Ford, MINI and Land Rover dealerships, offset partially by increases in retail new vehicle unit sales volume at our Honda dealerships. Our retail new vehicle gross profit decreased approximately $7.6 million, or 2.8%, primarily driven by decreases in retail new vehicle gross profit at our Land Rover, Ford, Porsche, General Motors (excluding Cadillac) and MINI dealerships, offset partially by increases in retail new vehicle gross profit at our Honda, Audi and Jaguar dealerships. Our gross profit per retail new unit decreased $11 per unit, or 0.6%, to $1,936 per unit, primarily driven by decreases in gross profit per retail new unit at our Land Rover, Porsche and Ford dealerships, offset partially by increases in gross profit per retail new unit at our Honda, Audi and Jaguar dealerships.
We believe the decline in retail new vehicle gross profit per unit is primarily due to downward pricing pressure in the Houston market as a result of a downturn in the energy sector and its effect on the local economy in addition to a higher supply of certain luxury models, including Land Rover, and downward pressure on pricing due to the availability of pricing information to consumers, increased competition for sales between similar branded dealerships and higher overall inventory levels. We anticipate that this trend may continue into 2017 and continue to impact new vehicle gross margins.
2015 Compared to 2014
Excluding fleet sales, our retail new vehicle revenue increased 4.9% and our retail new vehicle unit sales volume increased 3.4% driven primarily by increases in retail new vehicle unit sales volume at our Toyota, Honda, Land Rover and Mercedes dealerships, offset partially by decreases in retail new vehicle unit sales volume at our MINI, Volkswagen and Hyundai dealerships. Excluding fleet sales, our retail new vehicle gross profit decreased approximately $14.5 million, or 5.2%, primarily driven by decreases in retail new vehicle gross profit at our Toyota and Honda dealerships, offset partially by increases in retail new vehicle gross profit at our Land Rover and Lexus dealerships. Our gross profit per retail new unit decreased $176 per unit, or 8.3%, to $1,943 per unit, primarily driven by decreases in gross profit per retail new unit at our BMW, Audi, Toyota and Honda dealerships, offset partially by increases in gross profit per retail new unit at our Land Rover dealerships.
32
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Used Vehicles
Used vehicle revenues are directly affected by a number of factors including the level of manufacturer incentives on new vehicles, the number and quality of trade-ins and lease turn-ins, the availability and pricing of used vehicles acquired at auction and the availability of consumer credit.
The following tables provide a reconciliation of same store basis and reported basis for retail used vehicles:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total used vehicle revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
$ |
2,502,267 |
|
|
$ |
2,481,090 |
|
|
$ |
21,177 |
|
|
|
0.9 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
30,855 |
|
|
|
30,934 |
|
|
|
(79 |
) |
|
|
(0.3 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
|
$ |
2,533,122 |
|
|
$ |
2,512,024 |
|
|
$ |
21,098 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total used vehicle gross profit: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
$ |
156,841 |
|
|
$ |
161,743 |
|
|
$ |
(4,902 |
) |
|
|
(3.0 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
1,744 |
|
|
|
299 |
|
|
|
1,445 |
|
|
|
483.3 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
$ |
158,585 |
|
|
$ |
162,042 |
|
|
$ |
(3,457 |
) |
|
|
(2.1 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total used vehicle units: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
|
117,814 |
|
|
|
115,549 |
|
|
|
2,265 |
|
|
|
2.0 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
1,360 |
|
|
|
1,574 |
|
|
|
(214 |
) |
|
|
(13.6 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
|
|
119,174 |
|
|
|
117,123 |
|
|
|
2,051 |
|
|
|
1.8 |
% |
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total used vehicle revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
$ |
2,394,454 |
|
|
$ |
2,211,513 |
|
|
$ |
182,941 |
|
|
|
8.3 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
117,570 |
|
|
|
98,734 |
|
|
|
18,836 |
|
|
|
19.1 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
$ |
2,512,024 |
|
|
$ |
2,310,247 |
|
|
$ |
201,777 |
|
|
|
8.7 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total used vehicle gross profit: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
$ |
155,448 |
|
|
$ |
152,355 |
|
|
$ |
3,093 |
|
|
|
2.0 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
6,594 |
|
|
|
4,891 |
|
|
|
1,703 |
|
|
|
34.8 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
$ |
162,042 |
|
|
$ |
157,246 |
|
|
$ |
4,796 |
|
|
|
3.0 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total used vehicle units: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
|
111,212 |
|
|
|
105,161 |
|
|
|
6,051 |
|
|
|
5.8 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
5,911 |
|
|
|
4,952 |
|
|
|
959 |
|
|
|
19.4 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
|
117,123 |
|
|
|
110,113 |
|
|
|
7,010 |
|
|
|
6.4 |
% |
33
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Our reported used vehicle results are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reported used vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
2,533,122 |
|
|
$ |
2,512,024 |
|
|
$ |
21,098 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
158,585 |
|
|
$ |
162,042 |
|
|
$ |
(3,457 |
) |
|
|
(2.1 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
119,174 |
|
|
|
117,123 |
|
|
|
2,051 |
|
|
|
1.8 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
21,256 |
|
|
$ |
21,448 |
|
|
$ |
(192 |
) |
|
|
(0.9 |
%) |
|
Gross profit per unit |
|
$ |
1,331 |
|
|
$ |
1,384 |
|
|
$ |
(53 |
) |
|
|
(3.8 |
%) |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
6.3 |
% |
|
|
6.5 |
% |
|
|
(20 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reported used vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
2,512,024 |
|
|
$ |
2,310,247 |
|
|
$ |
201,777 |
|
|
|
8.7 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
162,042 |
|
|
$ |
157,246 |
|
|
$ |
4,796 |
|
|
|
3.0 |
% |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
117,123 |
|
|
|
110,113 |
|
|
|
7,010 |
|
|
|
6.4 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
21,448 |
|
|
$ |
20,981 |
|
|
$ |
467 |
|
|
|
2.2 |
% |
|
Gross profit per unit |
|
$ |
1,384 |
|
|
$ |
1,428 |
|
|
$ |
(44 |
) |
|
|
(3.1 |
%) |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
6.5 |
% |
|
|
6.8 |
% |
|
|
(30 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
Our same store used vehicle results are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Same store used vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
2,502,267 |
|
|
$ |
2,481,090 |
|
|
$ |
21,177 |
|
|
|
0.9 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
156,841 |
|
|
$ |
161,743 |
|
|
$ |
(4,902 |
) |
|
|
(3.0 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
117,814 |
|
|
|
115,549 |
|
|
|
2,265 |
|
|
|
2.0 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
21,239 |
|
|
$ |
21,472 |
|
|
$ |
(233 |
) |
|
|
(1.1 |
%) |
|
Gross profit per unit |
|
$ |
1,331 |
|
|
$ |
1,400 |
|
|
$ |
(69 |
) |
|
|
(4.9 |
%) |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
6.3 |
% |
|
|
6.5 |
% |
|
|
(20 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Same store used vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
2,394,454 |
|
|
$ |
2,211,513 |
|
|
$ |
182,941 |
|
|
|
8.3 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
155,448 |
|
|
$ |
152,355 |
|
|
$ |
3,093 |
|
|
|
2.0 |
% |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
111,212 |
|
|
|
105,161 |
|
|
|
6,051 |
|
|
|
5.8 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
21,531 |
|
|
$ |
21,030 |
|
|
$ |
501 |
|
|
|
2.4 |
% |
|
Gross profit per unit |
|
$ |
1,398 |
|
|
$ |
1,449 |
|
|
$ |
(51 |
) |
|
|
(3.5 |
%) |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
6.5 |
% |
|
|
6.9 |
% |
|
|
(40 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
During the year ended December 31, 2016, manufacturer “stop-sale” instructions for safety recalls on certain models increased our inventory on-hand by approximately 1,600 vehicles at March 31, 2016 , approximately 4,200 vehicles at June 30, 2016, approximately 1,800 vehicles at September 30, 2016, and approximately 600 vehicles at December 31, 2016, primarily in certain BMW, Honda and Mercedes models. We believe the “stop-sale” inventory negatively affected both our retail unit sales volume and
34
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
gross profit per unit during the year ended December 31, 2016 due to the inability to retail these units, which typically are in higher demand and can yield higher gross profit per unit.
In addition to the factors discussed below, incremental used vehicle unit sales volume during the year ended December 31, 2016 contributed to additional Fixed Operations gross profit (via reconditioning) and F&I gross profit as discussed under the headings “Parts, Service and Collision Repair (“Fixed Operations”)” and “Finance, Insurance and Other, Net (“F&I”)” below.
2016 Compared to 2015
Retail used vehicle revenue increased 0.9%, driven primarily by a 2.0% increase in retail used vehicle unit sales volume. This increase in retail used vehicle unit sales volume was primarily driven by increases in retail used vehicle unit sales volume at our BMW, Mercedes and Toyota dealerships and EchoPark® stores, offset partially by decreases in retail used vehicle unit sales volume at our Honda, Ford and General Motors (excluding Cadillac) dealerships. Retail used vehicle gross profit decreased approximately $4.9 million, or 3.0%, driven primarily by lower retail used vehicle unit sales volume and retail used vehicle gross profit per unit at our dealerships in the Houston market as a result of ongoing economic challenges in that market. Retail used vehicle gross profit per unit decreased $69 per unit, or 4.9%, driven primarily by lower retail used vehicle gross profit per unit at our Honda, General Motors (excluding Cadillac) and Mercedes dealerships. We believe that the decrease in overall retail used vehicle gross profit per unit is due in part to the positive effects of newly redesigned models in certain brands on new vehicle demand, which, in turn, put downward pricing pressure on similar pre-owned models in those brands. In addition, our Houston dealerships, particularly our General Motors (excluding Cadillac), Ford, Volkswagen and BMW dealerships, experienced significant decreases in retail used vehicle gross profit per unit based on both “stop-sale” vehicles in inventory and their exposure to the Houston energy market.
2015 Compared to 2014
Retail used vehicle revenue increased 8.3%, driven primarily by a 5.8% increase in retail used vehicle unit sales volume. This increase in retail used vehicle unit sales volume was primarily driven by increases in retail used vehicle unit sales volume at our BMW, Audi and Honda dealerships. Retail used vehicle gross profit increased approximately $3.1 million, or 2.0%, driven primarily by higher retail used vehicle unit sales volume, offset partially by a $51 per unit decrease in retail used vehicle gross profit per unit, driven primarily by lower retail used vehicle gross profit per unit at our Mercedes, Ford and Toyota dealerships. We believe that the decrease in overall retail used vehicle gross profit per unit is due in part to the positive effects of newly redesigned models in certain brands on new vehicle demand, which, in turn, put downward pricing pressure on similar pre-owned models in those brands. In addition, our Houston dealerships, particularly our Ford, General Motors (excluding Cadillac), BMW and Jaguar dealerships, experienced significant decreases in retail used vehicle gross profit per unit based on their exposure to the Houston energy market.
35
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Wholesale Vehicles
Wholesale vehicle revenues are highly correlated with new and used vehicle retail sales and the associated trade-in volume. Wholesale vehicle revenues are also significantly affected by our corporate inventory management policies, which are designed to optimize our total used vehicle inventory.
The following tables provide a reconciliation of same store basis and reported basis for wholesale vehicles:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total wholesale vehicle revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
$ |
209,323 |
|
|
$ |
153,705 |
|
|
$ |
55,618 |
|
|
|
36.2 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
1,725 |
|
|
|
1,634 |
|
|
|
91 |
|
|
|
5.6 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
$ |
211,048 |
|
|
$ |
155,339 |
|
|
$ |
55,709 |
|
|
|
35.9 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total wholesale vehicle gross profit (loss): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
$ |
(7,062 |
) |
|
$ |
(6,969 |
) |
|
$ |
(93 |
) |
|
|
(1.3 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
(254 |
) |
|
|
(399 |
) |
|
|
145 |
|
|
|
36.3 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
$ |
(7,316 |
) |
|
$ |
(7,368 |
) |
|
$ |
52 |
|
|
|
0.7 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total wholesale vehicle units: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
|
34,798 |
|
|
|
29,869 |
|
|
|
4,929 |
|
|
|
16.5 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
299 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
0.3 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
|
35,098 |
|
|
|
30,168 |
|
|
|
4,930 |
|
|
|
16.3 |
% |
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total wholesale vehicle revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
$ |
149,330 |
|
|
$ |
160,343 |
|
|
$ |
(11,013 |
) |
|
|
(6.9 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
6,009 |
|
|
|
5,815 |
|
|
|
194 |
|
|
|
3.3 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
$ |
155,339 |
|
|
$ |
166,158 |
|
|
$ |
(10,819 |
) |
|
|
(6.5 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total wholesale vehicle gross profit (loss): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
$ |
(6,689 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,303 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,386 |
) |
|
|
(102.5 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
(679 |
) |
|
|
(313 |
) |
|
|
(366 |
) |
|
|
(116.9 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
|
$ |
(7,368 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,616 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,752 |
) |
|
|
(103.8 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total wholesale vehicle units: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
|
|
28,723 |
|
|
|
28,968 |
|
|
|
(245 |
) |
|
|
(0.8 |
%) |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
|
1,445 |
|
|
|
978 |
|
|
|
467 |
|
|
|
47.8 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
|
|
30,168 |
|
|
|
29,946 |
|
|
|
222 |
|
|
|
0.7 |
% |
36
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Our reported wholesale vehicle results are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reported wholesale vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
211,048 |
|
|
$ |
155,339 |
|
|
$ |
55,709 |
|
|
|
35.9 |
% |
|
Gross profit (loss) |
|
$ |
(7,316 |
) |
|
$ |
(7,368 |
) |
|
$ |
52 |
|
|
|
0.7 |
% |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
35,098 |
|
|
|
30,168 |
|
|
|
4,930 |
|
|
|
16.3 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
6,013 |
|
|
$ |
5,149 |
|
|
$ |
864 |
|
|
|
16.8 |
% |
|
Gross profit (loss) per unit |
|
$ |
(208 |
) |
|
$ |
(244 |
) |
|
$ |
36 |
|
|
|
14.8 |
% |
|
Gross profit (loss) as a % of revenue |
|
|
(3.5 |
%) |
|
|
(4.7 |
%) |
|
|
120 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reported wholesale vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
155,339 |
|
|
$ |
166,158 |
|
|
$ |
(10,819 |
) |
|
|
(6.5 |
%) |
|
Gross profit (loss) |
|
$ |
(7,368 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,616 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,752 |
) |
|
|
(103.8 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
30,168 |
|
|
|
29,946 |
|
|
|
222 |
|
|
|
0.7 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
5,149 |
|
|
$ |
5,549 |
|
|
$ |
(400 |
) |
|
|
(7.2 |
%) |
|
Gross profit (loss) per unit |
|
$ |
(244 |
) |
|
$ |
(121 |
) |
|
$ |
(123 |
) |
|
|
(101.7 |
%) |
|
Gross profit (loss) as a % of revenue |
|
|
(4.7 |
%) |
|
|
(2.2 |
%) |
|
|
(250 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
Our same store wholesale vehicle results are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Same store wholesale vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
209,323 |
|
|
$ |
153,705 |
|
|
$ |
55,618 |
|
|
|
36.2 |
% |
|
Gross profit (loss) |
|
$ |
(7,062 |
) |
|
$ |
(6,969 |
) |
|
$ |
(93 |
) |
|
|
(1.3 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
34,798 |
|
|
|
29,869 |
|
|
|
4,929 |
|
|
|
16.5 |
% |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
6,015 |
|
|
$ |
5,146 |
|
|
$ |
869 |
|
|
|
16.9 |
% |
|
Gross profit (loss) per unit |
|
$ |
(203 |
) |
|
$ |
(233 |
) |
|
$ |
30 |
|
|
|
12.9 |
% |
|
Gross profit (loss) as a % of revenue |
|
|
(3.4 |
%) |
|
|
(4.5 |
%) |
|
|
110 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except units and per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Same store wholesale vehicle: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue |
|
$ |
149,330 |
|
|
$ |
160,343 |
|
|
$ |
(11,013 |
) |
|
|
(6.9 |
%) |
|
Gross profit (loss) |
|
$ |
(6,689 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,303 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,386 |
) |
|
|
(102.5 |
%) |
|
Unit sales |
|
|
28,723 |
|
|
|
28,968 |
|
|
|
(245 |
) |
|
|
(0.8 |
%) |
|
Revenue per unit |
|
$ |
5,199 |
|
|
$ |
5,535 |
|
|
$ |
(336 |
) |
|
|
(6.1 |
%) |
|
Gross profit (loss) per unit |
|
$ |
(233 |
) |
|
$ |
(114 |
) |
|
$ |
(119 |
) |
|
|
(104.4 |
%) |
|
Gross profit (loss) as a % of revenue |
|
|
(4.5 |
%) |
|
|
(2.1 |
%) |
|
|
(240 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
37
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Wholesale vehicle revenue and unit sales volume fluctuations are typically a result of retail new and used vehicle unit sales volumes that generate additional trade-in vehicle volume that we are not always able to sell as retail used vehicles and choose to sell at auction. Whenever possible, we prefer to sell a used vehicle through retail channels rather than wholesaling the vehicle at auction.
2016 Compared to 2015
Wholesale vehicle revenue, gross loss and unit sales volume increased due to higher levels of wholesale activity as a result of elevated inventory levels during the first quarter of 2016. Wholesale vehicle unit sales volume as a percentage of total used vehicle unit sales volume (retail plus wholesale) increased 230 basis points as we optimized our used vehicle inventory for current consumer demand heading into the fourth quarter.
2015 Compared to 2014
Wholesale vehicle revenue and unit sales volume decreased, while wholesale gross loss increased due to changes in auction prices and vehicle model mix. Wholesale vehicle unit sales volume as a percentage of total used vehicle unit sales volume (retail plus wholesale) decreased 110 basis points.
Parts, Service and Collision Repair (“Fixed Operations”)
Parts, service and collision repair revenue consists of customer requested orders (“customer pay”), warranty repairs, wholesale parts and internal, sublet and other. Parts and service revenue is driven by the mix of warranty repairs versus customer pay repairs, available service capacity, vehicle quality, manufacturer recalls, customer loyalty and manufacturer prepaid maintenance programs. Internal, sublet and other primarily relates to preparation and reconditioning work performed on vehicles that are sold to customers. When that work is performed by one of our dealerships, the work is classified as internal. In the event the work is performed by a third party on our behalf, it is classified as sublet.
We believe that over time, vehicle quality will improve, but vehicle complexity and the associated demand for repairs at franchised dealerships will offset any revenue lost from improvement in vehicle quality. We also believe that over the long term we have the ability to continue to add service capacity and increase revenues. Manufacturers continue to extend new vehicle warranty periods and have also begun to include regular maintenance items in the warranty coverage. These factors, over the long term, combined with the extended manufacturer warranties on certified pre-owned vehicles, should facilitate long-term growth in our service and parts business. Barriers to long-term growth may include reductions in the rate paid by manufacturers to dealers for warranty work performed, as well as the improved quality of vehicles that may affect the level and frequency of future warranty related revenues.
The following tables provide a reconciliation of same store basis and reported basis for Fixed Operations:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total Fixed Operations revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
1,405,928 |
|
|
$ |
1,348,457 |
|
|
$ |
57,471 |
|
|
|
4.3 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
3,891 |
|
|
|
16,490 |
|
|
|
(12,599 |
) |
|
|
(76.4 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
1,409,819 |
|
|
$ |
1,364,947 |
|
|
$ |
44,872 |
|
|
|
3.3 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Fixed Operations gross profit: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
671,573 |
|
|
$ |
657,374 |
|
|
$ |
14,199 |
|
|
|
2.2 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
2,553 |
|
|
|
8,047 |
|
|
|
(5,494 |
) |
|
|
(68.3 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
674,126 |
|
|
$ |
665,421 |
|
|
$ |
8,705 |
|
|
|
1.3 |
% |
38
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total Fixed Operations revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
1,335,084 |
|
|
$ |
1,249,756 |
|
|
$ |
85,328 |
|
|
|
6.8 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
29,863 |
|
|
|
46,814 |
|
|
|
(16,951 |
) |
|
|
(36.2 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
1,364,947 |
|
|
$ |
1,296,570 |
|
|
$ |
68,377 |
|
|
|
5.3 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Fixed Operations gross profit: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
651,228 |
|
|
$ |
600,585 |
|
|
$ |
50,643 |
|
|
|
8.4 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
14,193 |
|
|
|
22,964 |
|
|
|
(8,771 |
) |
|
|
(38.2 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
665,421 |
|
|
$ |
623,549 |
|
|
$ |
41,872 |
|
|
|
6.7 |
% |
Our reported Fixed Operations results are as follows:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reported Fixed Operations: |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
$ |
582,557 |
|
|
$ |
577,265 |
|
|
$ |
5,292 |
|
|
|
0.9 |
% |
|
Warranty |
|
240,415 |
|
|
|
228,093 |
|
|
|
12,322 |
|
|
|
5.4 |
% |
|
Wholesale parts |
|
176,870 |
|
|
|
181,296 |
|
|
|
(4,426 |
) |
|
|
(2.4 |
%) |
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
409,977 |
|
|
|
378,293 |
|
|
|
31,684 |
|
|
|
8.4 |
% |
|
Total revenue |
$ |
1,409,819 |
|
|
$ |
1,364,947 |
|
|
$ |
44,872 |
|
|
|
3.3 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
$ |
314,791 |
|
|
$ |
316,026 |
|
|
$ |
(1,235 |
) |
|
|
(0.4 |
%) |
|
Warranty |
|
129,924 |
|
|
|
126,571 |
|
|
|
3,353 |
|
|
|
2.6 |
% |
|
Wholesale parts |
|
30,754 |
|
|
|
32,249 |
|
|
|
(1,495 |
) |
|
|
(4.6 |
%) |
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
198,657 |
|
|
|
190,575 |
|
|
|
8,082 |
|
|
|
4.2 |
% |
|
Total gross profit |
$ |
674,126 |
|
|
$ |
665,421 |
|
|
$ |
8,705 |
|
|
|
1.3 |
% |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
|
54.0 |
% |
|
|
54.7 |
% |
|
|
(70 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Warranty |
|
54.0 |
% |
|
|
55.5 |
% |
|
|
(150 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Wholesale parts |
|
17.4 |
% |
|
|
17.8 |
% |
|
|
(40 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
48.5 |
% |
|
|
50.4 |
% |
|
|
(190 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Total gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
47.8 |
% |
|
|
48.8 |
% |
|
|
(100 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
39
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reported Fixed Operations: |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
$ |
577,265 |
|
|
$ |
565,144 |
|
|
$ |
12,121 |
|
|
|
2.1 |
% |
|
Warranty |
|
228,093 |
|
|
|
194,468 |
|
|
|
33,625 |
|
|
|
17.3 |
% |
|
Wholesale parts |
|
181,296 |
|
|
|
188,687 |
|
|
|
(7,391 |
) |
|
|
(3.9 |
%) |
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
378,293 |
|
|
|
348,271 |
|
|
|
30,022 |
|
|
|
8.6 |
% |
|
Total revenue |
$ |
1,364,947 |
|
|
$ |
1,296,570 |
|
|
$ |
68,377 |
|
|
|
5.3 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
$ |
316,026 |
|
|
$ |
309,885 |
|
|
$ |
6,141 |
|
|
|
2.0 |
% |
|
Warranty |
|
126,571 |
|
|
|
106,298 |
|
|
|
20,273 |
|
|
|
19.1 |
% |
|
Wholesale parts |
|
32,249 |
|
|
|
32,633 |
|
|
|
(384 |
) |
|
|
(1.2 |
%) |
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
190,575 |
|
|
|
174,733 |
|
|
|
15,842 |
|
|
|
9.1 |
% |
|
Total gross profit |
$ |
665,421 |
|
|
$ |
623,549 |
|
|
$ |
41,872 |
|
|
|
6.7 |
% |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
|
54.7 |
% |
|
|
54.8 |
% |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Warranty |
|
55.5 |
% |
|
|
54.7 |
% |
|
|
80 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Wholesale parts |
|
17.8 |
% |
|
|
17.3 |
% |
|
|
50 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
50.4 |
% |
|
|
50.2 |
% |
|
|
20 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Total gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
48.8 |
% |
|
|
48.1 |
% |
|
|
70 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
Our same store Fixed Operations results are as follows:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Same store Fixed Operations: |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
$ |
581,642 |
|
|
$ |
569,924 |
|
|
$ |
11,718 |
|
|
|
2.1 |
% |
|
Warranty |
|
240,065 |
|
|
|
225,572 |
|
|
|
14,493 |
|
|
|
6.4 |
% |
|
Wholesale parts |
|
176,850 |
|
|
|
178,958 |
|
|
|
(2,108 |
) |
|
|
(1.2 |
%) |
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
407,371 |
|
|
|
374,003 |
|
|
|
33,368 |
|
|
|
8.9 |
% |
|
Total revenue |
$ |
1,405,928 |
|
|
$ |
1,348,457 |
|
|
$ |
57,471 |
|
|
|
4.3 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
$ |
314,342 |
|
|
$ |
311,926 |
|
|
$ |
2,416 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
% |
|
Warranty |
|
129,721 |
|
|
|
125,255 |
|
|
|
4,466 |
|
|
|
3.6 |
% |
|
Wholesale parts |
|
30,752 |
|
|
|
31,770 |
|
|
|
(1,018 |
) |
|
|
(3.2 |
%) |
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
196,758 |
|
|
|
188,423 |
|
|
|
8,335 |
|
|
|
4.4 |
% |
|
Total gross profit |
$ |
671,573 |
|
|
$ |
657,374 |
|
|
$ |
14,199 |
|
|
|
2.2 |
% |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
|
54.0 |
% |
|
|
54.7 |
% |
|
|
(70 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Warranty |
|
54.0 |
% |
|
|
55.5 |
% |
|
|
(150 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Wholesale parts |
|
17.4 |
% |
|
|
17.8 |
% |
|
|
(40 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
48.3 |
% |
|
|
50.4 |
% |
|
|
(210 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Total gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
47.8 |
% |
|
|
48.8 |
% |
|
|
(100 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
40
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Same store Fixed Operations: |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
$ |
566,939 |
|
|
$ |
545,349 |
|
|
$ |
21,590 |
|
|
|
4.0 |
% |
|
Warranty |
|
224,478 |
|
|
|
187,094 |
|
|
|
37,384 |
|
|
|
20.0 |
% |
|
Wholesale parts |
|
178,113 |
|
|
|
181,878 |
|
|
|
(3,765 |
) |
|
|
(2.1 |
%) |
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
365,554 |
|
|
|
335,435 |
|
|
|
30,119 |
|
|
|
9.0 |
% |
|
Total revenue |
$ |
1,335,084 |
|
|
$ |
1,249,756 |
|
|
$ |
85,328 |
|
|
|
6.8 |
% |
|
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
$ |
310,297 |
|
|
$ |
299,075 |
|
|
$ |
11,222 |
|
|
|
3.8 |
% |
|
Warranty |
|
124,675 |
|
|
|
102,376 |
|
|
|
22,299 |
|
|
|
21.8 |
% |
|
Wholesale parts |
|
31,599 |
|
|
|
31,300 |
|
|
|
299 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
% |
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
184,657 |
|
|
|
167,834 |
|
|
|
16,823 |
|
|
|
10.0 |
% |
|
Total gross profit |
$ |
651,228 |
|
|
$ |
600,585 |
|
|
$ |
50,643 |
|
|
|
8.4 |
% |
|
Gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer pay |
|
54.7 |
% |
|
|
54.8 |
% |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Warranty |
|
55.5 |
% |
|
|
54.7 |
% |
|
|
80 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Wholesale parts |
|
17.7 |
% |
|
|
17.2 |
% |
|
|
50 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Internal, sublet and other |
|
50.5 |
% |
|
|
50.0 |
% |
|
|
50 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Total gross profit as a % of revenue |
|
48.8 |
% |
|
|
48.1 |
% |
|
|
70 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
2016 Compared to 2015
Our Fixed Operations customer pay revenue increased approximately $11.7 million, or 2.1%. Customer pay gross profit increased approximately $2.4 million, or 0.8%, driven primarily by increases at our Audi, Lexus, Honda and Land Rover dealerships, offset partially by a decrease at our BMW dealerships. Warranty revenue increased approximately $14.5 million, or 6.4%, driven primarily by increases at our Toyota, Honda and Mercedes dealerships, offset partially by decreases at our Lexus and Volkswagen dealerships. Warranty gross profit increased approximately $4.5 million, or 3.6%, driven primarily by increases at our Toyota, Honda, Mercedes and Land Rover dealerships, offset partially by a decrease at our Lexus dealerships. Wholesale parts revenue decreased approximately $2.1 million, or 1.2%, and wholesale parts gross profit decreased approximately $1.0 million, or 3.2%, driven primarily by a decrease at our BMW dealerships. Internal, sublet and other revenue increased approximately $33.4 million, or 8.9%, and internal, sublet and other gross profit increased approximately $8.3 million, or 4.4%, on higher levels of used vehicle reconditioning and hail damage repairs.
The increase in Fixed Operations revenue contributed approximately $28.0 million in additional gross profit, offset partially by a 100 basis point decrease in the gross margin rate, which reduced the revenue impact by approximately $13.8 million, for a net $14.2 million increase in Fixed Operations gross profit. The gross margin rate decreased primarily due to a customer pay gross margin decrease at our BMW dealerships and a shift in revenue mix from higher margin customer pay work to lower margin sublet business as a result of hail damage repairs and cost associated with loaner vehicles related to customer vehicles subject to safety recalls.
2015 Compared to 2014
Our Fixed Operations customer pay revenue increased approximately $21.6 million, or 4.0%, and customer pay gross profit increased approximately $11.2 million, or 3.8%, driven primarily by increases at our BMW, Audi, Mercedes and Porsche dealerships. Warranty revenue increased approximately $37.4 million, or 20.0%, and warranty gross profit increased approximately $22.3 million, or 21.8%, led by increases in warranty activity at our BMW, Honda, Cadillac and Audi dealerships. Wholesale parts revenue decreased approximately $3.8 million, or 2.1%, and wholesale parts gross profit increased approximately $0.3 million, or 1.0%, driven primarily by higher levels of sales activity and gross margin rate at our Audi dealerships. Internal, sublet and other revenue increased approximately increased $30.1 million, or 9.0%, and internal, sublet and other gross profit increased approximately $16.8 million, or 10.0%, on higher levels of used vehicle reconditioning.
41
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
The increase in Fixed Operations revenue contributed approximately $41.0 million in additional gross profit, which, combined with $9.6 million of additional gross profit due to a 70 basis point increase in the gross margin rate, resulted in a net $50.6 million increase in Fixed Operations gross profit. The gross margin rate increased primarily due to a shift in revenue mix away from lower margin wholesale parts to higher margin warranty work compared to the prior year.
Finance, Insurance and Other, Net (“F&I”)
Finance, insurance and other, net revenues include commissions for arranging vehicle financing and insurance, sales of third-party extended warranties and service contracts for vehicles, and other aftermarket products. In connection with vehicle financing, extended warranties, service contracts, other aftermarket products and insurance contracts, we receive commissions from the providers for originating contracts. F&I revenues are recognized net of estimated chargebacks and other costs associated with originating contracts. F&I revenues are driven by the level of new and used vehicle unit sales, manufacturer financing or leasing incentives and our F&I penetration rate. The F&I penetration rate represents the number of finance contracts, extended warranties and service contracts, other aftermarket products or insurance contracts that we are able to originate per vehicle sold, expressed as a percentage.
Rate spread is another term for the commission earned by our dealerships for arranging vehicle financing for consumers. The amount of the commission could be zero, a flat fee or an actual spread between the interest rate charged to the consumer and the interest rate provided by the direct financing source (bank, credit union or manufacturers’ captive finance company). We have established caps on the potential rate spread our dealerships can earn with all finance sources. We believe the rate spread we earn for arranging financing represents value to the consumer in numerous ways, including the following:
|
|
• |
lower cost, below-market financing is often available only from the manufacturers’ captives and franchised dealers; |
|
|
• |
generally easy access to multiple high-quality lending sources; |
|
|
• |
lease-financing alternatives are largely available only from manufacturers’ captives or other indirect lenders; |
|
|
• |
customers with substandard credit frequently do not have direct access to potential sources of sub-prime financing; and |
|
|
• |
customers with significant “negative equity” in their current vehicle (i.e., the customer’s current vehicle is worth less than the balance of their vehicle loan or lease obligation) frequently are unable to pay off the loan on their current vehicle and finance the purchase or lease of a replacement new or used vehicle without the assistance of a franchised dealer. |
The following tables provide a reconciliation of same store basis and reported basis for F&I:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands, except per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total F&I revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
338,733 |
|
|
$ |
323,556 |
|
|
$ |
15,177 |
|
|
|
4.7 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
4,552 |
|
|
|
3,032 |
|
|
|
1,520 |
|
|
|
50.1 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
343,285 |
|
|
$ |
326,588 |
|
|
$ |
16,697 |
|
|
|
5.1 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total F&I gross profit per retail unit (excludes fleet): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
1,346 |
|
|
$ |
1,281 |
|
|
$ |
65 |
|
|
|
5.1 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
1,354 |
|
|
$ |
1,279 |
|
|
$ |
75 |
|
|
|
5.9 |
% |
42
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands, except per unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total F&I revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
318,476 |
|
|
$ |
290,368 |
|
|
$ |
28,108 |
|
|
|
9.7 |
% |
|
Acquisitions and dispositions |
|
8,112 |
|
|
|
9,727 |
|
|
|
(1,615 |
) |
|
|
(16.6 |
%) |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
326,588 |
|
|
$ |
300,095 |
|
|
$ |
26,493 |
|
|
|
8.8 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total F&I gross profit per retail unit (excludes fleet): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Same store |
$ |
1,288 |
|
|
$ |
1,227 |
|
|
$ |
61 |
|
|
|
5.0 |
% |
|
Total as reported |
$ |
1,279 |
|
|
$ |
1,220 |
|
|
$ |
59 |
|
|
|
4.8 |
% |
2016 Compared to 2015
F&I revenues increased approximately $15.2 million, or 4.7%, and F&I gross profit per retail unit increased $65 per unit, or 5.1%, to $1,346 per unit. The growth in F&I revenues and gross profit is attributed to improved penetration rates on finance and service contracts as a result of increased visibility into performance drivers provided by our proprietary internal software applications, which more than offset the impact of lower combined retail new and used vehicle unit sales volume. Finance contract revenue increased 2.5% due to a 290 basis point increase in penetration rate and a 3.6% increase in finance contract volume, partially offset by a 1.0% decrease in gross profit per finance contract. Finance contract gross profit, particularly on new vehicles, may be under pressure in future periods if manufacturers offer attractive financing rates from their captive finance affiliates because we tend to earn lower commissions under these programs. Service contract gross profit increased 12.3% due to a 210 basis point increase in penetration rate, driving a 5.8% increase in service contract volume, in addition to a 6.2% increase in gross profit per service contract. Other aftermarket contract gross profit increased 0.3%, partially offset by a 1,000 basis point decrease in penetration rate. Finance, service and other aftermarket penetration rates were positively impacted by a strengthening economy and increasing consumer confidence, combined with continued positive results from our F&I playbook processes and customer-centric selling approach.
2015 Compared to 2014
F&I revenues increased approximately $28.1 million, or 9.7%, primarily due to a 4.4% increase in total retail (excluding fleet) new and used vehicle unit sales volume and a 5.0% increase in F&I gross profit per unit to $1,288 per unit. Finance contract gross profit increased 9.4%, due to a 240 basis point increase in penetration rate, driving an 8.0% increase in finance contract volume and a 1.3% increase in gross profit per finance contract. Service contract gross profit increased 7.0%, due to a 100 basis point increase in penetration rate, driving a 7.6% increase in service contract volume, partially offset by a 0.6% decrease in gross profit per service contract. Other aftermarket contract gross profit increased 12.1% due to a 440 basis point increase in penetration rate, driving a 7.8% increase in aftermarket contract volume and a 3.9% increase in gross profit per aftermarket contract.
43
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Segment Results
In the following table of financial data, total segment income of the operating segments is reconciled to consolidated operating income, less floor plan interest expense.
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
9,602,562 |
|
|
$ |
9,547,236 |
|
|
$ |
55,326 |
|
|
|
0.6 |
% |
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
129,217 |
|
|
|
77,063 |
|
|
|
52,154 |
|
|
|
67.7 |
% |
|
Total consolidated revenues |
|
$ |
9,731,779 |
|
|
$ |
9,624,299 |
|
|
$ |
107,480 |
|
|
|
1.1 |
% |
|
Segment income (loss) (1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
217,306 |
|
|
$ |
213,224 |
|
|
$ |
4,082 |
|
|
|
1.9 |
% |
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
(12,113 |
) |
|
|
(17,257 |
) |
|
|
5,144 |
|
|
|
29.8 |
% |
|
Total segment income (loss) |
|
|
205,193 |
|
|
|
195,967 |
|
|
|
9,226 |
|
|
|
4.7 |
% |
|
Interest expense, other, net |
|
|
(50,106 |
) |
|
|
(50,910 |
) |
|
|
804 |
|
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
Other income (expense), net |
|
|
125 |
|
|
|
99 |
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
26.3 |
% |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations before taxes |
|
$ |
155,212 |
|
|
$ |
145,156 |
|
|
$ |
10,056 |
|
|
|
6.9 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retail new and used vehicle unit sales volume: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
|
248,597 |
|
|
|
252,027 |
|
|
|
(3,430 |
) |
|
|
(1.4 |
%) |
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
4,865 |
|
|
|
3,225 |
|
|
|
1,640 |
|
|
|
50.9 |
% |
|
Total retail new and used vehicle unit sales volume |
|
|
253,462 |
|
|
|
255,252 |
|
|
|
(1,790 |
) |
|
|
(0.7 |
%) |
|
(1) |
Segment income (loss) for each segment is defined as operating income less floor plan interest expense. |
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except unit data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
9,547,236 |
|
|
$ |
9,191,661 |
|
|
$ |
355,575 |
|
|
|
3.9 |
% |
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
77,063 |
|
|
|
5,438 |
|
|
|
71,625 |
|
|
|
1317.1 |
% |
|
Total consolidated revenues |
|
$ |
9,624,299 |
|
|
$ |
9,197,099 |
|
|
$ |
427,200 |
|
|
|
4.6 |
% |
|
Segment income (loss) (1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
213,224 |
|
|
$ |
230,733 |
|
|
$ |
(17,509 |
) |
|
|
(7.6 |
%) |
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
(17,257 |
) |
|
|
(15,913 |
) |
|
|
(1,344 |
) |
|
|
(8.4 |
%) |
|
Total segment income (loss) |
|
|
195,967 |
|
|
|
214,820 |
|
|
|
(18,853 |
) |
|
|
(8.8 |
%) |
|
Interest expense, other, net |
|
|
(50,910 |
) |
|
|
(53,190 |
) |
|
|
2,280 |
|
|
|
4.3 |
% |
|
Other income (expense), net |
|
|
99 |
|
|
|
97 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2.1 |
% |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations before taxes |
|
$ |
145,156 |
|
|
$ |
161,727 |
|
|
$ |
(16,571 |
) |
|
|
(10.2 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retail new and used vehicle unit sales volume: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
|
252,027 |
|
|
|
245,833 |
|
|
|
6,194 |
|
|
|
2.5 |
% |
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
3,225 |
|
|
|
212 |
|
|
|
3,013 |
|
|
|
1421.2 |
% |
|
Total retail new and used vehicle unit sales volume |
|
|
255,252 |
|
|
|
246,045 |
|
|
|
9,207 |
|
|
|
3.7 |
% |
|
(1)Segment income (loss) for each segment is defined as operating income less floor plan interest expense.
|
||||||||||||||||
44
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Franchised Dealerships
See the previous headings “New Vehicles,” “Used Vehicles,” “Wholesale Vehicles,” “Parts, Service and Collision Repair (“Fixed Operations”)” and “Finance, Insurance and Other, Net (“F&I”)” for further discussion of the operating results of our Franchised Dealerships segment. The previous analyses and discussion include operating results for our EchoPark® segment as the results for EchoPark® are not material to the combined operating results.
EchoPark®
We opened the first two EchoPark® locations in November and December 2014, and we opened the third location in January 2015 and the fourth and fifth locations in June 2016. We expect to open an additional EchoPark® store in Colorado in the first half of 2017, and have begun the process of expanding EchoPark® operations into additional markets in North Carolina, South Carolina and Texas with operations in these markets expected to begin in 2017 and 2018. Our EchoPark® business operates independently from our franchised new and used dealership sales operations and offers customers an exciting shopping and buying experience.
During the year ended December 31, 2016, EchoPark® generated approximately $129.2 million of revenue, up $52.2 million, or 67.7%, from the prior year, and gross profit of approximately $15.7 million, up $6.0 million, or 61.8%, from the prior year. EchoPark® retail used vehicle unit sales volume was 4,865 units, up 1,640 units, or 50.9%, from the prior year, and retail used vehicle gross profit per unit was $1,133 per unit, a decrease of $208 per unit, or 15.5%, from the prior year, due primarily to the costs of acquiring sufficient inventory for two additional store openings in 2016. EchoPark® F&I gross profit per unit was $1,339 per unit, up $396 per unit, or 42.0%, from the prior year, as our training and playbook processes enabled our customer experience guides to more effectively provide F&I products to our customers. EchoPark® incurred a $12.7 million operating loss during the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to a $17.7 million operating loss in the prior year, which includes the effects of a $1.4 million impairment charge in 2015.
Selling, General and Administrative (“SG&A”) Expenses
SG&A expenses are comprised of four major groups: compensation expense, advertising expense, rent expense and other expense. Compensation expense primarily relates to dealership personnel who are paid a commission or a salary plus commission and support personnel who are paid a fixed salary. Commissions paid to dealership personnel typically vary depending on gross profits realized and sales volume objectives. Due to the salary component for certain dealership and corporate personnel, gross profits and compensation expense do not change in direct proportion to one another. Advertising expense and other expense vary based on the level of actual or anticipated business activity and number of dealerships in operation. Rent expense typically varies with the number of dealerships owned, investments made for facility improvements and interest rates. Other expense includes various fixed and variable expenses, including certain customer-related costs, insurance, training, legal and IT expenses, which may not change in proportion to gross profit levels.
The following tables set forth information related to our reported SG&A expenses:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
SG&A expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation |
$ |
674,617 |
|
|
$ |
666,668 |
|
|
$ |
(7,949 |
) |
|
|
(1.2 |
%) |
|
Advertising |
|
61,674 |
|
|
|
61,630 |
|
|
|
(44 |
) |
|
|
(0.1 |
%) |
|
Rent |
|
73,903 |
|
|
|
73,539 |
|
|
|
(364 |
) |
|
|
(0.5 |
%) |
|
Other |
|
300,662 |
|
|
|
308,728 |
|
|
|
8,066 |
|
|
|
2.6 |
% |
|
Total SG&A expenses |
$ |
1,110,856 |
|
|
$ |
1,110,565 |
|
|
$ |
(291 |
) |
|
|
(0.0 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SG&A expenses as a % of gross profit: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation |
|
47.2 |
% |
|
|
47.1 |
% |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Advertising |
|
4.3 |
% |
|
|
4.4 |
% |
|
|
10 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Rent |
|
5.2 |
% |
|
|
5.2 |
% |
|
|
- |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Other |
|
21.0 |
% |
|
|
21.8 |
% |
|
|
80 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Total SG&A expenses as a % of gross profit |
|
77.7 |
% |
|
|
78.5 |
% |
|
|
80 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
45
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
SG&A expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation |
$ |
666,668 |
|
|
$ |
638,875 |
|
|
$ |
(27,793 |
) |
|
|
(4.4 |
%) |
|
Advertising |
|
61,630 |
|
|
|
57,437 |
|
|
|
(4,193 |
) |
|
|
(7.3 |
%) |
|
Rent |
|
73,539 |
|
|
|
73,707 |
|
|
|
168 |
|
|
|
0.2 |
% |
|
Other |
|
308,728 |
|
|
|
297,414 |
|
|
|
(11,314 |
) |
|
|
(3.8 |
%) |
|
Total SG&A expenses |
$ |
1,110,565 |
|
|
$ |
1,067,433 |
|
|
$ |
(43,132 |
) |
|
|
(4.0 |
%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SG&A expenses as a % of gross profit: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation |
|
47.1 |
% |
|
|
46.8 |
% |
|
|
(30 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Advertising |
|
4.4 |
% |
|
|
4.2 |
% |
|
|
(20 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Rent |
|
5.2 |
% |
|
|
5.4 |
% |
|
|
20 |
|
|
bps |
|
|
|
Other |
|
21.8 |
% |
|
|
21.7 |
% |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
|
Total SG&A expenses as a % of gross profit |
|
78.5 |
% |
|
|
78.1 |
% |
|
|
(40 |
) |
|
bps |
|
|
2016 Compared to 2015
Overall SG&A expenses were flat in dollar amount and decreased 80 basis points as a percentage of gross profit, primarily due to an original equipment manufacturer (“OEM”) legal settlement benefit, offset partially by higher compensation and employee benefit-related expenses and IT expenses. Compensation costs increased both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit, primarily due to higher levels of employee benefit-related expenses, Fixed Operations compensation and F&I compensation, offset partially by lower medical insurance costs. Advertising expense was relatively flat both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit as we focused on targeted advertising where we would expect the best returns for our business. Rent expense was relatively flat both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit, primarily due to our strategy to own more of our dealership properties, offset by higher rent expense for additional inventory storage needs. Other SG&A expenses decreased both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit, primarily due to a $14.8 million benefit as a result of an OEM-related settlement, offset partially by higher IT expenses, repairs and maintenance expenses and a net gain on disposal of franchises in the prior year. On an adjusted basis, SG&A expenses as a percentage of gross profit were 78.5%, flat compared to the prior year. For the year ended December 31, 2016, adjusted SG&A expenses exclude an OEM legal settlement benefit of approximately $14.8 million, offset partially by charges of approximately $3.0 million related to hail damage and approximately $0.3 million of lease exit and other charges. For the year ended December 31, 2015, adjusted SG&A expenses exclude charges of approximately $3.5 million related to storm-related physical damage and approximately $1.7 million of legal and severance expenses, offset partially by a net gain on disposal of franchises of approximately $3.3 million.
2015 Compared to 2014
Overall SG&A expenses increased both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit, due in part to costs related to our EchoPark®, OSOE and other strategic initiatives, among other cost drivers as discussed below. Overall SG&A expenses as a percentage of gross profit increased 40 basis points. Excluding the effect of EchoPark® expenses, total SG&A expenses as a percentage of gross profit increased 50 basis points. Compensation costs increased both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit, primarily due to lower gross margins on new vehicles, increased headcount related to EchoPark® staffing and higher medical insurance costs. Advertising expense increased both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit due to increased advertising programs for expansion at EchoPark® and our OSOE initiative. Rent expense decreased both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit, primarily due to higher gross profit levels and the purchase of certain properties that were previously leased. Other SG&A expenses increased both in dollar amount and as a percentage of gross profit, primarily due to a gain on disposal of franchises in the prior year, increases in IT expenses related to EchoPark® and our OSOE initiative, legal fees and real estate taxes.
On an adjusted basis, SG&A expenses as a percentage of gross profit were 78.4%, down 20 basis points from the prior year. For the year ended December 31, 2015, adjusted SG&A expenses exclude charges of approximately $3.5 million related to storm-related physical damage and approximately $1.7 million of legal and severance expenses, offset partially by a net gain on disposal of franchises of approximately $3.3 million. For the year ended December 31, 2014, adjusted SG&A expenses exclude a net gain on
46
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
disposal of franchises of approximately $10.7 million, offset partially by charges of approximately $4.0 million related to storm-related physical damage and approximately $1.1 million of legal settlement and environmental expense.
Impairment Charges
Impairment charges decreased approximately $9.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to the prior year. Impairment charges increased $11.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the prior year. Impairment charges for the year ended December 31, 2016 include approximately $8.1 million of property and equipment charges due to the abandonment of construction and software development projects as well as our estimate that certain dealerships would not be able to recover these balances through operating activities. Impairment charges for the year ended December 31, 2015 include $5.2 million of franchise asset impairment charges and approximately $4.8 million of goodwill and franchise asset impairment charges related to the disposition of a dealership franchise, $0.9 million of franchise asset impairment charges and $7.1 million of property and equipment charges due to the abandonment of construction and software development projects as well as our estimate that certain dealerships would not be able to recover these balances through operating activities. Impairment charges for the year ended December 31, 2014 include $2.2 million of franchise asset impairment charges and approximately $4.4 million of property and equipment charges due to the abandonment of construction and software development projects as well as our estimate that certain dealerships would not be able to recover these balances through operating activities.
Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation expense increased approximately $8.6 million, or 12.6%, in the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to the prior year, and $10.5 million, or 18.1%, in the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to the prior year. The increases were primarily related to continuing operations net additions to gross property and equipment (excluding land and construction in progress) of approximately $144.1 million and $140.7 million in the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Interest Expense, Floor Plan
2016 Compared to 2015
Interest expense, floor plan for new vehicles incurred by continuing operations increased approximately $5.5 million, or 27.8%. The average new vehicle floor plan notes payable balance for continuing operations increased approximately $137.5 million, resulting in an increase in new vehicle floor plan interest expense of approximately $2.2 million. The average new vehicle floor plan interest rate incurred by continuing operations dealerships was 1.85%, up from 1.61% in the prior year, which resulted in an increase in interest expense of approximately $3.3 million.
Interest expense, floor plan for used vehicles incurred by continuing operations increased approximately $0.9 million, or 54.7%. The average used vehicle floor plan notes payable balance for continuing operations increased approximately $49.3 million, resulting in an increase in new vehicle floor plan interest expense of approximately $0.8 million. The average used vehicle floor plan interest rate incurred by continuing operations dealerships was 1.78%, up from 1.72% in the prior year, which resulted in an increase in interest expense of approximately $0.1 million.
2015 Compared to 2014
Interest expense, floor plan for new vehicles incurred by continuing operations increased approximately $2.1 million, or 11.8%. The average new vehicle floor plan notes payable balance for continuing operations increased approximately $101.4 million, resulting in an increase in new vehicle floor plan interest expense of approximately $1.6 million. The average new vehicle floor plan interest rate incurred by continuing operations dealerships was 1.61%, up from 1.57% in the prior year, which resulted in an increase in interest expense of approximately $0.5 million.
Interest expense, floor plan for used vehicles incurred by continuing operations increased approximately $0.5 million, or 37.7%. The average used vehicle floor plan notes payable balance for continuing operations increased approximately $30.4 million, resulting in an increase in new vehicle floor plan interest expense of approximately $0.6 million. The average used vehicle floor plan interest rate incurred by continuing operations dealerships was 1.72%, down from 1.80% in the prior year, which resulted in a decrease in interest expense of approximately $0.1 million, partially offsetting the impact of the higher average floor plan notes payable balances discussed above.
47
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Interest Expense, Other, Net
Interest expense, other, net is summarized in the tables below:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Stated/coupon interest |
|
$ |
44,689 |
|
|
$ |
42,321 |
|
|
$ |
(2,368 |
) |
|
|
(5.6 |
%) |
|
Discount/premium amortization |
|
|
163 |
|
|
|
152 |
|
|
|
(11 |
) |
|
|
(7.2 |
%) |
|
Deferred loan cost amortization |
|
|
2,641 |
|
|
|
2,489 |
|
|
|
(152 |
) |
|
|
(6.1 |
%) |
|
Cash flow swap interest |
|
|
4,934 |
|
|
|
7,178 |
|
|
|
2,244 |
|
|
|
31.3 |
% |
|
Capitalized interest |
|
|
(2,750 |
) |
|
|
(1,912 |
) |
|
|
838 |
|
|
|
43.8 |
% |
|
Other interest |
|
|
429 |
|
|
|
682 |
|
|
|
253 |
|
|
|
37.1 |
% |
|
Total interest expense, other, net |
|
$ |
50,106 |
|
|
$ |
50,910 |
|
|
$ |
804 |
|
|
|
1.6 |
% |
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Better / (Worse) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Change |
|
|
% Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Stated/coupon interest |
|
$ |
42,321 |
|
|
$ |
41,456 |
|
|
$ |
(865 |
) |
|
|
(2.1 |
%) |
|
Discount/premium amortization |
|
|
152 |
|
|
|
141 |
|
|
|
(11 |
) |
|
|
(7.8 |
%) |
|
Deferred loan cost amortization |
|
|
2,489 |
|
|
|
2,675 |
|
|
|
186 |
|
|
|
7.0 |
% |
|
Cash flow swap interest |
|
|
7,178 |
|
|
|
10,125 |
|
|
|
2,947 |
|
|
|
29.1 |
% |
|
Capitalized interest |
|
|
(1,912 |
) |
|
|
(1,921 |
) |
|
|
(9 |
) |
|
|
(0.5 |
%) |
|
Other interest |
|
|
682 |
|
|
|
714 |
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
4.5 |
% |
|
Total interest expense, other, net |
|
$ |
50,910 |
|
|
$ |
53,190 |
|
|
$ |
2,280 |
|
|
|
4.3 |
% |
2016 Compared to 2015
Interest expense, other, net decreased approximately $0.8 million, primarily due to a $2.2 million decrease in cash flow swap interest as a result of the expiration of several interest rate cash flow swaps that were replaced with cash flow swaps at a lower fixed rate and a $0.8 million decrease in capitalized interest associated with construction and software development projects, offset partially by a $2.4 million increase in stated/coupon interest as a result of additional mortgage notes payable.
2015 Compared to 2014
Interest expense, other, net decreased approximately $2.3 million, primarily due to a $2.9 million decrease in cash flow swap interest as a result of the expiration of several interest rate cash flow swaps that were replaced with cash flow swaps at a lower fixed rate, offset partially by a $0.9 million increase in stated/coupon interest as a result of additional mortgage notes payable.
Provision for Income Taxes
The effective tax rate from continuing operations was 39.1%, 39.3% and 39.1% for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Our effective tax rate varies from year to year based on the distribution of taxable income between states in which we operate and other tax adjustments. We expect the effective tax rate in future periods to fall within a range of 38.0% to 40.0% before the impact, if any, of changes in valuation allowances related to deferred income tax assets or unusual discrete tax adjustments. The effective tax rate in the future will be impacted by the required adoption of ASU 2016-09 which will require all book-tax differences related to the exercise of stock options or vesting of restricted stock to flow through the provision for income taxes rather than possibly be applied directly to equity.
48
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Discontinued Operations
The pre-tax losses from discontinued operations and the sale of dealerships were as follows:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Income (loss) from operations |
$ |
(1,100 |
) |
|
$ |
(1,421 |
) |
|
$ |
(2,515 |
) |
|
Gain (loss) on disposal |
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
199 |
|
|
Lease exit accrual adjustments and charges |
|
(1,020 |
) |
|
|
(1,462 |
) |
|
|
152 |
|
|
Pre-tax income (loss) |
$ |
(2,121 |
) |
|
$ |
(2,883 |
) |
|
$ |
(2,164 |
) |
|
Total revenues |
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
In the year ended December 31, 2014, lease exit accrual adjustments and charges includes a benefit of approximately $1.4 million related to the extension of a sublease, offsetting expense amounts related to ongoing lease exit accrual activity. We do not expect significant activity in discontinued operations in the future due to the change in the definition of a discontinued operation as a result of ASU 2014-08. The results of operations for those dealerships and franchises that were classified as discontinued operations as of March 31, 2014 will continue to be reported within discontinued operations in the future. See the discussion of our adoption of ASU 2014-08 in Note 1, “Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Use of Estimates and Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Critical accounting policies are those that are most important to the portrayal of our financial position and results of operations and require the most subjective and complex judgments. See Note 1, “Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for additional discussion regarding our critical accounting policies and estimates.
Finance, Insurance and Service Contracts
We arrange financing for customers through various financial institutions and receive a commission from the lender either in a flat fee amount or in an amount equal to the difference between the actual interest rates charged to customers and the predetermined interest rates set by the financial institution. We also receive commissions from the sale of various insurance contracts and non-recourse third-party extended service contracts to customers. Under these contracts, the applicable manufacturer or third-party warranty company is directly liable for all warranties provided within the contract.
In the event a customer terminates a financing, insurance or extended service contract prior to the original termination date, we may be required to return a portion of the commission revenue originally recorded to the third-party provider (“chargebacks”). The commission revenue for the sale of these products and services is recorded net of estimated chargebacks at the time of sale. Our estimate of future chargebacks is established based on our historical chargeback rates, termination provisions of the applicable contracts and industry data. While chargeback rates vary depending on the type of contract sold, a 100 basis point change in the estimated chargeback rates used in determining our estimates of future chargebacks would have changed our estimated reserve for chargebacks at December 31, 2016 by approximately $1.4 million. Our estimate of chargebacks (approximately $19.2 million as of December 31, 2016) is influenced by early contract termination events such as vehicle repossessions, refinancings and early pay-offs. If these factors negatively change, the resulting impact would affect our future estimate for chargebacks and could have a material adverse impact on our operations, financial position and cash flows. Our actual chargeback experience has not been materially different from our recorded estimates.
49
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Goodwill and Franchise Assets
In accordance with “Intangibles – Goodwill and Other” in the ASC, we test goodwill for impairment at least annually, or more frequently when events or circumstances indicate that impairment might have occurred. The ASC also states that if an entity determines, based on an assessment of certain qualitative factors, that it is not more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, then the first and second steps of the goodwill impairment test are unnecessary. For our annual impairment assessment as of October 1, 2016, we elected to perform a quantitative step-one assessment.
For purposes of goodwill impairment testing, we have two reporting units, which consist of our traditional franchised dealerships and EchoPark®. The carrying value of our goodwill (all of which is associated with our franchised dealerships reporting unit) totaled approximately $472.4 million at December 31, 2016. We utilized the Market Price (“MP”) method to estimate our reporting unit’s enterprise value. The significant inputs in our MP method include debt value, stock price and control premium. To the extent there are changes in one or more of these inputs that would result in lower valuation results, it could cause the carrying value of the reporting unit to exceed its fair value and thus require us to conduct the second step of the impairment test described under the heading “Goodwill,” in Note 1, “Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Based on the results of our step-one test as of October 1, 2016, our reporting unit’s fair value exceeded its carrying value. Our MP method is dependent on the inputs used and is sensitive to changes in those inputs. In order to determine the effects of changes in our inputs on our MP method and, consequently, our goodwill valuation, we ran multiple scenarios adjusting the debt value, stock price and control premium. In the event our debt value decreased by 10 percent, assuming all other factors remain the same, the calculated fair value estimate as of October 1, 2016 would change by approximately $88.6 million. In the event our stock price decreased by 20 percent, assuming all other factors remain the same, the calculated fair value estimate as of October 1, 2016 would change by approximately $185.6 million. Although we assumed a 10.0% control premium in our method, in the event of no control premium, assuming all other factors remain the same, the calculated fair value estimate as of October 1, 2016 would change by approximately $84.4 million. Based on our MP method, none of the scenarios tested, if realized, would have resulted in lowering the fair value of the reporting unit below the reporting unit’s carrying value. As such, we were not required to complete step two of the impairment evaluation according to “Intangibles – Goodwill and Other” in the ASC. See Note 1, “Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further discussion.
In accordance with “Intangibles – Goodwill and Other” in the ASC, we evaluate franchise assets for impairment annually (as of October 1) or more frequently if indicators of impairment exist. We estimate the fair value of our franchise assets using a discounted cash flow (“DCF”) model. The DCF model used contains inherent uncertainties, including significant estimates and assumptions related to growth rates, projected earnings and cost of capital. We are subject to financial risk to the extent that our franchise assets become impaired due to deterioration of the underlying businesses. The risk of a franchise asset impairment loss may increase to the extent the underlying businesses’ earnings or projected earnings decline. As a result of our impairment testing as of October 1, no impairment charges were recorded for franchise assets in the year ended December 31, 2016.
Insurance Reserves
We have various high deductible retention and insurance policies that require us to make estimates in determining the ultimate liability we may incur for claims arising under these policies. We accrue for insurance reserves throughout the year based on current information available. As of December 31, 2016, we estimated the ultimate liability under these programs to be between $21.2 million and $23.4 million, and had approximately $22.7 million reserved for such programs. Changes in significant assumptions used in the development of the ultimate liability for these programs could have a material impact on the level of reserves, our operating results, financial position and cash flows. These significant assumptions could include the volume of claims, medical cost trends, claims handling and reporting patterns, historical claims experience, the effect of related court rulings, current or projected changes in state laws or an assumed discount rate. From a sensitivity analysis perspective, it is difficult to quantify the effect of changes in any of these significant assumptions with the exception of the volume of claims. We believe a 10% change in the volume of claims would have a proportional effect on our reserves. Our actual loss experience has not been materially different from our recorded estimates.
Lease Exit Accruals
The majority of our dealership properties are leased under long-term operating lease arrangements. When leased properties are no longer utilized in operations, we record lease exit accruals. These situations could include the relocation of an existing facility or the sale of a dealership where the buyer will not be subleasing the property for either the remaining term of the lease or for an amount equal to our obligation under the lease, or situations where a store is closed as a result of the associated franchise being terminated by
50
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
us or the manufacturer and no other operations continue on the leased property. The lease exit accruals represent the present value of the lease payments, net of estimated sublease rentals, for the remaining life of the operating leases and other accruals necessary to satisfy lease commitments to the landlords. As of December 31, 2016, we had approximately $9.8 million accrued for lease exit costs. In addition, based on the terms and conditions negotiated in the sale of dealerships in the future, additional accruals may be necessary if the purchaser of the dealership does not assume any associated lease, or we are unable to negotiate a sublease with the buyer of the dealership on terms that are identical to or better than those associated with the original lease.
A summary of the activity of these operating lease exit accruals consists of the following:
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
14,527 |
|
|
Lease exit expense (1) |
|
|
1,386 |
|
|
Payments (2) |
|
|
(6,123 |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
9,790 |
|
|
(1) |
Expense of approximately $0.1 million is recorded in interest expense, other, net and expense of approximately $0.3 million is recorded in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. In addition, expense of approximately $1.0 million is recorded in income (loss) from discontinued operations in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. |
|
(2) |
Amount is recorded as an offset to rent expense in selling, general and administrative expenses, with approximately $0.7 million in continuing operations and approximately $5.4 million in income (loss) from discontinued operations, in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. |
Legal Proceedings
We are involved, and expect to continue to be involved, in numerous legal proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including litigation with customers, employment-related lawsuits, contractual disputes, class actions, purported class actions and actions brought by governmental authorities. As of December 31, 2016, we had accrued approximately $0.5 million in legal reserves. Although we vigorously defend ourselves in all legal and administrative proceedings, the outcomes of pending and future proceedings arising out of the conduct of our business, including litigation with customers, employment-related lawsuits, contractual disputes, class actions, purported class actions and actions brought by governmental authorities, cannot be predicted with certainty.
Income Taxes
As a matter of course, we are regularly audited by various taxing authorities and, from time to time, these audits result in proposed assessments where the ultimate resolution may result in us owing additional taxes. We believe that our tax positions comply, in all material respects, with applicable tax law and that we have adequately provided for any reasonably foreseeable outcome related to these matters. From time to time, we engage in transactions in which the tax consequences may be subject to uncertainty. Examples of such transactions include business acquisitions and disposals, including consideration paid or received in connection with such transactions. Significant judgment is required in assessing and estimating the tax consequences of these transactions. We determine whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination, including resolution of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits of the position. In evaluating whether a tax position has met the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold, we presume that the position will be examined by the appropriate taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information. A tax position that does not meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold is measured to determine the amount of benefit to be recognized in the financial statements. The tax position is measured at the largest amount of benefit that is likely to be realized upon ultimate settlement. We adjust our estimates periodically because of ongoing examinations by and settlements with the various taxing authorities, as well as changes in tax laws, regulations and precedent.
At December 31, 2016, there was approximately $5.2 million in reserves that we have provided for these matters (including estimates related to possible interest and penalties) with $0.5 million included in other accrued liabilities and approximately $4.7 million recorded in other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The effects on our financial statements of income tax uncertainties are discussed in Note 7, “Income Taxes,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
51
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
We periodically review all deferred tax asset positions (including state net operating loss carryforwards) to determine whether it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized. Certain factors considered in evaluating the potential for realization of deferred tax assets include the time remaining until expiration (related to state net operating loss carryforwards) and various sources of taxable income that may be available under the tax law to realize a tax benefit related to a deferred tax asset. This evaluation requires management to make certain assumptions about future profitability, the execution of tax strategies that may be available to us and the likelihood that these assumptions or execution of tax strategies would occur. This evaluation is highly judgmental. The results of future operations, regulatory framework of these taxing authorities and other related matters cannot be predicted with certainty. Therefore, actual realization of these deferred tax assets may be materially different from management’s estimate.
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, we had a valuation allowance recorded totaling approximately $7.2 million and $5.9 million, respectively, related to certain state net operating loss carryforwards because we concluded we would not be able to generate sufficient state taxable income in the related entities to realize the accumulated net operating loss carryforward balances.
We accrue for income taxes on a pro-rata basis throughout the year based on the expected year-end liability. These estimates, judgments and assumptions are updated quarterly by our management based on available information and take into consideration estimated income taxes based on prior year income tax returns, changes in income tax law, our income tax strategies and other factors. If our management receives information which causes us to change our estimate of the year-end liability, the amount of expense or expense reduction required to be recorded in any particular quarter could be material to our operating results, financial position and cash flows.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-17 to simplify the presentation of deferred income taxes. The amendments in this ASU require deferred tax liabilities and assets to be classified as noncurrent in a classified statement of financial position. The current requirement that deferred tax liabilities and assets of a tax-paying component of an entity must be netted and presented as a single amount is not affected by this ASU. For public companies, this ASU is effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods (early adoption is permitted). We adopted this ASU prospectively effective October 1, 2016, and prior periods were not retrospectively adjusted. Accordingly, as of December 31, 2016, a deferred tax asset of approximately $2.4 million and deferred tax liability of approximately $76.4 million are included in other assets and deferred income taxes, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. We did not adjust prior periods retrospectively for the new ASU, therefore, as of December 31, 2015, a current deferred tax asset of approximately $13.6 million, a current deferred tax liability of approximately $0.1 million, a noncurrent deferred tax asset of approximately $2.8 million and a noncurrent deferred tax liability of approximately $73.3 million are included in other current assets, other accrued liabilities, other assets and deferred income taxes, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (the “FASB”) issued ASU 2014-09 to amend the accounting guidance on revenue recognition. The amendments in this ASU are intended to provide a more robust framework for addressing revenue issues, improve comparability of revenue recognition practices and improve disclosure requirements. The amendments in this ASU will be applied using either of the following transition methods: (i) a full retrospective approach reflecting the application of the standard in each prior reporting period with the option to elect certain practical expedients, or (ii) a modified retrospective approach with the cumulative effect of initially adopting the standard recognized at the date of adoption (which requires additional footnote disclosures). This ASU is effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Earlier application is permitted only as of reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. We plan to adopt this ASU effective January 1, 2018. While we are still evaluating the method of adoption and the impact of the provisions of this ASU, we expect similar performance obligations to result under this update as compared with deliverables and separate units of accounting currently identified. As a result, we expect the timing of our revenue recognition to generally remain the same.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02 to increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. The amendments in this ASU require that leases are classified as either finance or operating leases, a right-of-use asset and lease liability is recognized in the statement of financial position, and repayments are classified within operating activities in the statement of cash flows. The amendments in this ASU are to be applied using a modified retrospective approach and are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2018 (early adoption is permitted). We plan to adopt this ASU effective January 1, 2019. While we are still evaluating the impact of adopting the provisions of this ASU, we expect that upon
52
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
adoption of this ASU, the presentation of certain items in our consolidated financial position, cash flows and other disclosures will be materially impacted, primarily due to the recognition of a right-of-use asset and an associated liability.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09 to simplify several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions. For public companies, this ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2016 (early adoption is permitted). We plan to adopt this ASU effective January 1, 2017. Upon adoption of this ASU, interim period and annual period income tax expense will be affected by stock option exercises and restricted stock vesting activity, potentially creating volatility in our effective income tax rate from period to period.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15 related to the classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments on the statement of cash flows. For public companies, this ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2017 (early adoption is permitted). We plan to adopt this ASU effective January 1, 2018. Upon adoption of this ASU, the presentation of certain items in our cash flows and other disclosures may be impacted.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We require cash to fund debt service, operating lease obligations, working capital requirements, facility improvements and other capital improvements, and dividends on our common stock and to finance acquisitions and otherwise invest in our business. We rely on cash flows from operations, borrowings under our revolving credit and floor plan borrowing arrangements, real estate mortgage financing, asset sales and offerings of debt and equity securities to meet these requirements. We closely monitor our available liquidity and projected future operating results in order to remain in compliance with restrictive covenants under our 2016 Credit Facilities and other debt obligations and lease arrangements. However, our liquidity could be negatively affected if we fail to comply with the financial covenants in our existing debt or lease arrangements. There are no restrictions under our borrowing arrangements on retained earnings or net income. Cash flows provided by our dealerships are derived from various sources. The primary sources include individual consumers, automobile manufacturers, automobile manufacturers’ captive finance subsidiaries and finance companies. Disruptions in these cash flows could have a material and adverse impact on our operations and overall liquidity.
Because the majority of our consolidated assets are held by our dealership subsidiaries, the majority of our cash flows from operations are generated by these subsidiaries. As a result, our cash flows and ability to service our obligations depend to a substantial degree on the cash generated from the operations of these dealership subsidiaries.
We had the following liquidity resources available as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
3,108 |
|
|
$ |
3,625 |
|
|
Availability under our revolving credit facility |
|
|
207,053 |
|
|
|
181,058 |
|
|
Availability under our new and used vehicle floor plan facilities |
|
|
46,423 |
|
|
|
21,192 |
|
|
Floor plan deposit balance |
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
74,000 |
|
|
Total available liquidity resources |
|
$ |
266,584 |
|
|
$ |
279,875 |
|
We participate in a program with two of our manufacturer-affiliated finance companies (the floor plan deposit balance in the table above) wherein we maintain a deposit balance with the lender that earns interest based on the agreed upon rate. This deposit balance is not designated as a pre-payment of notes payable – floor plan, nor is it our intent to use this amount to offset principal amounts owed under notes payable – floor plan in the future, although we have the right and ability to do so. The deposit balance of $10.0 million and $74.0 million as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, is classified in other current assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Please see the discussion under the heading “Concentrations of Credit and Business Risk” in Note 1, “Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further information.
53
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Long-Term Debt and Credit Facilities
2014 Credit Facilities
Prior to November 30, 2016, we had a syndicated revolving credit facility (the “2014 Revolving Credit Facility”) and syndicated new and used vehicle floor plan credit facilities (the “2014 Floor Plan Facilities” and, together with the 2014 Revolving Credit Facility, the “2014 Credit Facilities”), which were scheduled to mature on August 15, 2019. On November 30, 2016, we amended and restated the 2014 Credit Facilities to, among other things, extend the maturity to November 30, 2021. See the heading “2016 Credit Facilities” below for additional information.
2016 Credit Facilities
On November 30, 2016, we entered into an amended and restated syndicated revolving credit facility (the “2016 Revolving Credit Facility”) and amended and restated syndicated new and used vehicle floor plan credit facilities (the “2016 Floor Plan Facilities” and, together with the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility, the “2016 Credit Facilities”), which are scheduled to mature on November 30, 2021.
Availability under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility is calculated as the lesser of $250.0 million or a borrowing base calculated based on certain eligible assets, less the aggregate face amount of any outstanding letters of credit under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility (the “2016 Revolving Borrowing Base”). The 2016 Revolving Credit Facility may be increased at our option up to $300.0 million upon satisfaction of certain conditions. Based on balances as of December 31, 2016, the 2016 Revolving Borrowing Base was approximately $228.5 million. As of December 31, 2016, Sonic had no outstanding borrowings and approximately $21.4 million in outstanding letters of credit under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility, resulting in total borrowing availability of $207.1 million under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility.
The 2016 Floor Plan Facilities are comprised of a new vehicle revolving floor plan facility (the “2016 New Vehicle Floor Plan Facility”) and a used vehicle revolving floor plan facility (the “2016 Used Vehicle Floor Plan Facility”), subject to a borrowing base, in a combined amount up to $1.015 billion. We may, under certain conditions, request an increase in the 2016 Floor Plan Facilities to a maximum borrowing limit of up to $1.265 billion, which shall be allocated between the 2016 New Vehicle Floor Plan Facility and the 2016 Used Vehicle Floor Plan Facility as we request, with no more than 30% of the aggregate commitments allocated to the commitments under the 2016 Used Vehicle Floor Plan Facility.
We agreed under the 2016 Credit Facilities not to pledge any assets to any third party (other than those explicitly allowed under the amended terms of the 2016 Credit Facilities), including other lenders, subject to certain stated exceptions, including floor plan financing arrangements. In addition, the 2016 Credit Facilities contain certain negative covenants, including covenants which could restrict or prohibit indebtedness, liens, the payment of dividends, capital expenditures and material dispositions and acquisitions of assets as well as other customary covenants and default provisions. Specifically, the 2016 Credit Facilities permit cash dividends on our Class A and Class B common stock so long as no event of default (as defined in the 2016 Credit Facilities) has occurred and is continuing and provided that we remain in compliance with all financial covenants under the 2016 Credit Facilities.
7.0% Notes
On July 2, 2012, we issued $200.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 7.0% Notes which mature on July 15, 2022. The 7.0% Notes were issued at a price of 99.11% of the principal amount thereof, resulting in a yield to maturity of 7.125%. Interest is payable semi-annually in arrears on January 15 and July 15 of each year. We may redeem the 7.0% Notes in whole or in part at any time on or after July 15, 2017 at the redemption prices in the following table, which are expressed as percentages of the principal amount.
|
|
|
Redemption Price |
|
|
|
Beginning on July 15, 2017 |
|
|
103.500 |
% |
|
Beginning on July 15, 2018 |
|
|
102.333 |
% |
|
Beginning on July 15, 2019 |
|
|
101.167 |
% |
|
Beginning on July 15, 2020 and thereafter |
|
|
100.000 |
% |
54
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
In addition, the indenture provides that holders of the 7.0% Notes may require us to repurchase the 7.0% Notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of the par value of the 7.0% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if we undergo a change of control (as defined in the indenture).
The indenture governing the 7.0% Notes contains certain specified restrictive covenants. We have agreed not to pledge any assets to any third-party lender of senior subordinated debt except under certain limited circumstances. We also have agreed to certain other limitations or prohibitions concerning the incurrence of other indebtedness, guarantees, liens, certain types of investments, certain transactions with affiliates, mergers, consolidations, issuance of preferred stock, cash dividends to stockholders, distributions, redemptions and the sale, assignment, lease, conveyance or disposal of certain assets. Specifically, the indenture governing the 7.0% Notes limits our ability to pay quarterly cash dividends on our Class A and Class B common stock in excess of $0.10 per share. We may only pay quarterly cash dividends on our Class A and Class B common stock if we comply with the terms of the indenture governing the 7.0% Notes.
Our obligations under the 7.0% Notes may be accelerated by the holders of 25% of the outstanding principal amount of the 7.0% Notes then outstanding if certain events of default occur, including: (1) defaults in the payment of principal or interest when due; (2) defaults in the performance, or breach, of our covenants under the 7.0% Notes; and (3) certain defaults under other agreements under which we or our subsidiaries have outstanding indebtedness in excess of $35.0 million. See Note 6, “Long-Term Debt,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further discussion of the 7.0% Notes.
5.0 % Notes
On May 9, 2013, we issued $300.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 5.0% Notes which mature on May 15, 2023. The 5.0% Notes were issued at a price of 100.0% of the principal amount thereof. Interest is payable semi-annually in arrears on May 15 and November 15 of each year. During the year ended December 31, 2016, Sonic repurchased approximately $10.7 million of its outstanding 5.0% Notes for approximately $10.6 million in cash, plus accrued and unpaid interest related thereto.
We may redeem the 5.0% Notes in whole or in part at any time on or after May 15, 2018 at the redemption prices in the following table, which are expressed as percentages of the principal amount.
|
|
|
Redemption Price |
|
|
|
Beginning on May 15, 2018 |
|
|
102.500 |
% |
|
Beginning on May 15, 2019 |
|
|
101.667 |
% |
|
Beginning on May 15, 2020 |
|
|
100.833 |
% |
|
Beginning on May 15, 2021 and thereafter |
|
|
100.000 |
% |
In addition, before May 15, 2018, we may redeem all or a part of the aggregate principal amount of the 5.0% Notes at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 5.0% Notes redeemed plus an applicable premium (as defined in the indenture) and any accrued and unpaid interest as of the redemption date. The indenture also provides that holders of the 5.0% Notes may require us to repurchase the 5.0% Notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of the par value of the 5.0% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if we undergo a change of control (as defined in the indenture).
The indenture governing the 5.0% Notes contains certain specified restrictive covenants. We have agreed not to pledge any assets to any third-party lender of senior subordinated debt except under certain limited circumstances. We also have agreed to certain other limitations or prohibitions concerning the incurrence of other indebtedness, guarantees, liens, certain types of investments, certain transactions with affiliates, mergers, consolidations, issuance of preferred stock, cash dividends to stockholders, distributions, redemptions and the sale, assignment, lease, conveyance or disposal of certain assets. Specifically, the indenture governing the 5.0% Notes limits our ability to pay quarterly cash dividends on our Class A and Class B common stock in excess of $0.10 per share. We may only pay quarterly cash dividends on our Class A and Class B common stock if we comply with the terms of the indenture governing the 5.0% Notes.
Our obligations under the 5.0% Notes may be accelerated by the holders of 25% of the outstanding principal amount of the 5.0% Notes then outstanding if certain events of default occur, including: (1) defaults in the payment of principal or interest when due; (2) defaults in the performance, or breach, of our covenants under the 5.0% Notes; and (3) certain defaults under other agreements under which we or our subsidiaries have outstanding indebtedness in excess of $50.0 million. See Note 6, “Long-Term Debt,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further discussion of the 5.0% Notes.
55
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
Mortgage Notes
During the year ended December 31, 2016, we obtained approximately $103.4 million in mortgage financing related to ten of our dealership properties. As of December 31, 2016, the weighted average interest rate was 3.74% and the total outstanding principal balance was approximately $403.7 million, related to approximately 45% of our operating locations. These mortgage notes require monthly payments of principal and interest through maturity, are secured by the underlying properties and contain certain cross-default provisions. Maturity dates for these mortgage notes range between 2017 and 2033.
Operating Leases
We lease facilities for the majority of our dealership operations under operating lease arrangements. These facility lease arrangements normally have fifteen- to twenty-year terms with one or two five- to ten-year renewal options and do not contain provisions for contingent rent related to the dealership’s operations. Many of the leases are subject to the provisions of a guaranty and subordination agreement that contains financial and affirmative covenants. Approximately 10% of these facility leases have payments that vary based on interest rates. See the table under the heading “Future Liquidity Outlook” below for our future minimum lease payment obligations, net of sublease proceeds.
Floor Plan Facilities
We finance our new and certain of our used vehicle inventory through standardized floor plan facilities with manufacturer captive finance companies and a syndicate of manufacturer-affiliated finance companies and commercial banks. These floor plan facilities are due on demand and bear interest at variable rates based on LIBOR and prime. The weighted average interest rate for our new and used floor plan facilities for continuing operations was 1.84%, 1.62% and 1.58% for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. We receive floor plan assistance from certain manufacturers. Floor plan assistance received is capitalized in inventory and charged against cost of sales when the associated inventory is sold. We received approximately $45.3 million, $42.3 million and $39.0 million in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, and recognized in cost of sales for continuing operations approximately $45.0 million, $42.1 million and $39.7 million in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, in manufacturer assistance. Interest payments under each of our floor plan facilities are due monthly and we are not required to make principal repayments prior to the sale of the vehicles.
Covenants and Default Provisions
Non-compliance with covenants, including a failure to make any payment when due, under our 2016 Credit Facilities, Silo Floor Plan Facilities, operating lease agreements, mortgage notes, 5.0% Notes and 7.0% Notes (collectively, our “Significant Debt Agreements”) could result in a default and an acceleration of our repayment obligation under our 2016 Credit Facilities. A default under our 2016 Credit Facilities would constitute a default under our Silo Floor Plan Facilities and could entitle these lenders to accelerate our repayment obligations under one or more of the floor plan facilities. Certain defaults under our 2016 Credit Facilities and one or more Silo Floor Plan Facilities, or certain other debt obligations would not result in a default under the 5.0% Notes or the 7.0% Notes unless our repayment obligations under the 2016 Credit Facilities and/or one or more of the Silo Floor Plan Facilities or such other debt obligations were accelerated. An acceleration of our repayment obligation under any of our Significant Debt Agreements could result in an acceleration of our repayment obligations under our other Significant Debt Agreements. The failure to repay principal amounts of the Significant Debt Agreements when due would create cross-default situations related to other indebtedness. The 2016 Credit Facilities include the following financial covenants:
|
|
|
Covenant |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Minimum Consolidated Liquidity Ratio |
|
|
Minimum Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio |
|
|
Maximum Consolidated Total Lease Adjusted Leverage Ratio |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Required ratio |
|
|
1.05 |
|
|
|
1.20 |
|
|
|
5.75 |
|
|
December 31, 2016 actual |
|
|
1.17 |
|
|
|
1.92 |
|
|
|
4.08 |
|
56
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
In addition, many of our facility leases are governed by a guarantee agreement between the landlord and us that contains financial and operating covenants. The financial covenants are identical to those under the 2016 Credit Facilities with the exception of one financial covenant related to the ratio of EBTDAR to rent (as such term is defined in the guarantee agreement) with a required ratio of no less than 1.50 to 1.00. As of December 31, 2016, the ratio was 4.01 to 1.00.
We were in compliance with all of the restrictive and financial covenants on all of our floor plan, long-term debt facilities and lease agreements as of December 31, 2016. After giving effect to the applicable restrictions on the payment of dividends and certain other transactions under our debt agreements, as of December 31, 2016, we had at least $127.4 million of net income and retained earnings free of such restrictions. Please refer to Note 6, “Long-Term Debt,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further discussion of the 2016 Credit Facilities.
Acquisitions and Dispositions
During the year ended December 31, 2016, Sonic acquired three stand-alone used vehicle dealership businesses and real estate for approximately $15.9 million. Sonic did not dispose of any franchises during the year ended December 31, 2016. See Note 2, “Business Acquisitions and Dispositions,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further discussion.
Under the 2016 Credit Facilities, we are restricted from making dealership acquisitions in any fiscal year if the aggregate cost of all such acquisitions occurring in any fiscal year is above specific amounts without the written consent of the required lenders (as that term is defined in the 2016 Credit Facilities).
Capital Expenditures
Our capital expenditures include the purchase of land and buildings, construction of new dealerships, EchoPark® stores and collision repair centers, building improvements and equipment purchased for use in our dealerships and EchoPark® stores. We selectively construct or improve new dealership facilities to maintain compliance with manufacturers’ image requirements. We typically finance these projects through new mortgages or, alternatively, through our credit facilities. We also fund these improvements through cash flows from operations.
Capital expenditures for the year ended December 31, 2016 were approximately $206.2 million. Of this amount, approximately $123.1 million was related to facility construction projects, $51.2 million was related to real estate acquisitions and $31.9 million was for other fixed assets utilized in our dealership operations. Of the capital expenditures in the year ended December 31, 2016, approximately $103.4 million was funded through mortgage financing and approximately $102.8 million was funded through cash from operations and use of our credit facilities. We expect to receive approximately $70.1 million of additional mortgage funding in the year ending December 31, 2017 related to capital expenditures that occurred prior to December 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2016, commitments for facilities construction projects totaled approximately $56.5 million. We expect investments related to capital expenditures to be partly dependent upon the availability of mortgage financing to fund significant capital projects.
Stock Repurchase Program
Our Board of Directors has authorized us to repurchase shares of our Class A common stock. Historically, we have used our share repurchase authorization to offset dilution caused by the exercise of stock options or the vesting of equity compensation awards and to maintain our desired capital structure. During the year ended December 31, 2016, we repurchased approximately 5.6 million shares of our Class A common stock for approximately $100.0 million in open-market transactions at prevailing market prices, including two separate private block trades, and in connection with tax withholdings on the vesting of equity compensation awards. As of December 31, 2016, our total remaining repurchase authorization was approximately $45.0 million. Under our 2016 Credit Facilities, share repurchases are permitted to the extent that no event of default exists and we do not exceed the restrictions set forth in the agreements. After giving effect to the applicable restrictions on share repurchases and certain other transactions under our debt agreements, as of December 31, 2016, we had at least $127.4 million of net income and retained earnings free of such restrictions.
Subsequent to December 31, 2016, our Board of Directors authorized an additional $100.0 million to repurchase shares of our Class A common stock, increasing our remaining repurchase authorization to approximately $145.0 million before including the effect of any share repurchases subsequent to December 31, 2016. Our share repurchase activity is subject to the business judgment of our Board of Directors and management, taking into consideration our historical and projected results of operations, financial condition,
57
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
cash flows, capital requirements, covenant compliance, current economic environment and other factors considered relevant. These factors are considered each quarter and will be scrutinized as our Board of Directors and management determine our share repurchase policy in the future.
Dividends
Our Board of Directors approved four quarterly cash dividends on all outstanding shares of Class A and Class B common stock totaling approximately $0.20 per share during the year ended December 31, 2016. Subsequent to December 31, 2016, our Board of Directors approved a cash dividend on all outstanding shares of Class A and Class B common stock of $0.05 per share for stockholders of record on March 15, 2017 to be paid on April 14, 2017. Under our 2016 Credit Facilities, dividends are permitted to the extent that no event of default exists and we are in compliance with the financial covenants contained therein. The indentures governing our outstanding 5.0% Notes and 7.0% Notes also contain restrictions on our ability to pay dividends. After giving effect to the applicable restrictions on share repurchases and certain other transactions under our debt agreements, as of December 31, 2016, we had at least $127.4 million of net income and retained earnings free of such restrictions. The payment of any future dividend is subject to the business judgment of our Board of Directors, taking into consideration our historical and projected results of operations, financial condition, cash flows, capital requirements, covenant compliance, share repurchases, current economic environment and other factors considered relevant. These factors are considered each quarter and will be scrutinized as our Board of Directors determines our future dividend policy. There is no guarantee that additional dividends will be declared and paid at any time in the future. See Note 6, “Long-Term Debt,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for a description of restrictions on the payment of dividends.
Cash Flows
Cash Flows from Operating Activities - Net cash provided by operating activities was approximately $216.4 million, $69.7 million and $161.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The net cash provided by operations for the year ended December 31, 2016 consisted primarily of net income (less non-cash items) and a decrease in inventory and other assets, offset partially by a decrease in notes payable - floor plan - trade. The net cash provided by operations for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 consisted primarily of net income (less non-cash items) and an increase in notes payable - floor plan – trade, offset partially by an increase in inventory.
We arrange our inventory floor plan financing through both manufacturer captive finance companies and a syndicate of manufacturer-affiliated finance companies and commercial banks. Our floor plan financed with manufacturer captives is recorded as trade floor plan liabilities (with the resulting change being reflected as operating cash flows). Our dealerships that obtain floor plan financing from a syndicate of manufacturer-affiliated finance companies and commercial banks record their obligation as non-trade floor plan liabilities (with the resulting change being reflected as financing cash flows).
Due to the presentation differences for changes in trade floor plan and non-trade floor plan in the consolidated statements of cash flows, decisions made by us to move dealership floor plan financing arrangements from one finance source to another may cause significant variations in operating and financing cash flows without affecting our overall liquidity, working capital or cash flow.
Net cash provided by combined trade and non-trade floor plan financing was approximately $7.1 million, $256.1 million and $11.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Accordingly, if all changes in floor plan notes payable were classified as an operating activity, the result would have been net cash provided by operating activities of approximately $266.4 million, $144.0 million and $141.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities - Cash used in investing activities during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 was approximately $220.8 million, $163.9 million and $108.4 million, respectively. The use of cash during the year ended December 31, 2016 was primarily comprised of purchases of land, property and equipment and the acquisition of three stand-alone pre-owned automobile dealership businesses. The use of cash during the year ended December 31, 2015 was primarily comprised of the purchases of land, property and equipment, offset partially by proceeds from sales of dealerships. The use of cash during the year ended December 31, 2014 was primarily comprised of purchases of land, property and equipment and the acquisition of four dealership franchise operations, offset partially by proceeds from sales of dealerships.
The significant components of capital expenditures relate primarily to dealership renovations, the purchase of certain existing dealership facilities which had previously been financed under long-term operating leases, and the purchase and development of new
58
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
real estate parcels for the relocation of existing dealerships and construction of EchoPark® stores. During the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, we generated net proceeds from mortgage financing in the amount of approximately $103.4 million, $69.1 million and $44.5 million, respectively, to purchase certain existing dealership facilities and to fund certain capital expenditures.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities - Net cash provided by financing activities was approximately $3.9 million and $93.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Net cash used in financing activities was approximately $51.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. For the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, cash provided by financing activities was comprised primarily of net borrowings on notes payable - floor plan - non-trade and proceeds from mortgage notes, offset partially by repurchases of treasury stock and scheduled principal payments and repayments of long-term debt. During the year ended December 31, 2014, cash used in financing activities was comprised primarily of net repayments on notes payable - floor plan - non-trade, scheduled principal payments on term notes and repurchases of treasury stock, offset partially by proceeds from mortgage notes.
Cash Flows from Discontinued Operations – The accompanying consolidated statements of cash flows include both continuing and discontinued operations. Net cash flows from operating activities associated with discontinued operations for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 were not material to total cash flows.
Future Liquidity Outlook
Our future contractual obligations are as follows:
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Floor Plan Facilities |
|
$ |
1,525,890 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
1,525,890 |
|
|
Long-Term Debt (1) |
|
|
43,127 |
|
|
|
55,986 |
|
|
|
19,605 |
|
|
|
51,523 |
|
|
|
45,434 |
|
|
|
681,589 |
|
|
|
897,264 |
|
|
Letters of Credit |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Estimated Interest Payments on Floor Plan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facilities (2) |
|
|
5,272 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
5,272 |
|
|
Estimated Interest Payments on Long-Term |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Debt (3) |
|
|
48,820 |
|
|
|
46,015 |
|
|
|
42,938 |
|
|
|
39,272 |
|
|
|
37,062 |
|
|
|
57,723 |
|
|
|
271,830 |
|
|
Operating Leases (Net of Sublease Rentals) |
|
|
87,663 |
|
|
|
79,585 |
|
|
|
64,550 |
|
|
|
41,319 |
|
|
|
32,217 |
|
|
|
96,657 |
|
|
|
401,991 |
|
|
Construction Contracts |
|
|
56,525 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
56,525 |
|
|
Other Purchase Obligations (4) |
|
|
9,075 |
|
|
|
8,000 |
|
|
|
1,800 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
18,875 |
|
|
FIN 48 Liability (5) |
|
|
500 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
4,697 |
|
|
|
5,197 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
1,776,872 |
|
|
$ |
189,586 |
|
|
$ |
128,893 |
|
|
$ |
132,114 |
|
|
$ |
114,713 |
|
|
$ |
840,666 |
|
|
$ |
3,182,844 |
|
|
(1) |
Long-term debt amounts consist only of principal obligations. |
|
(2) |
Floor plan facilities balances are correlated with the amount of vehicle inventory and are generally due at the time that a vehicle is sold. Estimated interest payments were calculated using the December 31, 2016 floor plan facilities balance, the weighted average interest rate for the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2016 of 2.07% and the assumption that floor plan balances at December 31, 2016 would be relieved within 60 days in connection with the sale of the associated vehicle inventory. |
|
(3) |
Estimated interest payments include payments related to interest rate swaps. |
|
(4) |
Other purchase obligations include contracts for real estate purchases, office supplies, utilities and various other items or other services. |
|
(5) |
Amount represents recorded liability, including interest and penalties, related to “Accounting for Uncertain Income Tax Positions” in the ASC. See Note 1, “Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and Note 7, “Income Taxes,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements. |
We believe our best sources of liquidity for operations and debt service remain cash flows generated from operations combined with our availability of borrowings under our floor plan facilities (or any replacements thereof), our 2016 Credit Facilities, real estate mortgage financing, selected dealership and other asset sales and our ability to raise funds in the capital markets through offerings of debt or equity securities. Because the majority of our consolidated assets are held by our dealership subsidiaries, the majority of our
59
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
cash flows from operations are generated by these subsidiaries. As a result, our cash flows and ability to service our obligations depend to a substantial degree on the results of operations of these subsidiaries and their ability to provide us with cash.
Seasonality
Our operations are subject to seasonal variations. The first quarter normally contributes less operating profit than the second, third and fourth quarters. Weather conditions, the timing of manufacturer incentive programs and model changeovers cause seasonality and may adversely affect vehicle demand and, consequently, our profitability. Comparatively, parts and service demand remains stable throughout the year.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Guarantees and Indemnification Obligations
In connection with the operation and disposition of our dealerships, we have entered into various guarantees and indemnification obligations. When we sell dealerships, we attempt to assign any related lease to the buyer of the dealership to eliminate any future liability. However, if we are unable to assign the related leases to the buyer, we will attempt to sublease the leased properties to the buyer at a rate equal to the terms of the original leases. In the event we are unable to sublease the properties to the buyer with terms at least equal to our lease, we may be required to record lease exit accruals. As of December 31, 2016, our future gross minimum lease payments related to properties subleased to buyers of sold dealerships totaled approximately $51.6 million. Future sublease payments expected to be received related to these lease payments were approximately $37.7 million at December 31, 2016.
In accordance with the terms of agreements entered into for the sale of our dealerships, we generally agree to indemnify the buyer from certain liabilities and costs arising subsequent to the date of sale, including environmental exposure and exposure resulting from the breach of representations or warranties made in accordance with the agreement. While our exposure with respect to environmental remediation and repairs is difficult to quantify, our maximum exposure associated with these general indemnifications was approximately $0.5 million at December 31, 2016. These indemnifications expire within a period of one to three years following the date of sale. The estimated fair value of these indemnifications was not material and the amount recorded for this contingency was not significant at December 31, 2016. We also guarantee the floor plan commitments of our 50%-owned joint venture, the amount of which was approximately $2.8 million at December 31, 2016. We expect the aggregate amount of the obligations we guarantee to fluctuate based on dealership disposition activity. Although we seek to mitigate our exposure in connection with these matters, these guarantees and indemnification obligations, including environmental exposures and the financial performance of lease assignees and sublessees, cannot be predicted with certainty. An unfavorable resolution of one or more of these matters could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity and capital resources. See Note 12, “Commitments and Contingencies,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further discussion regarding these guarantees and indemnification obligations.
60
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Interest Rate Risk
Our variable rate floor plan facilities, 2016 Revolving Credit Facility borrowings and other variable rate notes expose us to risks caused by fluctuations in the applicable interest rates. The total outstanding balance of such variable instruments after considering the effect of our interest rate swaps (see below) was approximately $1.2 billion at December 31, 2016 and 2015. A change of 100 basis points in the underlying interest rate would have caused a change in interest expense of approximately $11.7 million in the year ended December 31, 2016 and approximately $10.3 million in the year ended December 31, 2015. Of the total change in interest expense, approximately $10.0 million and $9.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, would have resulted from the floor plan facilities.
In addition to our variable rate debt, as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, certain of our dealership lease facilities had monthly lease payments that fluctuated based on LIBOR interest rates. An increase in interest rates of 100 basis points would not have had a significant impact on rent expense in the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 due to the leases containing LIBOR floors which were above the LIBOR rate during the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2015.
We also have various cash flow swaps to effectively convert a portion of our LIBOR-based variable rate debt to a fixed rate. Under the terms of these cash flow swaps, interest rates reset monthly. The fair value of these swap positions at December 31, 2016 was a net liability of approximately $3.7 million, with $4.1 million included in other accrued liabilities and $2.4 million included in other long-term liabilities, offset partially by an asset of approximately $2.8 million included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The fair value of these swap positions at December 31, 2015 was a liability of approximately $10.0 million, with $5.1 million included in other accrued liabilities and $4.9 million included in other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. We will receive and pay interest based on the following:
|
Notional Amount |
|
|
Pay Rate |
|
|
Receive Rate (1) |
|
Maturing Date |
||
|
(In millions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
2.3 |
|
|
|
7.100% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR + 1.50% |
|
July 10, 2017 |
|
$ |
7.3 |
|
|
|
4.655% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
December 10, 2017 |
|
$ |
6.6 |
|
(2) |
|
6.860% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR + 1.25% |
|
August 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
6.0 |
|
(2) |
|
6.410% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR + 1.25% |
|
September 12, 2017 |
|
$ |
100.0 |
|
|
|
2.065% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
June 30, 2017 |
|
$ |
100.0 |
|
|
|
2.015% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
June 30, 2017 |
|
$ |
50.0 |
|
|
|
1.320% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
250.0 |
|
(3) |
|
1.887% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
June 30, 2018 |
|
$ |
25.0 |
|
|
|
2.080% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
100.0 |
|
|
|
1.560% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
125.0 |
|
|
|
1.303% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
125.0 |
|
(4) |
|
1.900% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2018 |
|
$ |
50.0 |
|
(5) |
|
2.320% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2019 |
|
$ |
200.0 |
|
(5) |
|
2.313% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2019 |
|
$ |
100.0 |
|
(6) |
|
1.384% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2020 |
|
$ |
125.0 |
|
(5) |
|
1.158% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2019 |
|
$ |
150.0 |
|
(6) |
|
1.310% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2020 |
|
$ |
125.0 |
|
(4) |
|
1.020% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2018 |
|
(1) |
The one-month LIBOR rate was approximately 0.772% at December 31, 2016. |
|
(2) |
Changes in fair value are recorded through earnings. |
|
(3) |
The effective date of this forward-starting swap is July 3, 2017. |
|
(4) |
The effective date of these forward-starting swaps is July 1, 2017. |
|
(5) |
The effective date of these forward-starting swaps is July 2, 2018. |
|
(6) |
The effective date of these forward-starting swaps is July 1, 2019. |
During the year ended December 31, 2016, we entered into four forward-starting interest rate cash flow swap agreements. These interest rate swaps have been designated and qualify as cash flow hedges and, as a result, changes in the fair value of these swaps are recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) before taxes in the accompanying consolidated statements of comprehensive income.
61
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
Absent the acceleration of payments of principal that may result from non-compliance with financial and operational covenants under our various indebtedness, future principal maturities of variable and fixed rate debt and related interest rate swaps are as follows:
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
Total |
|
|
Liability Fair Value |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Long-term debt: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed rate maturities |
|
$ |
18,744 |
|
|
$ |
33,938 |
|
|
$ |
8,056 |
|
|
$ |
12,945 |
|
|
$ |
8,443 |
|
|
$ |
587,796 |
|
|
$ |
669,922 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed rate outstanding (1) |
|
$ |
669,922 |
|
|
$ |
651,178 |
|
|
$ |
617,240 |
|
|
$ |
609,184 |
|
|
$ |
596,239 |
|
|
$ |
587,796 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
685,970 |
|
|
Average rate on fixed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
outstanding debt (1) |
|
|
5.57 |
% |
|
|
5.60 |
% |
|
|
5.64 |
% |
|
|
5.65 |
% |
|
|
5.87 |
% |
|
|
5.68 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable rate maturities |
|
$ |
24,383 |
|
|
$ |
22,048 |
|
|
$ |
11,549 |
|
|
$ |
38,578 |
|
|
$ |
36,991 |
|
|
$ |
93,793 |
|
|
$ |
227,342 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable rate outstanding (1) |
|
$ |
227,342 |
|
|
$ |
202,959 |
|
|
$ |
180,911 |
|
|
$ |
169,362 |
|
|
$ |
130,784 |
|
|
$ |
93,793 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
228,203 |
|
|
Average rate on variable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
outstanding debt (1) |
|
|
2.92 |
% |
|
|
2.99 |
% |
|
|
3.02 |
% |
|
|
3.03 |
% |
|
|
3.08 |
% |
|
|
3.18 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flow interest rate swaps: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable to fixed maturities |
|
$ |
515,524 |
|
|
$ |
506,646 |
|
|
$ |
375,000 |
|
|
$ |
250,000 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
1,647,170 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable to fixed outstanding (1) |
|
$ |
506,646 |
|
|
$ |
375,000 |
|
|
$ |
250,000 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
3,709 |
|
|
Average rate on outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
swaps (1) |
|
|
1.71 |
% |
|
|
1.93 |
% |
|
|
1.34 |
% |
|
|
1.34% |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
(1) |
Based on amounts outstanding at December 31 of each respective period. |
Foreign Currency Risk
We purchase certain of our new vehicle and parts inventories from foreign manufacturers. Although we purchase our inventories in U.S. Dollars, our business is subject to foreign exchange rate risk that may influence automobile manufacturers’ ability to provide their products at competitive prices in the United States. To the extent that we cannot recapture this volatility in prices charged to customers or if this volatility negatively impacts consumer demand for our products, this volatility could adversely affect our future operating results.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
Our consolidated financial statements and the related notes begin on page F-1 herein.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
Disclosure Controls and Procedures. Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), we evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of December 31, 2016. Based upon that evaluation, our CEO and CFO concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2016.
Our CEO and CFO have each concluded that the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position, results of operations and cash flows of the Company and its subsidiaries in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f). Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our CEO and CFO, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016 based on the framework in Internal Control - Integrated Framework published in 2013 by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (“COSO”) of the Treadway Commission. Based on this evaluation, management concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of
62
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
December 31, 2016. The attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is set forth in Part II, ‘‘Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data’’ in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting can provide only reasonable assurance that the objectives of the control system are met and may not prevent or detect misstatements. In addition, any evaluation of the effectiveness of internal controls over financial reporting in future periods is subject to risk that those internal controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting. There has been no change in Sonic’s internal control over financial reporting during the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2016, that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, Sonic’s internal control over financial reporting.
None.
63
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
The information required by this item with respect to our executive officers appears in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the heading “Executive Officers of the Registrant.” The other information required by this item is furnished by incorporation by reference to the information under the headings “Election of Directors,” “Corporate Governance and Board of Directors,” “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” and “Additional Corporate Governance and Other Information – Corporate Governance Guidelines, Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and Committee Charters” in the definitive Proxy Statement (to be filed hereafter) for our 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “Proxy Statement”).
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
The information required by this item is furnished by incorporation by reference to the information under the headings “Executive Compensation” and “Director Compensation” in the Proxy Statement.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The information required by this item is furnished by incorporation by reference to the information under the headings “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in the Proxy Statement.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The information required by this item is furnished by incorporation by reference to the information under the headings “Corporate Governance and Board of Directors – Policies and Procedures for Review, Approval or Ratification of Transactions with Affiliates,” “Corporate Governance and Board of Directors – Transactions with Affiliates” and “Corporate Governance and Board of Directors - Director Independence” in the Proxy Statement.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
The information required by this item is furnished by incorporation by reference to the information under the heading “Ratification of the Appointment of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in the Proxy Statement.
64
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
The exhibits and other documents filed as a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including those exhibits that are incorporated by reference herein, are:
|
(1) |
Financial Statements: consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015. Consolidated statements of income for the Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014. Consolidated statements of comprehensive income for the Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014. Consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2014, 2015 and 2016. Consolidated statements of cash flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014. |
|
(2) |
Financial Statement Schedules: No financial statement schedules are required to be filed (no respective financial statement captions) as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
|
(3) |
Exhibits: Exhibits required in connection with this Annual Report on Form 10-K are listed below. Certain of such exhibits are hereby incorporated by reference to other documents on file with the SEC with which they are physically filed, to be a part hereof as of their respective dates. |
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
3.1 |
|
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Sonic Automotive, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed August 8, 1997 (File No. 333-33295)). |
|
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
Certificate of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Sonic Automotive, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1999 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
3.3 |
|
Certificate of Designation, Preferences and Rights of Class A Convertible Preferred Stock (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 1998 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
3.4 |
|
Amended and Restated Bylaws of Sonic Automotive, Inc., as of February 13, 2017 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 16, 2017 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
Specimen Class A Common Stock Certificate (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1/A filed October 17, 1997 (File No. 333-33295)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of July 2, 2012, by and among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the guarantors set forth on the signature pages thereto and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as representative of the several initial purchasers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 9, 2012 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.3 |
|
Indenture, dated as of July 2, 2012, by and among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 9, 2012 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.4 |
|
Form of 7.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2022 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 9, 2012 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of May 9, 2013, by and among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the guarantors set forth on the signature pages thereto and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as representative of the several initial purchasers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 13, 2013 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.6 |
|
Indenture, dated as of May 9, 2013, by and among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 13, 2013 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.7 |
|
Form of 5.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 13, 2013 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
65
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
10.1 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc.; each lender a party thereto; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, swing line lender and an l/c issuer; and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as an l/c issuer (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
|
Form of Promissory Note, dated July 23, 2014, executed by Sonic Automotive, Inc., as borrower, in favor of each of the lenders to the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Subsidiary Guaranty Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, by the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as guarantors, to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.4 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Securities Pledge Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.5 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Escrow and Security Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.6 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Security Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.7 |
|
Second Amended and Restated Syndicated New and Used Vehicle Floorplan Credit Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc.; the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein; each lender a party thereto; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, new vehicle swing line lender and used vehicle swing line lender; and Bank of America, N.A. as revolving administrative agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.8 |
|
Form of Promissory Note, dated July 23, 2014, executed by Sonic Automotive, Inc. and the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as borrowers, in favor of each of the lenders to the Second Amended and Restated Syndicated New and Used Vehicle Floorplan Credit Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.9 |
|
Second Amended and Restated Company Guaranty Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, by Sonic Automotive, Inc. to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
66
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
10.10
10.11*
10.12*
10.13*
10.14*
10.15*
10.16*
10.17*
10.18*
10.19*
10.20*
|
|
Second Amended and Restated Subsidiary Guaranty Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, by the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as guarantors, to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)).
Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc.; each lender a party thereto; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, swing line lender and an l/c issuer; and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as an l/c issuer.
Form of Promissory Note, dated November 30, 2016, executed by Sonic Automotive, Inc., as borrower, in favor of each of the lenders to the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement.
Fourth Amended and Restated Subsidiary Guaranty Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, by the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as guarantors, to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Fourth Amended and Restated Securities Pledge Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Fourth Amended and Restated Escrow and Security Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Fourth Amended and Restated Security Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Third Amended and Restated Syndicated New and Used Vehicle Floorplan Credit Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc.; the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein; each lender a party thereto; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, new vehicle swing line lender and used vehicle swing line lender; and Bank of America, N.A., as revolving administrative agent.
Form of Promissory Note, dated November 30, 2016, executed by Sonic Automotive, Inc. and the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as borrowers, in favor of each of the lenders to the Third Amended and Restated Syndicated New and Used Vehicle Floorplan Credit Agreement.
Third Amended and Restated Company Guaranty Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, by Sonic Automotive, Inc. to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Third Amended and Restated Subsidiary Guaranty Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, by the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as guarantors, to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders. |
|
|
|
|
|
10.21 |
|
Standard Form of Lease executed with Capital Automotive L.P. or its affiliates (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.38 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.22 |
|
Standard Form of Lease Guaranty executed with Capital Automotive L.P. or its affiliates (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.39 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.23 |
|
Amendment to Guaranty and Subordination Agreements, dated as of January 1, 2005, by and between Sonic Automotive, Inc., as guarantor, and Capital Automotive L.P. and its affiliates named therein, as landlord (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.40 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.24 |
|
Second Amendment to Guaranty and Subordination Agreements, dated as of March 12, 2009, by and between Sonic Automotive, Inc., as guarantor, and Capital Automotive L.P. and its affiliates named therein, as landlord (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.41 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
67
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
10.25 |
|
Side Letter to Second Amendment to Guaranty and Subordination Agreements, dated as of March 12, 2009, by and between Sonic Automotive, Inc., as guarantor, and Capital Automotive L.P. and its affiliates named therein, as landlord (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.42 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.26 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan, amended and restated as of May 8, 2002 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2002 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.27 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. Nonqualified Employee Stock Purchase Plan, amended and restated as of October 23, 2002 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2002 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.28 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 1997 Stock Option Plan, amended and restated as of April 22, 2003 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2003 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.29 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2004 Stock Incentive Plan, amended and restated as of February 11, 2009 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4 to the Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed June 2, 2009 (File No. 333-159674)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.30 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2004 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.33 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.31 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2004 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.34 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.32 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. Incentive Compensation Plan, amended and restated as of October 16, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed March 4, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.33 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, effective January 1, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.46 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.34 |
|
First Amendment to Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, effective January 1, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.47 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.35 |
|
Second Amendment to Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, effective January 1, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.59 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.36 |
|
Third Amendment to Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, effective February 12, 2015 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 13, 2015 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.37 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan, amended and restated as of February 11, 2015 (incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed March 3, 2015 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.38 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Incentive Stock Option Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.39 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Nonstatutory Stock Option Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.40 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
68
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
10.41 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.42 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement for Retention Grant, dated May 6, 2015, between Sonic Automotive, Inc. and Jeff Dyke (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 8, 2015 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.43 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.44 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.45 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Stock Appreciation Rights Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.46 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Formula Restricted Stock Plan for Non-Employee Directors (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed April 19, 2012 (File No. 333-180815)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.47 |
|
Director Compensation Policy (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 15, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.48 |
|
Employment Agreement of Heath R. Byrd, dated October 18, 2007, as amended December 19, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.54 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2013 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.49 |
|
Form of Change in Control Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 8, 2015 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
12.1* |
|
Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges. |
|
21.1* |
|
Subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
23.1* |
|
Consent of KPMG LLP. |
|
31.1* |
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
31.2* |
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
32.1** |
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
32.2** |
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS* |
|
XBRL Instance Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
69
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
* |
Filed herewith. |
|
** |
Furnished herewith. |
|
(1) |
Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
70
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
71
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
BY |
|
/s/ HEATH R. BYRD |
|
Mr. Heath R. Byrd |
||
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
||
|
Date: February 24, 2017 |
||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Signature |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ O. BRUTON SMITH |
|
Executive Chairman and Director |
|
February 24, 2017 |
|
O. Bruton Smith |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ B. SCOTT SMITH |
|
President, Chief Executive Officer (principal |
|
February 24, 2017 |
|
B. Scott Smith |
|
executive officer) and Director |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ HEATH R. BYRD |
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
|
February 24, 2017 |
|
Heath R. Byrd |
|
(principal financial officer and principal accounting officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ DAVID BRUTON SMITH |
|
Vice Chairman and Director |
|
February 24, 2017 |
|
David Bruton Smith |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ WILLIAM I. BELK |
|
Director |
|
February 24, 2017 |
|
William I. Belk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ WILLIAM R. BROOKS |
|
Director |
|
February 24, 2017 |
|
William R. Brooks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ VICTOR H. DOOLAN |
|
Director |
|
February 13, 2017 |
|
Victor H. Doolan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ JOHN W. HARRIS III |
|
Director |
|
February 13, 2017 |
|
John W. Harris III |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ H. ROBERT HELLER |
|
Director |
|
February 24, 2017 |
|
H. Robert Heller |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
/s/ R. EUGENE TAYLOR |
|
Director |
|
February 24, 2017 |
|
R. Eugene Taylor |
|
|
|
|
72
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
3.1 |
|
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Sonic Automotive, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed August 8, 1997 (File No. 333-33295)). |
|
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
Certificate of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Sonic Automotive, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1999 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
3.3 |
|
Certificate of Designation, Preferences and Rights of Class A Convertible Preferred Stock (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 1998 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
3.4 |
|
Amended and Restated Bylaws of Sonic Automotive, Inc., as of February 13, 2017 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 16, 2017 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
Specimen Class A Common Stock Certificate (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1/A filed October 17, 1997 (File No. 333-33295)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of July 2, 2012, by and among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the guarantors set forth on the signature pages thereto and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as representative of the several initial purchasers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 9, 2012 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.3 |
|
Indenture, dated as of July 2, 2012, by and among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 9, 2012 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.4 |
|
Form of 7.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2022 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 9, 2012 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of May 9, 2013, by and among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the guarantors set forth on the signature pages thereto and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as representative of the several initial purchasers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 13, 2013 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.6 |
|
Indenture, dated as of May 9, 2013, by and among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 13, 2013 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
4.7 |
|
Form of 5.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 13, 2013 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.1 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc.; each lender a party thereto; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, swing line lender and an l/c issuer; and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as an l/c Issuer (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
|
Form of Promissory Note, dated July 23, 2014, executed by Sonic Automotive, Inc., as borrower, in favor of each of the lenders to the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Subsidiary Guaranty Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, by the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as guarantors, to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.4 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Securities Pledge Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
73
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
10.5 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Escrow and Security Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.6 |
|
Third Amended and Restated Security Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.7 |
|
Second Amended and Restated Syndicated New and Used Vehicle Floorplan Credit Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, among Sonic Automotive, Inc.; the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein; each lender a party thereto; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, new vehicle swing line lender and used vehicle swing line lender; and Bank of America, N.A. as revolving administrative agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.8 |
|
Form of Promissory Note, dated July 23, 2014, executed by Sonic Automotive, Inc. and the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as borrowers, in favor of each of the lenders to the Second Amended and Restated Syndicated New and Used Vehicle Floorplan Credit Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.9 |
|
Second Amended and Restated Company Guaranty Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, by Sonic Automotive, Inc. to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
74
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
10.10
10.11*
10.12*
10.13*
10.14*
10.15*
10.16*
10.17*
10.18*
10.19*
10.20* |
|
Second Amended and Restated Subsidiary Guaranty Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2014, by the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as guarantors, to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)).
Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc.; each lender a party thereto; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, swing line lender and an l/c issuer; and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as an l/c issuer.
Form of Promissory Note, dated November 30, 2016, executed by Sonic Automotive, Inc., as borrower, in favor of each of the lenders to the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement.
Fourth Amended and Restated Subsidiary Guaranty Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, by the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as guarantors, to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Fourth Amended and Restated Securities Pledge Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Fourth Amended and Restated Escrow and Security Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Fourth Amended and Restated Security Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc., the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Third Amended and Restated Syndicated New and Used Vehicle Floorplan Credit Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, among Sonic Automotive, Inc.; the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein; each lender a party thereto; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, new vehicle swing line lender and used vehicle swing line lender; and Bank of America, N.A., as revolving administrative agent.
Form of Promissory Note, dated November 30, 2016, executed by Sonic Automotive, Inc. and the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as borrowers, in favor of each of the lenders to the Third Amended and Restated Syndicated New and Used Vehicle Floorplan Credit Agreement.
Third Amended and Restated Company Guaranty Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, by Sonic Automotive, Inc. to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
Third Amended and Restated Subsidiary Guaranty Agreement, dated as of November 30, 2016, by the subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. named therein, as guarantors, to Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders.
|
|
10.21 |
|
Standard Form of Lease executed with Capital Automotive L.P. or its affiliates (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.38 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.22 |
|
Standard Form of Lease Guaranty executed with Capital Automotive L.P. or its affiliates (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.39 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.23 |
|
Amendment to Guaranty and Subordination Agreements, dated as of January 1, 2005, by and between Sonic Automotive, Inc., as guarantor, and Capital Automotive L.P. and its affiliates named therein, as landlord (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.40 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.24 |
|
Second Amendment to Guaranty and Subordination Agreements, dated as of March 12, 2009, by and between Sonic Automotive, Inc., as guarantor, and Capital Automotive L.P. and its affiliates named therein, as landlord (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.41 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
75
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
10.25 |
|
Side Letter to Second Amendment to Guaranty and Subordination Agreements, dated as of March 12, 2009, by and between Sonic Automotive, Inc., as guarantor, and Capital Automotive L.P. and its affiliates named therein, as landlord (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.42 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 001-13395)). |
|
|
|
|
|
10.26 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan, amended and restated as of May 8, 2002 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2002 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.27 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. Nonqualified Employee Stock Purchase Plan, amended and restated as of October 23, 2002 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2002 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.28 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 1997 Stock Option Plan, amended and restated as of April 22, 2003 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2003 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.29 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2004 Stock Incentive Plan, amended and restated as of February 11, 2009 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4 to the Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed June 2, 2009 (File No. 333-159674)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.30 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2004 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.33 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.31 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2004 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.34 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.32 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. Incentive Compensation Plan, amended and restated as of October 16, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed March 4, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.33 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, effective January 1, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.46 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.34 |
|
First Amendment to Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, effective January 1, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.47 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.35 |
|
Second Amendment to Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, effective January 1, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.59 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.36 |
|
Third Amendment to Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, effective February 12, 2015 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 13, 2015 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.37 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan, amended and restated as of February 11, 2015 (incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed March 3, 2015 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.38 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Incentive Stock Option Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.39 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Nonstatutory Stock Option Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.40 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
76
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
10.41 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.42 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement for Retention Grant, dated May 6, 2015, between Sonic Automotive, Inc. and Jeff Dyke (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 8, 2015 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.43 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.44 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.45 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan Form of Stock Appreciation Rights Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.46 |
|
Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Formula Restricted Stock Plan for Non-Employee Directors (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-8 filed April 19, 2012 (File No. 333-180815)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.47 |
|
Director Compensation Policy (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 15, 2014 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.48 |
|
Employment Agreement of Heath R. Byrd, dated October 18, 2007, as amended December 19, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.54 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2013 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.49 |
|
Form of Change in Control Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 8, 2015 (File No. 001-13395)). (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
12.1* |
|
Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges. |
|
21.1* |
|
Subsidiaries of Sonic Automotive, Inc. |
|
23.1* |
|
Consent of KPMG LLP. |
|
|
|
|
|
31.1* |
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
31.2* |
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
32.1** |
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
32.2** |
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS* |
|
XBRL Instance Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
77
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
|
EXHIBIT NO. |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
101.PRE* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Filed herewith. |
|
** |
Furnished herewith. |
|
(1) |
Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
78
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Sonic Automotive, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Sonic Automotive, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three‑year period ended December 31, 2016. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Sonic Automotive, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three‑year period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Sonic Automotive, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated February 24, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Charlotte, North Carolina
February 24, 2017
F-1
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Sonic Automotive, Inc.:
We have audited Sonic Automotive, Inc.’s (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016, and our report dated February 24, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Charlotte, North Carolina
February 24, 2017
F-2
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(Dollars in thousands) |
|
|||||
|
ASSETS |
|
|||||||
|
Current Assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
3,108 |
|
|
$ |
3,625 |
|
|
Receivables, net |
|
|
430,242 |
|
|
|
378,520 |
|
|
Inventories |
|
|
1,570,701 |
|
|
|
1,599,581 |
|
|
Other current assets |
|
|
26,993 |
|
|
|
101,386 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
2,031,044 |
|
|
|
2,083,112 |
|
|
Property and Equipment, net |
|
|
1,010,380 |
|
|
|
886,902 |
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
472,437 |
|
|
|
471,493 |
|
|
Other Intangible Assets, net |
|
|
80,233 |
|
|
|
80,876 |
|
|
Other Assets |
|
|
45,242 |
|
|
|
39,998 |
|
|
Total Assets |
|
$ |
3,639,336 |
|
|
$ |
3,562,381 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|||||||
|
Current Liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes payable - floor plan - trade |
|
$ |
850,537 |
|
|
$ |
893,466 |
|
|
Notes payable - floor plan - non-trade |
|
|
675,353 |
|
|
|
625,367 |
|
|
Trade accounts payable |
|
|
117,740 |
|
|
|
131,204 |
|
|
Accrued interest |
|
|
13,265 |
|
|
|
12,640 |
|
|
Other accrued liabilities |
|
|
236,982 |
|
|
|
218,507 |
|
|
Current maturities of long-term debt |
|
|
43,003 |
|
|
|
33,437 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
1,936,880 |
|
|
|
1,914,621 |
|
|
Long-Term Debt |
|
|
839,675 |
|
|
|
781,145 |
|
|
Other Long-Term Liabilities |
|
|
61,170 |
|
|
|
64,245 |
|
|
Deferred Income Taxes |
|
|
76,447 |
|
|
|
73,322 |
|
|
Commitments and Contingencies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders’ Equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A convertible preferred stock, none issued |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Class A common stock, $0.01 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 62,967,061 shares issued and 32,703,865 shares outstanding at December 31, 2016; 62,586,381 shares issued and 37,910,938 shares outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
|
|
630 |
|
|
|
626 |
|
|
Class B common stock, $0.01 par value; 30,000,000 shares authorized; 12,029,375 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015 |
|
|
121 |
|
|
|
121 |
|
|
Paid-in capital |
|
|
721,695 |
|
|
|
713,118 |
|
|
Retained earnings |
|
|
541,146 |
|
|
|
457,010 |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(2,262 |
) |
|
|
(5,632 |
) |
|
Treasury stock, at cost; 30,263,196 Class A common stock shares held at December 31, 2016 and 24,675,443 Class A common stock shares held at December 31, 2015 |
|
|
(536,166 |
) |
|
|
(436,195 |
) |
|
Total Stockholders’ Equity |
|
|
725,164 |
|
|
|
729,048 |
|
|
Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity |
|
$ |
3,639,336 |
|
|
$ |
3,562,381 |
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-3
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(Dollars and shares in thousands, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
except per share amounts) |
|
|||||||||
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New vehicles |
|
$ |
5,234,505 |
|
|
$ |
5,265,401 |
|
|
$ |
5,124,029 |
|
|
Used vehicles |
|
|
2,533,122 |
|
|
|
2,512,024 |
|
|
|
2,310,247 |
|
|
Wholesale vehicles |
|
|
211,048 |
|
|
|
155,339 |
|
|
|
166,158 |
|
|
Total vehicles |
|
|
7,978,675 |
|
|
|
7,932,764 |
|
|
|
7,600,434 |
|
|
Parts, service and collision repair |
|
|
1,409,819 |
|
|
|
1,364,947 |
|
|
|
1,296,570 |
|
|
Finance, insurance and other, net |
|
|
343,285 |
|
|
|
326,588 |
|
|
|
300,095 |
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
9,731,779 |
|
|
|
9,624,299 |
|
|
|
9,197,099 |
|
|
Cost of Sales: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New vehicles |
|
|
(4,973,911 |
) |
|
|
(4,997,472 |
) |
|
|
(4,835,403 |
) |
|
Used vehicles |
|
|
(2,374,537 |
) |
|
|
(2,349,982 |
) |
|
|
(2,153,001 |
) |
|
Wholesale vehicles |
|
|
(218,364 |
) |
|
|
(162,707 |
) |
|
|
(169,774 |
) |
|
Total vehicles |
|
|
(7,566,812 |
) |
|
|
(7,510,161 |
) |
|
|
(7,158,178 |
) |
|
Parts, service and collision repair |
|
|
(735,693 |
) |
|
|
(699,526 |
) |
|
|
(673,021 |
) |
|
Total cost of sales |
|
|
(8,302,505 |
) |
|
|
(8,209,687 |
) |
|
|
(7,831,199 |
) |
|
Gross profit |
|
|
1,429,274 |
|
|
|
1,414,612 |
|
|
|
1,365,900 |
|
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
(1,110,856 |
) |
|
|
(1,110,565 |
) |
|
|
(1,067,433 |
) |
|
Impairment charges |
|
|
(8,063 |
) |
|
|
(17,955 |
) |
|
|
(6,594 |
) |
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
(77,446 |
) |
|
|
(68,799 |
) |
|
|
(58,260 |
) |
|
Operating income (loss) |
|
|
232,909 |
|
|
|
217,293 |
|
|
|
233,613 |
|
|
Other income (expense): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense, floor plan |
|
|
(27,716 |
) |
|
|
(21,326 |
) |
|
|
(18,793 |
) |
|
Interest expense, other, net |
|
|
(50,106 |
) |
|
|
(50,910 |
) |
|
|
(53,190 |
) |
|
Other income (expense), net |
|
|
125 |
|
|
|
99 |
|
|
|
97 |
|
|
Total other income (expense) |
|
|
(77,697 |
) |
|
|
(72,137 |
) |
|
|
(71,886 |
) |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations before taxes |
|
|
155,212 |
|
|
|
145,156 |
|
|
|
161,727 |
|
|
Provision for income taxes for continuing operations - benefit (expense) |
|
|
(60,696 |
) |
|
|
(57,065 |
) |
|
|
(63,168 |
) |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations |
|
|
94,516 |
|
|
|
88,091 |
|
|
|
98,559 |
|
|
Discontinued operations: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (loss) from discontinued operations before taxes |
|
|
(2,121 |
) |
|
|
(2,883 |
) |
|
|
(2,164 |
) |
|
Provision for income taxes for discontinued operations - benefit (expense) |
|
|
798 |
|
|
|
1,103 |
|
|
|
822 |
|
|
Income (loss) from discontinued operations |
|
|
(1,323 |
) |
|
|
(1,780 |
) |
|
|
(1,342 |
) |
|
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
93,193 |
|
|
$ |
86,311 |
|
|
$ |
97,217 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) per common share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings (loss) per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
2.07 |
|
|
$ |
1.74 |
|
|
$ |
1.89 |
|
|
Earnings (loss) per share from discontinued operations |
|
|
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
(0.03 |
) |
|
Earnings (loss) per common share |
|
$ |
2.04 |
|
|
$ |
1.71 |
|
|
$ |
1.86 |
|
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
45,637 |
|
|
|
50,489 |
|
|
|
52,065 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per common share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings (loss) per share from continuing operations |
|
$ |
2.06 |
|
|
$ |
1.73 |
|
|
$ |
1.87 |
|
|
Earnings (loss) per share from discontinued operations |
|
|
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
(0.03 |
) |
|
Earnings (loss) per common share |
|
$ |
2.03 |
|
|
$ |
1.70 |
|
|
$ |
1.84 |
|
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
45,948 |
|
|
|
50,883 |
|
|
|
52,563 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends declared per common share |
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
$ |
0.11 |
|
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-4
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
(Dollars in thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Net income (loss) |
$ |
93,193 |
|
|
$ |
86,311 |
|
|
$ |
97,217 |
|
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) before taxes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change in fair value of interest rate swap agreements |
|
5,731 |
|
|
|
540 |
|
|
|
4,655 |
|
|
Pension actuarial income (loss) |
|
(295 |
) |
|
|
737 |
|
|
|
(1,174 |
) |
|
Total other comprehensive income (loss) before taxes |
|
5,436 |
|
|
|
1,277 |
|
|
|
3,481 |
|
|
Provision for income tax benefit (expense) related to components of other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
(2,066 |
) |
|
|
(485 |
) |
|
|
(1,323 |
) |
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
3,370 |
|
|
|
792 |
|
|
|
2,158 |
|
|
Comprehensive income (loss) |
$ |
96,563 |
|
|
$ |
87,103 |
|
|
$ |
99,375 |
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-5
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A |
|
|
Class A |
|
|
Class B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Treasury Stock |
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Paid-In |
|
|
Retained |
|
|
Comprehensive |
|
|
Stockholders’ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Earnings |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
Equity |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
|
|
61,584 |
|
|
$ |
616 |
|
|
|
(20,900 |
) |
|
$ |
(348,666 |
) |
|
|
12,029 |
|
|
$ |
121 |
|
|
$ |
685,782 |
|
|
$ |
284,368 |
|
|
$ |
(8,582 |
) |
|
$ |
613,639 |
|
|
Shares awarded under stock compensation plans |
|
|
440 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
3,270 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
3,274 |
|
|
Purchases of treasury stock |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(2,256 |
) |
|
|
(53,046 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(53,046 |
) |
|
Income tax benefit associated with stock compensation plans |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
1,033 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
1,033 |
|
|
Change in fair value of interest rate swap agreements, net of tax expense of $1,769 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
2,886 |
|
|
|
2,886 |
|
|
Pension actuarial loss, net of tax benefit of $446 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(728 |
) |
|
|
(728 |
) |
|
Restricted stock amortization |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
7,675 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
7,675 |
|
|
Other |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
97,217 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
97,217 |
|
|
Dividends declared ($0.10 per share) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(5,232 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(5,232 |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
|
62,047 |
|
|
$ |
620 |
|
|
|
(23,156 |
) |
|
$ |
(401,712 |
) |
|
|
12,029 |
|
|
$ |
121 |
|
|
$ |
697,760 |
|
|
$ |
376,353 |
|
|
$ |
(6,424 |
) |
|
$ |
666,718 |
|
|
Shares awarded under stock compensation plans |
|
|
518 |
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
3,656 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
3,662 |
|
|
Purchases of treasury stock |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(1,519 |
) |
|
|
(34,483 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(34,483 |
) |
|
Income tax benefit associated with stock compensation plans |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
1,888 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
1,888 |
|
|
Change in fair value of interest rate swap agreements, net of tax expense of $205 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
335 |
|
|
|
335 |
|
|
Pension actuarial income, net of tax expense of $280 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
457 |
|
|
|
457 |
|
|
Restricted stock amortization |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
9,814 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
9,814 |
|
|
Other |
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
86,311 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
86,311 |
|
|
Dividends declared ($0.11 per share) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(5,654 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(5,654 |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
|
62,586 |
|
|
$ |
626 |
|
|
|
(24,675 |
) |
|
$ |
(436,195 |
) |
|
|
12,029 |
|
|
$ |
121 |
|
|
$ |
713,118 |
|
|
$ |
457,010 |
|
|
$ |
(5,632 |
) |
|
$ |
729,048 |
|
|
Shares awarded under stock compensation plans |
|
|
381 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
Purchases of treasury stock |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(5,588 |
) |
|
|
(99,971 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(99,971 |
) |
|
Income tax expense associated with stock compensation plans |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(2,611 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(2,611 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of interest rate swap agreements, net of tax expense of $2,178 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
3,553 |
|
|
|
3,553 |
|
|
Pension actuarial loss, net of tax benefit of $112 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(183 |
) |
|
|
(183 |
) |
|
Restricted stock amortization |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
11,165 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
11,165 |
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
93,193 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
93,193 |
|
|
Dividends declared ($0.20 per share) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(9,057 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(9,057 |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
62,967 |
|
|
$ |
630 |
|
|
|
(30,263 |
) |
|
$ |
(536,166 |
) |
|
|
12,029 |
|
|
$ |
121 |
|
|
$ |
721,695 |
|
|
$ |
541,146 |
|
|
$ |
(2,262 |
) |
|
$ |
725,164 |
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-6
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
(Dollars in thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) |
$ |
93,193 |
|
|
$ |
86,311 |
|
|
$ |
97,217 |
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization of property, plant and equipment |
|
77,532 |
|
|
|
68,793 |
|
|
|
58,254 |
|
|
Provision for bad debt expense |
|
389 |
|
|
|
1,909 |
|
|
|
516 |
|
|
Other amortization |
|
649 |
|
|
|
649 |
|
|
|
1,165 |
|
|
Debt issuance cost amortization |
|
2,641 |
|
|
|
2,489 |
|
|
|
2,135 |
|
|
Debt discount amortization, net of premium amortization |
|
303 |
|
|
|
199 |
|
|
|
67 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
11,165 |
|
|
|
9,814 |
|
|
|
7,675 |
|
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
14,465 |
|
|
|
15,996 |
|
|
|
28,470 |
|
|
Net distributions from equity investee |
|
(300 |
) |
|
|
(263 |
) |
|
|
117 |
|
|
Asset impairment charges |
|
8,063 |
|
|
|
17,955 |
|
|
|
6,594 |
|
|
Loss (gain) on disposal of dealerships and property and equipment |
|
(331 |
) |
|
|
(3,089 |
) |
|
|
(13,323 |
) |
|
Loss (gain) on exit of leased dealerships |
|
1,386 |
|
|
|
1,848 |
|
|
|
302 |
|
|
Changes in assets and liabilities that relate to operations: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Receivables |
|
(62,894 |
) |
|
|
(9,048 |
) |
|
|
(2,436 |
) |
|
Inventories |
|
35,545 |
|
|
|
(291,100 |
) |
|
|
(56,203 |
) |
|
Other assets |
|
62,538 |
|
|
|
(19,785 |
) |
|
|
(278 |
) |
|
Notes payable - floor plan - trade |
|
(42,929 |
) |
|
|
181,848 |
|
|
|
30,588 |
|
|
Trade accounts payable and other liabilities |
|
14,953 |
|
|
|
5,190 |
|
|
|
190 |
|
|
Total adjustments |
|
123,175 |
|
|
|
(16,595 |
) |
|
|
63,833 |
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
|
216,368 |
|
|
|
69,716 |
|
|
|
161,050 |
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase of businesses, net of cash acquired |
|
(15,861 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(50,867 |
) |
|
Purchases of land, property and equipment |
|
(206,232 |
) |
|
|
(173,249 |
) |
|
|
(146,432 |
) |
|
Proceeds from sales of property and equipment |
|
1,319 |
|
|
|
1,397 |
|
|
|
14,122 |
|
|
Proceeds from sales of dealerships |
|
- |
|
|
|
7,978 |
|
|
|
74,823 |
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
|
(220,774 |
) |
|
|
(163,874 |
) |
|
|
(108,354 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net (repayments) borrowings on notes payable - floor plan - non-trade |
|
49,986 |
|
|
|
74,249 |
|
|
|
(19,543 |
) |
|
Borrowings on revolving credit facilities |
|
209,287 |
|
|
|
402,093 |
|
|
|
179,791 |
|
|
Repayments on revolving credit facilities |
|
(213,490 |
) |
|
|
(397,890 |
) |
|
|
(179,791 |
) |
|
Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt |
|
103,395 |
|
|
|
69,075 |
|
|
|
44,454 |
|
|
Debt issuance costs |
|
(3,084 |
) |
|
|
(491 |
) |
|
|
(2,959 |
) |
|
Principal payments and repurchase of long-term debt |
|
(30,949 |
) |
|
|
(19,424 |
) |
|
|
(19,482 |
) |
|
Purchases of treasury stock |
|
(99,971 |
) |
|
|
(34,483 |
) |
|
|
(53,046 |
) |
|
Income tax benefit (expense) associated with stock compensation plans |
|
(2,611 |
) |
|
|
1,888 |
|
|
|
1,033 |
|
|
Issuance of shares under stock compensation plans |
|
27 |
|
|
|
3,662 |
|
|
|
3,274 |
|
|
Dividends paid |
|
(8,701 |
) |
|
|
(5,078 |
) |
|
|
(5,261 |
) |
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
3,889 |
|
|
|
93,601 |
|
|
|
(51,530 |
) |
|
NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
|
(517 |
) |
|
|
(557 |
) |
|
|
1,166 |
|
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF YEAR |
|
3,625 |
|
|
|
4,182 |
|
|
|
3,016 |
|
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF YEAR |
$ |
3,108 |
|
|
$ |
3,625 |
|
|
$ |
4,182 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL SCHEDULE OF NON-CASH FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change in fair value of cash flow interest rate swap agreements (net of tax expense of $2,178, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$205 and $1,769 in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively) |
$ |
3,553 |
|
|
$ |
335 |
|
|
$ |
2,886 |
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid (received) during the period for: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest, including amount capitalized |
$ |
77,289 |
|
|
$ |
71,328 |
|
|
$ |
71,776 |
|
|
Income taxes |
$ |
28,459 |
|
|
$ |
38,474 |
|
|
$ |
50,525 |
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-7
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(All tables in thousands except per share amounts)
1. Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Organization and Business - Sonic Automotive, Inc. (“Sonic” or the “Company”) is one of the largest automotive retailers in the United States (as measured by total revenue). As of December 31, 2016, Sonic operated 116 franchises in 13 states (representing 25 different brands of cars and light trucks) and 18 collision repair centers. For management and operational reporting purposes, Sonic groups certain franchises together that share management and inventory (principally used vehicles) into “stores.” As of December 31, 2016, Sonic operated 107 franchised dealership stores and five EchoPark® stores. Sonic’s franchised dealerships provide comprehensive services, including (1) sales of both new and used cars and light trucks; (2) sales of replacement parts and performance of vehicle maintenance, manufacturer warranty repairs, and paint and collision repair services (collectively, “Fixed Operations”); and (3) arrangement of extended warranties, service contracts, financing, insurance and other aftermarket products (collectively, “F&I”) for its customers. EchoPark® provides the same services (excluding new vehicle sales and manufacturer warranty repairs) in unique stand-alone specialty retail locations. Sonic’s EchoPark® business operates independently from its franchised new and used dealership sales operations. Sales operations in the first EchoPark® market in Denver, Colorado began in the fourth quarter of 2014.
Principles of Consolidation - All of Sonic’s dealership and non-dealership subsidiaries are wholly owned and consolidated in the accompanying consolidated financial statements except for one 50%-owned dealership that is accounted for under the equity method. All material intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements – In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-17 to simplify the presentation of deferred income taxes. The amendments in this ASU require deferred tax liabilities and assets to be classified as noncurrent in a classified statement of financial position. The current requirement that deferred tax liabilities and assets of a tax-paying component of an entity must be netted and presented as a single amount is not affected by this ASU. For public companies, this ASU is effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods (early adoption is permitted). Sonic adopted this ASU prospectively effective October 1, 2016, and prior periods were not retrospectively adjusted. Accordingly, as of December 31, 2016, a deferred tax asset of approximately $2.4 million and deferred tax liability of approximately $76.4 million are included in other assets and deferred income taxes, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Sonic did not adjust prior periods retrospectively for the new ASU, therefore, as of December 31, 2015, a current deferred tax asset of approximately $13.6 million, a current deferred tax liability of approximately $0.1 million, a noncurrent deferred tax asset of approximately $2.8 million and a noncurrent deferred tax liability of approximately $73.3 million are included in other current assets, other accrued liabilities, other assets and deferred income taxes, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (the “FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2014-09 to amend the accounting guidance on revenue recognition. The amendments in this ASU are intended to provide a more robust framework for addressing revenue issues, improve comparability of revenue recognition practices and improve disclosure requirements. The amendments in this ASU will be applied using either of the following transition methods: (i) a full retrospective approach reflecting the application of the standard in each prior reporting period with the option to elect certain practical expedients, or (ii) a modified retrospective approach with the cumulative effect of initially adopting the standard recognized at the date of adoption (which requires additional footnote disclosures). This ASU is effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Earlier application is permitted only as of reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. Sonic plans to adopt this ASU effective January 1, 2018. While management is still evaluating the method of adoption and the impact of the provisions of this ASU, management expects similar performance obligations to result under this update as compared with deliverables and separate units of accounting currently identified. As a result, management expects the timing of Sonic’s revenue recognition to generally remain the same.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02 to increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. The amendments in this ASU require that leases are classified as either finance or operating leases, a right-of-use asset and lease liability is recognized in the statement of financial position, and repayments are classified within operating activities in the statement of cash flows. The amendments in this ASU are to be applied using a modified retrospective approach and are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2018 (early adoption is permitted). Sonic plans to adopt this ASU effective January 1, 2019. While management is still evaluating the impact of adopting the provisions of this ASU, management
F-8
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
expects that upon adoption of this ASU, the presentation of certain items in Sonic’s consolidated financial position, cash flows and other disclosures will be materially impacted, primarily due to the recognition of a right-of-use asset and an associated liability.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09 to simplify several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions. For public companies, this ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2016 (early adoption is permitted). Sonic adopted this ASU effective January 1, 2017. Upon adoption of this ASU, interim period and annual income tax expense will be affected by stock option exercises and restricted stock vesting activity, potentially creating volatility in Sonic’s effective income tax rate from period to period.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15 related to the classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments on the statement of cash flows. For public companies, this ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2017 (early adoption is permitted). Sonic plans to adopt this ASU effective January 1, 2018. Upon adoption of this ASU, the presentation of certain items in Sonic’s cash flows and other disclosures may be impacted.
Reclassifications - Prior to Sonic’s adoption of ASU 2014-08 beginning with its Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2014, individual dealership franchises sold, terminated or classified as held for sale were reported as discontinued operations. The results of operations of these dealership franchises for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 are reported as discontinued operations for all periods presented. Dealership franchises sold during the year ended December 31, 2014 have not been reclassified to discontinued operations since they were disposed of after March 31, 2014 and they did not meet the criteria in ASU 2014-08. If, in future periods, Sonic determines that a dealership franchise should be reclassified from continuing operations to discontinued operations, previously reported consolidated statements of income will be reclassified in order to reflect the most recent classification.
Use of Estimates - The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires Sonic’s management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the accompanying consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates, particularly related to allowance for credit loss, realization of inventory, intangible asset and deferred tax asset values, reserves for tax contingencies, legal matters, reserves for future commission revenue to be returned to the third-party provider for early termination of customer contracts (“chargebacks”), results reported as continuing and discontinued operations, insurance reserves, lease exit accruals and certain accrued expenses.
Cash and Cash Equivalents - Sonic classifies cash and all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less at the date of purchase, including short-term time deposits and government agency and corporate obligations, as cash and cash equivalents. In the event that Sonic is in a book overdraft cash position as of a reporting date, the book overdraft position is reclassified from cash and cash equivalents to trade accounts payable in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and is reflected as activity in trade accounts payable and other liabilities in the accompanying consolidated statements of cash flows. Sonic was in a book overdraft position in an amount of approximately $8.0 million and $38.5 million, as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Revenue Recognition - Sonic records revenue when vehicles are delivered to customers, when vehicle service work is performed and when parts are delivered. Conditions for completing a sale include having an agreement with the customer, including pricing, and the sales price must be reasonably expected to be collected.
Sonic arranges financing for customers through various financial institutions and receives a commission from the financial institution either in a flat fee amount or in an amount equal to the difference between the interest rates charged to customers over the predetermined interest rates set by the financial institution. Sonic also receives commissions from the sale of various insurance contracts to customers. Sonic may be assessed a chargeback fee in the event of early cancellation of a loan or insurance contract by the customer. Finance and insurance commission revenue is recorded net of estimated chargebacks at the time the related contract is placed with the financial institution.
Sonic also receives commissions from the sale of non-recourse third-party extended service contracts to customers. Under these contracts, the applicable manufacturer or third-party warranty company is directly liable for all warranties provided within the contract. Commission revenue from the sale of these third-party extended service contracts is recorded net of estimated chargebacks at the time of sale.
F-9
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the amounts recorded as allowances for finance, insurance and service contract commission chargeback reserves were $19.2 million and $17.0 million, respectively, and were classified as other accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Floor Plan Assistance - Sonic receives floor plan assistance payments from certain manufacturers. This assistance reduces the carrying value of Sonic’s new vehicle inventory and is recognized as a reduction of cost of sales at the time the vehicle is sold. Amounts recognized as a reduction of cost of sales for continuing operations were $45.0 million, $42.1 million and $39.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Contracts in Transit - Contracts in transit represent customer finance contracts evidencing loan agreements or lease agreements between Sonic, as creditor, and the customer, as borrower, to acquire or lease a vehicle in situations where a third-party finance source has given Sonic initial, non-binding approval to assume Sonic’s position as creditor. Funding and final approval from the finance source is provided upon the finance source’s review of the loan or lease agreement and related documentation executed by the customer at the dealership. These finance contracts are typically funded within ten days of the initial approval of the finance transaction given by the third-party finance source. The finance source is not contractually obligated to make the loan or lease to the customer until it gives its final approval and funds the transaction, and until such final approval is given, the contracts in transit represent amounts due from the customer to Sonic. Contracts in transit are included in receivables, net, on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and totaled $236.4 million at December 31, 2016 and $196.3 million at December 31, 2015.
Accounts Receivable - In addition to contracts in transit, Sonic’s accounts receivable primarily consist of amounts due from the manufacturers for repair services performed on vehicles with a remaining factory warranty and amounts due from third parties from the sale of parts. Sonic evaluates receivables for collectability based on the age of the receivable, the credit history of the customer and past collection experience. The allowance for doubtful accounts receivable was not significant at December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Inventories - Inventories of new vehicles, recorded net of manufacturer credits, and used vehicles, including demonstrators, are stated at the lower of specific cost or market. Inventories of parts and accessories are accounted for using the “first-in, first-out” (“FIFO”) method of inventory accounting and are stated at the lower of FIFO cost or market. Other inventories are primarily service loaner vehicles and, to a lesser extent, vehicle chassis, other supplies and capitalized customer work-in-progress (open customer vehicle repair orders). Other inventories are stated at the lower of specific cost (depreciated cost for service loaner vehicles) or market.
Sonic assesses the valuation of all its vehicle and parts inventories and maintains a reserve where the cost basis exceeds the fair market value. In making this assessment for new vehicles, used vehicles, service loaners and parts inventory, Sonic considers recent internal and external market data and the age of the vehicles to estimate the inventory’s fair market value. The risk with vehicle inventory is minimized by the fact that vehicles can be transferred within Sonic’s network of dealerships. The risk with parts inventories is minimized by the fact that excess or obsolete parts can also be transferred within Sonic’s network of dealerships or can usually be returned to the manufacturer. Recorded inventory reserves were not significant at December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Property and Equipment - Property and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation and amortization are computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Sonic amortizes leasehold improvements over the shorter of the estimated useful life or the remaining lease life. This lease life includes renewal options if a renewal has been determined to be reasonably assured. The range of estimated useful lives is as follows:
|
Leasehold and land improvements |
|
10-30 years |
|
Buildings |
|
10-30 years |
|
Parts and service equipment |
|
7-10 years |
|
Office equipment and fixtures |
|
3-10 years |
|
Company vehicles |
|
3-5 years |
Sonic reviews the carrying value of property and equipment and other long-term assets (other than goodwill and franchise assets) for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. If such an indication is present, Sonic compares the carrying amount of the asset to the estimated undiscounted cash flows related to those assets. Sonic concludes that an asset is impaired if the sum of such expected future cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the related asset. If Sonic determines an asset is impaired, the impairment loss would be the amount by which the carrying amount of the related asset exceeds its fair value. The fair value of the asset would be determined based on the quoted market prices, if available. If quoted market prices are not available, Sonic determines fair value by using a discounted cash flow model. See Note 4, “Property and Equipment,” for a discussion of impairment charges.
F-10
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities - Sonic utilizes derivative financial instruments for the purpose of hedging the risks of certain identifiable and anticipated transactions. Commonly, the types of risks being hedged are those relating to the variability of cash flows caused by fluctuations in interest rates. Sonic documents its risk management strategy and hedge effectiveness at the inception of and during the term of each hedge. As of December 31, 2016, Sonic utilized interest rate cash flow swap agreements to effectively convert a portion of its LIBOR-based variable rate debt to a fixed rate. See Note 6, “Long-Term Debt,” for further discussion of derivative instruments and hedging activities.
Goodwill - Goodwill is recognized to the extent that the purchase price of the acquisition exceeds the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired, including other identifiable intangible assets. In accordance with “Intangibles – Goodwill and Other” in the Accounting Standards Codification (the “ASC”), goodwill is tested for impairment at least annually, or more frequently when events or circumstances indicate that impairment might have occurred. The ASC also states that if an entity determines, based on an assessment of certain qualitative factors, that it is not more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, then the first and second steps of the goodwill impairment test are unnecessary. For its annual impairment assessment as of October 1, 2016, Sonic elected to perform a quantitative step-one assessment. For purposes of goodwill impairment testing, Sonic has two reporting units, which consist of its traditional franchised dealerships and EchoPark®. The carrying value of Sonic’s goodwill (all of which is associated with its franchised dealerships reporting unit) totaled approximately $472.4 million at December 31, 2016.
In evaluating goodwill for impairment, if the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, Sonic would have been required to proceed to the second step of the impairment test. The second step involves allocating the calculated fair value to all of the assets and liabilities of the reporting unit as if the calculated fair value was the purchase price in a business combination. This allocation would include assigning value to any previously unrecognized identifiable assets (including franchise assets) which means the remaining fair value that would be allocated to goodwill would be significantly reduced. See discussion regarding franchise and dealer agreements acquired prior to July 1, 2001 under the heading “Other Intangible Assets” below. Sonic would then compare the fair value of the goodwill resulting from this allocation process to the carrying value of the goodwill with the difference representing the amount of impairment. The purpose of this second step is only to determine the amount of goodwill that should be recorded at fair value on the balance sheet. The recorded amounts of other items on the balance sheet are not adjusted. In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04 to simplify the subsequent measurement of goodwill by eliminating step two from the goodwill impairment test. For public companies, this ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2019 (early adoption is permitted for impairment testing dates after January 1, 2017). Sonic plans to adopt this ASU prior to its impairment test as of October 1, 2017.
Sonic utilized the Market Price (“MP”) method to estimate its enterprise value. The significant inputs in Sonic’s MP method include debt value, stock price and control premium. To the extent the reporting unit’s earnings decline significantly or there are changes in one or more of these inputs that would result in lower valuation results, it could cause the carrying value of the reporting unit to exceed its fair value and thus require Sonic to conduct the second step of the impairment test described above.
Based on the results of Sonic’s step-one test as of October 1, 2016, its Franchised Dealerships’ fair value exceeds its carrying value. As a result, Sonic was not required to complete step two of the impairment evaluation according to “Intangibles – Goodwill and Other” in the ASC. See Note 5, “Intangible Assets and Goodwill,” for further discussion of goodwill.
Other Intangible Assets - The principal identifiable intangible assets other than goodwill acquired in an acquisition are rights under franchise or dealer agreements with manufacturers. Sonic classifies franchise and dealer agreements as indefinite lived intangible assets as it has been Sonic’s experience that renewals have occurred without substantial cost or material modifications to the underlying agreements. As such, Sonic believes that its franchise and dealer agreements will contribute to cash flows for an indefinite period, therefore the carrying amount of franchise rights is not amortized. Franchise and dealer agreements acquired after July 1, 2001 have been included in other intangible assets, net on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Prior to July 1, 2001, franchise and dealer agreements were recorded and amortized as part of goodwill and remain as part of goodwill on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Other intangible assets acquired in acquisitions include favorable lease agreements with definite lives which are amortized on a straight-line basis over the remaining lease term. In accordance with “Intangibles – Goodwill and Other” in the ASC, Sonic evaluates other intangible assets for impairment annually (as of October 1) or more frequently if indicators of impairment exist.
Sonic utilized a discounted cash flow (“DCF”) model to estimate the fair value of the franchise assets for each of its franchises with recorded franchise assets. The significant assumptions in Sonic’s DCF model include projected revenue, weighted average cost of capital (and estimates in the weighted average cost of capital inputs) and residual growth rates. In projecting the franchises’ revenue and growth rates, Sonic develops many assumptions which may include, but are not limited to, revenue growth, internal revenue enhancement initiatives, cost control initiatives, internal investment programs (such as training, technology and infrastructure) and
F-11
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
inventory floor plan borrowing rates. Sonic’s expectation of revenue growth is in part driven by its estimates of new vehicle industry sales volume in future periods. Sonic believes the historic and projected industry sales volume is a good indicator of growth or contraction in the retail automotive industry.
Based on the October 1, 2016 impairment test, Sonic determined that the fair value of the franchise assets exceeded the carrying value of the franchise assets for all of its franchises, requiring no franchise asset impairment charges during the year ended December 31, 2016. See Note 5, “Intangible Assets and Goodwill,” for further discussion of franchise and dealer agreements.
In evaluating its definite life favorable lease assets for impairment, Sonic considered whether the leased asset was being utilized by the dealership and if the dealership operating activities could recover the value of the recorded favorable lease asset. Sonic evaluated its favorable lease assets for impairment as of October 1, 2016 and determined that no impairment was required.
Insurance Reserves - Sonic has various self-insured and high deductible casualty and other insurance programs which require the Company to make estimates in determining the ultimate liability it may incur for claims arising under these programs. These insurance reserves are estimated by management using actuarial evaluations based on historical claims experience, claims processing procedures, medical cost trends and, in certain cases, a discount factor. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, Sonic had $22.7 million and $24.9 million, respectively, reserved for such programs.
Lease Exit Accruals - The majority of Sonic’s dealership properties are leased under long-term operating lease arrangements. When situations arise where the leased properties are no longer utilized in operations, Sonic records accruals for the present value of the lease payments, net of estimated sublease rentals, for the remaining life of the operating leases and other accruals necessary to satisfy the lease commitment to the landlord. These situations could include the relocation of an existing facility or the sale of a dealership where the buyer will not be subleasing the property for either the remaining term of the lease or for an amount of rent equal to Sonic’s obligation under the lease, or situations where a store is closed as a result of the associated franchise being terminated by the manufacturer or Sonic and no other operations continue on the leased property. See Note 12, “Commitments and Contingencies,” for further discussion.
Income Taxes - Income taxes are provided for the tax effects of transactions reported in the accompanying consolidated financial statements and consist of taxes currently due plus deferred taxes. Deferred taxes are provided at enacted tax rates for the tax effects of carryforward items and temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts. As a matter of course, the Company is regularly audited by various taxing authorities and, from time to time, these audits result in proposed assessments where the ultimate resolution may result in the Company owing additional taxes. Sonic’s management believes that the Company’s tax positions comply, in all material respects, with applicable tax law and that the Company has adequately provided for any reasonably foreseeable outcome related to these matters.
From time to time, Sonic engages in transactions in which the tax consequences may be subject to uncertainty. Significant judgment is required in assessing and estimating the tax consequences of these transactions. Sonic determines whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination, including resolution of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits of the position. In evaluating whether a tax position has met the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold, Sonic presumes that the position will be examined by the appropriate taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information. A tax position that does not meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold is measured to determine the amount of benefit to be recognized in the financial statements. The tax position is measured at the largest amount of benefit that is likely to be realized upon ultimate settlement. Sonic adjusts its estimates periodically because of ongoing examinations by and settlements with the various taxing authorities, as well as changes in tax laws, regulations and precedent. See Note 7, “Income Taxes,” for further discussion of Sonic’s uncertain tax positions.
Concentrations of Credit and Business Risk - Financial instruments that potentially subject Sonic to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of cash on deposit with financial institutions. At times, amounts invested with financial institutions exceed Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insurance limits. Concentrations of credit risk with respect to receivables are limited primarily to automobile manufacturers, totaling approximately $92.8 million and $90.3 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and financial institutions (which includes manufacturer-affiliated finance companies and contracts in transit), totaling approximately $265.3 million and $221.6 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Credit risk arising from trade receivables from commercial customers is reduced by the large number of customers comprising the trade receivables balances.
Sonic participates in a program with two of its manufacturer-affiliated finance companies wherein Sonic maintains a deposit balance with the lender that earns floor plan interest rebates based on the agreed upon rate. This deposit balance is not designated as a pre-payment of notes payable – floor plan, nor is it Sonic’s intent to use this amount to offset principal amounts owed under notes
F-12
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
payable – floor plan in the future, although Sonic has the right and ability to do so. The deposit balance of $10.0 million and $74.0 million as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, is classified in other current assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets, because there are restrictions on Sonic’s availability to withdraw these funds under certain circumstances. Changes in this deposit balance are classified as changes in other assets in the cash flows from operating activities section of the accompanying consolidated statements of cash flows. The interest rebate as a result of this deposit balance is classified as a reduction in interest expense, floor plan in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. In the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the reduction in interest expense, floor plan was approximately $0.6 million, $1.5 million and $2.1 million, respectively.
Sonic is subject to a concentration of risk in the event of financial distress or other adverse events related to any of the automobile manufacturers whose franchised dealerships are included in Sonic’s brand portfolio. Sonic purchases its new vehicle inventory from various automobile manufacturers at the prevailing prices available to all franchised dealerships. In addition, Sonic finances a substantial portion of its new vehicle inventory with manufacturer-affiliated finance companies. Sonic’s results of operations could be adversely affected by the manufacturers’ inability to supply Sonic’s dealerships with an adequate supply of new vehicle inventory and related floor plan financing. Sonic also has concentrations of risk related to geographic markets in which its dealerships operate. Changes in overall economic, retail automotive or regulatory environments in one or more of these markets could adversely impact Sonic’s results of operations.
Financial Instruments and Market Risks - As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the fair values of Sonic’s financial instruments including receivables, notes receivable from finance contracts, notes payable - floor plan, trade accounts payable, borrowings under the revolving credit facilities and certain mortgage notes approximated their carrying values due either to length of maturity or existence of variable interest rates that approximate prevailing market rates. See Note 11, “Fair Value Measurements,” for further discussion of the fair value and carrying value of Sonic’s fixed rate long-term debt.
Sonic has variable rate notes payable - floor plan, revolving credit facilities and other variable rate notes that expose Sonic to risks caused by fluctuations in the underlying interest rates. The counterparties to Sonic’s swap transactions consist of large financial institutions. Sonic could be exposed to loss in the event of non-performance by any of these counterparties. See further discussion in Note 6, “Long-Term Debt.”
Advertising - Sonic expenses advertising costs in the period incurred, net of earned cooperative manufacturer credits that represent reimbursements for specific, identifiable and incremental advertising costs. Advertising expense for continuing operations amounted to approximately $61.7 million, $61.6 million and $57.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, and is classified as selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of income.
Sonic has cooperative advertising reimbursement agreements with certain automobile manufacturers it represents. These agreements require Sonic to provide the manufacturer with support for qualified, actual advertising expenditures in order to receive reimbursement under the agreements. It is uncertain whether or not Sonic would maintain the same level of advertising expenditures if these manufacturers discontinued their cooperative programs. Cooperative manufacturer credits classified as an offset to advertising expenses were approximately $26.2 million, $24.2 million and $23.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Segment Information - Sonic has determined it has two reporting segments, Franchised Dealerships and EchoPark®, for purposes of reporting financial condition and results of operations. The Franchised Dealerships segment is comprised of retail automotive franchises that sell new vehicles and buy and sell used vehicles, sell replacement parts, perform vehicle repair and maintenance services, and arrange finance and insurance products. The EchoPark® segment is comprised of stand-alone specialty retail locations that provide customers an opportunity to search, buy, service, finance and sell pre-owned vehicles.
F-13
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
2. Business Acquisitions and Dispositions
Acquisitions
Sonic acquired three stand-alone used vehicle dealership businesses and real estate for approximately $15.9 during the year ended December 31, 2016. These cash outflows were funded by cash from operations and borrowings under Sonic’s floor plan facilities. Sonic did not acquire any businesses during the year ended December 31, 2015. Sonic acquired two luxury franchises, one mid-line import franchise and one domestic franchise during the year ended December 31, 2014, for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $50.9 million in cash, net of cash acquired, including the underlying assets and real estate.
In addition to the three stand-alone used vehicle dealership businesses discussed above, Sonic opened two new manufacturer-awarded open point franchised dealerships and two new EchoPark® stores during the year ended December 31, 2016.
Dispositions
Sonic did not dispose of any dealerships during the year ended December 31, 2016, and disposed of four dealership franchises during the year ended December 31, 2015 and nine dealership franchises during the year ended December 31, 2014. The dispositions during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 generated cash of approximately $ 8.0 million and $74.8 million, respectively. In conjunction with dealership dispositions, Sonic has agreed to indemnify the buyers from certain liabilities and costs arising from operations or events that occurred prior to sale but which may or may not be known at the time of sale, including environmental liabilities and liabilities associated from the breach of representations or warranties made under the agreements. See Note 12, “Commitments and Contingencies,” for further discussion.
Results associated with dealerships classified as discontinued operations were as follows:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Income (loss) from operations |
$ |
(1,100 |
) |
|
$ |
(1,421 |
) |
|
$ |
(2,515 |
) |
|
Gain (loss) on disposal |
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
199 |
|
|
Lease exit accrual adjustments and charges |
|
(1,020 |
) |
|
|
(1,462 |
) |
|
|
152 |
|
|
Pre-tax income (loss) |
$ |
(2,121 |
) |
|
$ |
(2,883 |
) |
|
$ |
(2,164 |
) |
|
Total revenues |
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
Revenues and other activities associated with disposed dealerships that remain in continuing operations were as follows:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Income (loss) from operations |
$ |
(364 |
) |
|
$ |
(4,958 |
) |
|
$ |
(2,475 |
) |
|
Gain (loss) on disposal |
|
(47 |
) |
|
|
2,748 |
|
|
|
11,079 |
|
|
Property and equipment impairment charges |
|
(4 |
) |
|
|
(10,096 |
) |
|
|
(125 |
) |
|
Pre-tax income (loss) |
$ |
(415 |
) |
|
$ |
(12,306 |
) |
|
$ |
8,479 |
|
|
Total revenues |
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
95,168 |
|
|
$ |
311,978 |
|
In the ordinary course of business, Sonic evaluates its dealership franchises for possible disposition based on various strategic and performance criteria. As of December 31, 2016, Sonic did not have any franchises classified as held for sale; however, in the future, Sonic may sell other franchises that are not currently held for sale.
F-14
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
3. Inventories and Related Notes Payable - Floor Plan
Inventories consist of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
New vehicles |
|
$ |
1,088,814 |
|
|
$ |
1,161,490 |
|
|
Used vehicles |
|
|
282,288 |
|
|
|
251,103 |
|
|
Service loaners |
|
|
128,821 |
|
|
|
121,946 |
|
|
Parts, accessories and other |
|
|
70,778 |
|
|
|
65,042 |
|
|
Net inventories |
|
$ |
1,570,701 |
|
|
$ |
1,599,581 |
|
Sonic finances all of its new and certain of its used vehicle inventory through standardized floor plan facilities with a syndicate of financial institutions and manufacturer-affiliated finance companies. The new and used vehicle floor plan facilities bear interest at variable rates based on prime and LIBOR. The weighted average interest rate for Sonic’s new vehicle floor plan facilities, for continuing operations and discontinued operations, was 1.85%, 1.61% and 1.57% for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Sonic’s floor plan interest expense related to the new vehicle floor plan arrangements is partially offset by amounts received from manufacturers in the form of floor plan assistance. Floor plan assistance received is capitalized in inventory and charged against cost of sales when the associated inventory is sold. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, for continuing operations and discontinued operations, Sonic recognized a reduction in cost of sales of approximately $45.0 million, $42.1 million and $39.7 million, respectively, related to manufacturer floor plan assistance.
The weighted average interest rate for Sonic’s used vehicle floor plan facilities, for continuing operations and discontinued operations, was 1.78%, 1.72% and 1.80% for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
The new and used vehicle floor plan facilities are collateralized by vehicle inventories and other assets, excluding franchise and dealer agreements, of the relevant dealership subsidiary. The new and used vehicle floor plan facilities contain a number of covenants, including, among others, covenants restricting Sonic with respect to the creation of liens and changes in ownership, officers and key management personnel. Sonic was in compliance with all of these restrictive covenants as of December 31, 2016.
4. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consists of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Land |
|
$ |
306,457 |
|
|
$ |
260,275 |
|
|
Building and improvements |
|
|
777,766 |
|
|
|
679,712 |
|
|
Software and computer equipment |
|
|
128,366 |
|
|
|
107,086 |
|
|
Parts and service equipment |
|
|
93,901 |
|
|
|
79,219 |
|
|
Office equipment and fixtures |
|
|
86,216 |
|
|
|
76,810 |
|
|
Company vehicles |
|
|
9,107 |
|
|
|
8,478 |
|
|
Construction in progress |
|
|
62,982 |
|
|
|
55,010 |
|
|
Total, at cost |
|
|
1,464,795 |
|
|
|
1,266,590 |
|
|
Less accumulated depreciation |
|
|
(450,184 |
) |
|
|
(379,688 |
) |
|
Subtotal |
|
|
1,014,611 |
|
|
|
886,902 |
|
|
Less assets held for sale (1) |
|
|
(4,231 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
$ |
1,010,380 |
|
|
$ |
886,902 |
|
|
(1) |
Classified in other current assets |
Interest capitalized in conjunction with construction projects and software development was approximately $2.8 million, $1.9 million and $1.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, commitments for facility construction projects totaled approximately $56.5 million.
F-15
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
During the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, property and equipment impairment charges were recorded in continuing operations as noted in the following table:
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|
2016 |
|
$ |
8,063 |
|
|
2015 |
|
$ |
12,210 |
|
|
2014 |
|
$ |
4,394 |
|
Impairment charges related to continuing operations were due to the abandonment of construction and software development projects, the abandonment and disposal of dealership equipment or Sonic’s estimate that based on historical and projected operating losses for certain dealerships, these dealerships would not be able to recover recorded property and equipment asset balances.
5. Intangible Assets and Goodwill
The changes in the carrying amount of franchise assets and goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
|
|
|
Franchise Assets |
|
|
Net Goodwill |
|
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
77,100 |
|
|
$ |
475,929 |
|
(1) |
|
Prior year acquisition allocations |
|
|
1,100 |
|
|
|
(870 |
) |
|
|
Reductions from dispositions |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(1,121 |
) |
|
|
Reductions from impairment |
|
|
(3,300 |
) |
|
|
(2,445 |
) |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
74,900 |
|
|
$ |
471,493 |
|
(1) |
|
Additions through current year acquisitions |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
944 |
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
74,900 |
|
|
$ |
472,437 |
|
(1) |
|
(1) |
Net of accumulated impairment losses of $796,725. |
Goodwill
There was no impairment of goodwill in the year ended December 31, 2016. Sonic impaired approximately $2.4 million of goodwill in the year ended December 31, 2015 related to the disposition of a franchise that was acquired in 2014 and disposed of in 2015.
Other Intangible Assets
Other intangible assets consists of franchise assets and definite life intangible assets, and is presented net of accumulated amortization on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Pursuant to applicable accounting pronouncements, Sonic evaluates its franchise assets and definite life intangible assets for impairment annually (as of October 1) or more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of the asset below its carrying amount. There were no franchise asset impairment charges in the year ended December 31, 2016. Franchise asset impairment charges of $0.9 million and $2.2 million were recorded in continuing operations for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, based on the impairment evaluations performed as of October 1, 2015 and 2014, respectively. In addition, Sonic impaired approximately $2.4 million of franchise assets in the year ended December 31, 2015 related to the disposition of a dealership that was acquired in 2014 and disposed of in 2015. There were no definite life intangible asset impairment charges in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014.
Definite life intangible assets consist of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Favorable lease agreements |
|
$ |
17,318 |
|
|
$ |
17,318 |
|
|
Less accumulated amortization |
|
|
(11,985 |
) |
|
|
(11,342 |
) |
|
Definite life intangibles, net |
|
$ |
5,333 |
|
|
$ |
5,976 |
|
F-16
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
Amortization expense for definite life intangible assets was approximately $0.6 million, $0.6 million and $1.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The initial weighted average amortization period for lease agreements and definite life intangible assets outstanding at December 31, 2016 was 17 years. Expiration dates for these lease agreements range between 2020 and 2027.
Future amortization expense is as follows:
|
Year Ending December 31, |
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
$ |
644 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
644 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
644 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
614 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
475 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
2,312 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
5,333 |
|
6. Long-Term Debt
Long-term debt consists of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
2014 Revolving Credit Facility (1) |
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
4,203 |
|
|
2016 Revolving Credit Facility (2) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
7.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2022 (the “7.0% Notes”) |
|
|
200,000 |
|
|
|
200,000 |
|
|
5.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 (the “5.0% Notes”) |
|
|
289,273 |
|
|
|
300,000 |
|
|
Mortgage notes to finance companies-fixed rate, bearing interest from 3.51% to 7.03% |
|
|
176,369 |
|
|
|
168,410 |
|
|
Mortgage notes to finance companies-variable rate, bearing interest at 1.25 to 2.80 percentage points above one-month or three-month LIBOR |
|
|
227,342 |
|
|
|
150,961 |
|
|
Net debt discount and premium (3) |
|
|
(1,258 |
) |
|
|
(1,562 |
) |
|
Debt issuance costs |
|
|
(13,328 |
) |
|
|
(12,884 |
) |
|
Other |
|
|
4,280 |
|
|
|
5,454 |
|
|
Total debt |
|
$ |
882,678 |
|
|
$ |
814,582 |
|
|
Less current maturities |
|
|
(43,003 |
) |
|
|
(33,437 |
) |
|
Long-term debt |
|
$ |
839,675 |
|
|
$ |
781,145 |
|
F-17
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
|
(1) |
The interest rate on the 2014 Revolving Credit Facility was 225 basis points above LIBOR at December 31, 2015. |
|
(2) |
The interest rate on the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility was 225 basis points above LIBOR at December 31, 2016. |
|
(3) |
December 31, 2016 includes a $1.1 million discount associated with the 7.0% Notes and a $0.2 million discount associated with mortgage notes payable. |
December 31, 2015 includes a $1.3 million discount associated with the 7.0% Notes and a $0.3 million discount associated with mortgage notes payable.
Future maturities of long-term debt are as follows:
|
|
|
Principal |
|
|
Net of Discount/ Premium |
|
||
|
Year Ending December 31, |
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
2017 |
|
$ |
43,127 |
|
|
$ |
43,003 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
55,986 |
|
|
|
55,986 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
19,605 |
|
|
|
19,605 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
51,523 |
|
|
|
51,523 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
45,434 |
|
|
|
45,434 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
681,589 |
|
|
|
680,455 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
897,264 |
|
|
$ |
896,006 |
|
2014 Credit Facilities
Prior to November 30, 2016, Sonic had a syndicated revolving credit facility (the “2014 Revolving Credit Facility”) and syndicated new and used vehicle floor plan credit facilities (the “2014 Floor Plan Facilities” and, together with the 2014 Revolving Credit Facility, the “2014 Credit Facilities”), which were scheduled to mature on August 15, 2019. On November 30 2016, Sonic amended and restated the 2014 Credit Facilities to, among other things, extend the maturity to November 30, 2021. See the heading “2016 Credit Facilities” below for additional information.
2016 Credit Facilities
On November 30, 2016, Sonic entered into an amended and restated syndicated revolving credit facility (the “2016 Revolving Credit Facility”) and amended and restated syndicated new and used vehicle floor plan credit facilities (the “2016 Floor Plan Facilities” and, together with the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility, the “2016 Credit Facilities”), which are scheduled to mature on November 30, 2021. The amended and restated 2016 Credit Facilities extended the scheduled maturity date, increased availability under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility by $25.0 million and increased availability under the 2016 Floor Plan Facilities by $200.0 million, among other things.
Availability under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility is calculated as the lesser of $250.0 million or a borrowing base calculated based on certain eligible assets, less the aggregate face amount of any outstanding letters of credit under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility (the “2016 Revolving Borrowing Base”). The 2016 Revolving Credit Facility may be increased at Sonic’s option up to $300.0 million upon satisfaction of certain conditions. Based on balances as of December 31, 2016, the 2016 Revolving Borrowing Base was approximately $228.5 million. As of December 31, 2016, Sonic had no outstanding borrowings and approximately $21.4 million in outstanding letters of credit under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility, resulting in total borrowing availability of $207.1 million under the 2016 Revolving Credit Facility.
F-18
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
The 2016 Floor Plan Facilities are comprised of a new vehicle revolving floor plan facility (the “2016 New Vehicle Floor Plan Facility”) and a used vehicle revolving floor plan facility (the “2016 Used Vehicle Floor Plan Facility”), subject to a borrowing base, in a combined amount up to $1.015 billion. Sonic may, under certain conditions, request an increase in the 2016 Floor Plan Facilities to a maximum borrowing limit of up to $1.265 billion, which shall be allocated between the 2016 New Vehicle Floor Plan Facility and the 2016 Used Vehicle Floor Plan Facility as Sonic requests, with no more than 30% of the aggregate commitments allocated to the commitments under the 2016 Used Vehicle Floor Plan Facility. Outstanding obligations under the 2016 Floor Plan Facilities are guaranteed by Sonic and certain of its subsidiaries and are secured by a pledge of substantially all of the assets of Sonic and its subsidiaries. The amounts outstanding under the 2016 Credit Facilities bear interest at variable rates based on specified percentages above LIBOR.
Sonic agreed under the 2016 Credit Facilities not to pledge any assets to any third party (other than those explicitly allowed under the amended terms of the 2016 Credit Facilities), including other lenders, subject to certain stated exceptions, including floor plan financing arrangements. In addition, the 2016 Credit Facilities contain certain negative covenants, including covenants which could restrict or prohibit indebtedness, liens, the payment of dividends, capital expenditures and material dispositions and acquisitions of assets as well as other customary covenants and default provisions. Specifically, the 2016 Credit Facilities permit cash dividends on Sonic’s Class A and Class B common stock so long as no event of default (as defined in the 2016 Credit Facilities) has occurred and is continuing and provided that Sonic remains in compliance with all financial covenants under the 2016 Credit Facilities.
7.0% Notes
On July 2, 2012, Sonic issued $200.0 million in aggregate principal amount of unsecured senior subordinated 7.0% Notes which mature on July 15, 2022. The 7.0% Notes were issued at a price of 99.11% of the principal amount thereof, resulting in a yield to maturity of 7.125%. Sonic used the net proceeds from the issuance of the 7.0% Notes and issued approximately 4.1 million shares of its Class A common stock to repurchase all of the outstanding 5.0% Convertible Senior Notes due 2029. Remaining proceeds from the issuance of the 7.0% Notes were used for general corporate purposes, including repurchases of shares of Class A common stock. Interest is payable semi-annually in arrears on January 15 and July 15 of each year.
Sonic may redeem the 7.0% Notes in whole or in part at any time on or after July 15, 2017 at the following redemption prices, which are expressed as percentages of the principal amount:
|
|
|
Redemption Price |
|
|
|
Beginning on July 15, 2017 |
|
|
103.500 |
% |
|
Beginning on July 15, 2018 |
|
|
102.333 |
% |
|
Beginning on July 15, 2019 |
|
|
101.167 |
% |
|
Beginning on July 15, 2020 and thereafter |
|
|
100.000 |
% |
In addition, the indenture provides that holders of the 7.0% Notes may require Sonic to repurchase the 7.0% Notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of the par value of the 7.0% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if Sonic undergoes a change of control (as defined in the indenture).
The indenture governing the 7.0% Notes contains certain specified restrictive covenants. Sonic has agreed not to pledge any assets to any third-party lender of senior subordinated debt except under certain limited circumstances. Sonic also has agreed to certain other limitations or prohibitions concerning the incurrence of other indebtedness, guarantees, liens, certain types of investments, certain transactions with affiliates, mergers, consolidations, issuance of preferred stock, cash dividends to stockholders, distributions, redemptions and the sale, assignment, lease, conveyance or disposal of certain assets. Specifically, the indenture governing the 7.0% Notes limits Sonic’s ability to pay quarterly cash dividends on Sonic’s Class A and Class B common stock in excess of $0.10 per share. Sonic may only pay quarterly cash dividends on Sonic’s Class A and Class B common stock if Sonic complies with the terms of the indenture governing the 7.0% Notes. After giving effect to the applicable restrictions on the payment of dividends under its debt agreements, as of December 31, 2016, Sonic had at least $127.4 million of its net income and retained earnings free of such restrictions. Sonic was in compliance with all restrictive covenants as of December 31, 2016.
Balances outstanding under the 7.0% Notes are guaranteed by all of Sonic’s operating domestic subsidiaries. These guarantees are full and unconditional and joint and several. The parent company has no independent assets or operations. The subsidiaries that are not guarantors are considered to be minor.
Sonic’s obligations under the 7.0% Notes may be accelerated by the holders of 25% of the outstanding principal amount of the 7.0% Notes then outstanding if certain events of default occur, including: (1) defaults in the payment of principal or interest when due;
F-19
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
(2) defaults in the performance, or breach, of Sonic’s covenants under the 7.0% Notes; and (3) certain defaults under other agreements under which Sonic or its subsidiaries have outstanding indebtedness in excess of $35.0 million.
5.0% Notes
On May 9, 2013, Sonic issued $300.0 million in aggregate principal amount of unsecured senior subordinated 5.0% Notes which mature on May 15, 2023. The 5.0% Notes were issued at a price of 100.0% of the principal amount thereof. Sonic used the net proceeds from the issuance of the 5.0% Notes to repurchase all of the outstanding 9.0% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2018. Remaining proceeds from the issuance of the 5.0% Notes were used for general corporate purposes. Interest is payable semi-annually in arrears on May 15 and November 15 of each year. During the year ended December 31, 2016, Sonic repurchased approximately $10.7 million of its outstanding 5.0% Notes for approximately $10.6 million in cash, plus accrued and unpaid interest related thereto.
Sonic may redeem the 5.0% Notes in whole or in part at any time on or after May 15, 2018 at the following redemption prices, which are expressed as percentages of the principal amount:
|
|
|
Redemption Price |
|
|
|
Beginning on May 15, 2018 |
|
|
102.500 |
% |
|
Beginning on May 15, 2019 |
|
|
101.667 |
% |
|
Beginning on May 15, 2020 |
|
|
100.833 |
% |
|
Beginning on May 15, 2021 and thereafter |
|
|
100.000 |
% |
In addition, before May 15, 2018, Sonic may redeem all or a part of the aggregate principal amount of the 5.0% Notes at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 5.0% Notes redeemed plus an applicable premium (as defined in the indenture) and any accrued and unpaid interest as of the redemption date. The indenture also provides that holders of the 5.0% Notes may require Sonic to repurchase the 5.0% Notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of the par value of the 5.0% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if Sonic undergoes a change of control (as defined in the indenture).
The indenture governing the 5.0% Notes contains certain specified restrictive covenants. Sonic has agreed not to pledge any assets to any third-party lender of senior subordinated debt except under certain limited circumstances. Sonic also has agreed to certain other limitations or prohibitions concerning the incurrence of other indebtedness, guarantees, liens, certain types of investments, certain transactions with affiliates, mergers, consolidations, issuance of preferred stock, cash dividends to stockholders, distributions, redemptions and the sale, assignment, lease, conveyance or disposal of certain assets. Specifically, the indenture governing the 5.0% Notes limits Sonic’s ability to pay quarterly cash dividends on Sonic’s Class A and Class B common stock in excess of $0.10 per share. Sonic may only pay quarterly cash dividends on Sonic’s Class A and Class B common stock if Sonic complies with the terms of the indenture governing the 5.0% Notes.
Balances outstanding under the 5.0% Notes are guaranteed by all of Sonic’s operating domestic subsidiaries. These guarantees are full and unconditional and joint and several. The parent company has no independent assets or operations. The subsidiaries that are not guarantors are considered to be minor.
Sonic’s obligations under the 5.0% Notes may be accelerated by the holders of 25% of the outstanding principal amount of the 5.0% Notes then outstanding if certain events of default occur, including: (1) defaults in the payment of principal or interest when due; (2) defaults in the performance, or breach, of Sonic’s covenants under the 5.0% Notes; and (3) certain defaults under other agreements under which Sonic or its subsidiaries have outstanding indebtedness in excess of $50.0 million.
Mortgage Notes
During the year ended December 31, 2016, Sonic obtained approximately $103.4 million in mortgage financing related to ten of its dealership properties. As of December 31, 2016, the weighted average interest rate was 3.74% and the total outstanding principal balance was approximately $403.7 million, related to approximately 45% of Sonic’s operating locations. These mortgage notes require monthly payments of principal and interest through maturity, are secured by the underlying properties and contain certain cross-default provisions. Maturity dates for these mortgage notes range between 2017 and 2033.
Covenants
Sonic agreed under the 2016 Credit Facilities not to pledge any assets to any third party (other than those explicitly allowed under the amended terms of the 2016 Credit Facilities), including other lenders, subject to certain stated exceptions, including floor
F-20
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
plan financing arrangements. In addition, the 2016 Credit Facilities contain certain negative covenants, including covenants which could restrict or prohibit the payment of dividends, capital expenditures and material dispositions of assets as well as other customary covenants and default provisions.
Sonic was in compliance with the covenants under the 2016 Credit Facilities as of December 31, 2016. Financial covenants include required specified ratios (as each is defined in the 2016 Credit Facilities) of:
|
|
|
Covenant |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Minimum Consolidated Liquidity Ratio |
|
|
Minimum Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio |
|
|
Maximum Consolidated Total Lease Adjusted Leverage Ratio |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Required ratio |
|
|
1.05 |
|
|
|
1.20 |
|
|
|
5.75 |
|
|
December 31, 2016 actual |
|
|
1.17 |
|
|
|
1.92 |
|
|
|
4.08 |
|
The 2016 Credit Facilities contain events of default, including cross defaults to other material indebtedness, change of control events and events of default customary for syndicated commercial credit facilities. Upon the future occurrence of an event of default, Sonic could be required to immediately repay all outstanding amounts under the 2016 Credit Facilities.
After giving effect to the applicable restrictions on the payment of dividends under its debt agreements, as of December 31, 2016, Sonic had at least $127.4 million of its net income and retained earnings free of such restrictions. Sonic was in compliance with all restrictive covenants as of December 31, 2016.
In addition, many of Sonic’s facility leases are governed by a guarantee agreement between the landlord and Sonic that contains financial and operating covenants. The financial covenants are identical to those under the 2016 Credit Facilities with the exception of one financial covenant related to the ratio of EBTDAR to rent (as defined in the guarantee agreement) with a required ratio of no less than 1.50 to 1.00. As of December 31, 2016, the ratio was 4.01 to 1.00.
F-21
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
Sonic has interest rate cash flow swap agreements to effectively convert a portion of its LIBOR-based variable rate debt to a fixed rate. The fair value of these swap positions at December 31, 2016 was a net liability of approximately $3.7 million, with $4.1 million included in other accrued liabilities and $2.4 million included in other long-term liabilities, offset partially by an asset of approximately $2.8 million included in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The fair value of these swap positions at December 31, 2015 was a net liability of approximately $10.0 million, with $5.1 million included in other accrued liabilities and $4.9 million included in other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Under the terms of these cash flow swaps, Sonic will receive and pay interest based on the following:
|
Notional Amount |
|
|
Pay Rate |
|
|
Receive Rate (1) |
|
Maturing Date |
||
|
(In millions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
2.3 |
|
|
|
7.100% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR + 1.50% |
|
July 10, 2017 |
|
$ |
7.3 |
|
|
|
4.655% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
December 10, 2017 |
|
$ |
6.6 |
|
(2) |
|
6.860% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR + 1.25% |
|
August 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
6.0 |
|
(2) |
|
6.410% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR + 1.25% |
|
September 12, 2017 |
|
$ |
100.0 |
|
|
|
2.065% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
June 30, 2017 |
|
$ |
100.0 |
|
|
|
2.015% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
June 30, 2017 |
|
$ |
50.0 |
|
|
|
1.320% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
250.0 |
|
(3) |
|
1.887% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
June 30, 2018 |
|
$ |
25.0 |
|
|
|
2.080% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
100.0 |
|
|
|
1.560% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
125.0 |
|
|
|
1.303% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
125.0 |
|
(4) |
|
1.900% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2018 |
|
$ |
50.0 |
|
(5) |
|
2.320% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2019 |
|
$ |
200.0 |
|
(5) |
|
2.313% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2019 |
|
$ |
100.0 |
|
(6) |
|
1.384% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2020 |
|
$ |
125.0 |
|
(5) |
|
1.158% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2019 |
|
$ |
150.0 |
|
(6) |
|
1.310% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2020 |
|
$ |
125.0 |
|
(4) |
|
1.020% |
|
|
one-month LIBOR |
|
July 1, 2018 |
|
(1) |
The one-month LIBOR rate was approximately 0.772% at December 31, 2016. |
|
(2) |
Changes in fair value are recorded through earnings. |
|
(3) |
The effective date of this forward-starting swap is July 3, 2017. |
|
(4) |
The effective date of these forward-starting swaps is July 1, 2017. |
|
(5) |
The effective date of these forward-starting swaps is July 2, 2018. |
|
(6) |
The effective date of these forward-starting swaps is July 1, 2019. |
During the year ended December 31, 2016, Sonic entered into four forward-starting interest rate cash flow swap agreements. These interest rate swaps have been designated and qualify as cash flow hedges and, as a result, changes in the fair value of these swaps are recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) before taxes in the accompanying consolidated statements of comprehensive income.
For interest rate swaps not designated as cash flow hedges, the changes in the fair value of these swaps are recognized through earnings and are included in interest expense, other, net, in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, these items were a benefit of approximately $0.6 million, $0.6 million and $0.5 million, respectively.
For the interest rate swaps that qualify as cash flow hedges, the changes in the fair value of these swaps are recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) in the accompanying consolidated statements of comprehensive income and are disclosed in the supplemental schedule of non-cash financing activities in the accompanying consolidated statements of cash flows. The incremental interest expense (the difference between interest paid and interest received) related to these cash flow swaps was approximately $5.5 million, $7.8 million and $10.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, and is included in interest expense, other, net, in the accompanying consolidated statements of income and the interest paid amount disclosed in the supplemental disclosures of cash flow information in the accompanying consolidated statements of cash flows. The estimated net
F-22
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
expense expected to be reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) into results of operations during the next twelve months is approximately $2.5 million.
7. Income Taxes
The provision for income taxes for continuing operations - (benefit) expense consists of the following:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Current: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
$ |
43,655 |
|
|
$ |
36,241 |
|
|
$ |
36,874 |
|
|
State |
|
|
3,766 |
|
|
|
6,414 |
|
|
|
5,771 |
|
|
Total current |
|
|
47,421 |
|
|
|
42,655 |
|
|
|
42,645 |
|
|
Deferred |
|
|
13,275 |
|
|
|
14,410 |
|
|
|
20,523 |
|
|
Total provision for income taxes for continuing operations - (benefit) expense |
|
$ |
60,696 |
|
|
$ |
57,065 |
|
|
$ |
63,168 |
|
The reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate with Sonic’s federal and state overall effective income tax rate from continuing operations is as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Statutory federal income tax rate |
|
|
35.00 |
% |
|
|
35.00 |
% |
|
|
35.00 |
% |
|
Effective state income tax rate |
|
|
2.04 |
% |
|
|
3.26 |
% |
|
|
3.15 |
% |
|
Valuation allowance adjustments |
|
|
0.85 |
% |
|
|
(0.45 |
%) |
|
|
(0.14 |
%) |
|
Uncertain tax positions |
|
|
0.17 |
% |
|
|
(0.14 |
%) |
|
|
(0.08 |
%) |
|
Other |
|
|
1.05 |
% |
|
|
1.64 |
% |
|
|
1.13 |
% |
|
Effective income tax rate |
|
|
39.11 |
% |
|
|
39.31 |
% |
|
|
39.06 |
% |
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of the temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for tax purposes. Significant components of Sonic’s deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Deferred tax assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accruals and reserves |
|
$ |
34,884 |
|
|
$ |
33,397 |
|
|
State net operating loss carryforwards |
|
|
10,777 |
|
|
|
10,187 |
|
|
Fair value of interest rate swaps |
|
|
1,406 |
|
|
|
3,793 |
|
|
Interest and state taxes associated with the liability for uncertain income tax positions |
|
|
1,746 |
|
|
|
1,725 |
|
|
Other |
|
|
774 |
|
|
|
864 |
|
|
Total deferred tax assets |
|
|
49,587 |
|
|
|
49,966 |
|
|
Deferred tax liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basis difference in inventory |
|
|
(1,506 |
) |
|
|
(1,530 |
) |
|
Basis difference in property and equipment |
|
|
(9,335 |
) |
|
|
(9,850 |
) |
|
Basis difference in goodwill |
|
|
(101,999 |
) |
|
|
(86,504 |
) |
|
Other |
|
|
(3,540 |
) |
|
|
(3,249 |
) |
|
Total deferred tax liability |
|
|
(116,380 |
) |
|
|
(101,133 |
) |
|
Valuation allowance |
|
|
(7,211 |
) |
|
|
(5,880 |
) |
|
Net deferred tax asset (liability) |
|
$ |
(74,004 |
) |
|
$ |
(57,047 |
) |
Net short-term deferred tax asset balances were zero and approximately $13.6 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and are recorded in other current assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Net long-term deferred tax asset balances were approximately $2.4 million and $2.8 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and are recorded in other assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Net short-term deferred tax liability balances were zero and
F-23
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
approximately $0.1 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and are recorded in other accrued liabilities on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Net long-term deferred tax liability balances were approximately $76.4 million and $73.3 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and are recorded in deferred income taxes on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. See Note 1, “Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” for discussion of the adoption of ASU 2015-17 during the year ended December 31, 2016.
Sonic has approximately $294.5 million in gross state net operating loss carryforwards that will expire between 2017 and 2036. Management reviews these carryforward positions, the time remaining until expiration and other opportunities to realize these carryforwards in making an assessment as to whether it is more likely than not that these carryforwards will be realized. The results of future operations, regulatory framework of the taxing authorities and other related matters cannot be predicted with certainty and, therefore, differences from the assumptions used in the development of management’s judgment could occur. As of December 31, 2016, Sonic had recorded a valuation allowance amount of approximately $7.2 million related to certain state net operating loss carryforward deferred tax assets as Sonic determined that it would not be able to generate sufficient state taxable income in the related entities to realize the accumulated net operating loss carryforward balances.
At January 1, 2016, Sonic had liabilities of approximately $5.8 million recorded related to unrecognized tax benefits. Included in the liabilities related to unrecognized tax benefits at January 1, 2016, was approximately $1.1 million related to interest and penalties which Sonic has estimated may be paid as a result of its tax positions. It is Sonic’s policy to classify the expense related to interest and penalties to be paid on underpayments of income taxes within income tax expense. A summary of the changes in the liability related to Sonic’s unrecognized tax benefits is presented below.
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Unrecognized tax benefit liability, January 1 (1) |
|
$ |
4,755 |
|
|
$ |
5,740 |
|
|
$ |
6,693 |
|
|
Prior period positions: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Increases |
|
|
939 |
|
|
|
175 |
|
|
|
181 |
|
|
Decreases |
|
|
(415 |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(66 |
) |
|
Increases from current period positions |
|
|
615 |
|
|
|
184 |
|
|
|
195 |
|
|
Settlements |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
(897 |
) |
|
Lapse of statute of limitations |
|
|
(1,290 |
) |
|
|
(1,114 |
) |
|
|
(170 |
) |
|
Other |
|
|
(247 |
) |
|
|
(230 |
) |
|
|
(196 |
) |
|
Unrecognized tax benefit liability, December 31 (2) |
|
$ |
4,357 |
|
|
$ |
4,755 |
|
|
$ |
5,740 |
|
|
(1) |
Excludes accrued interest and penalties of $1.1 million, $1.2 million and $1.1 million at January 1, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
|
(2) |
Excludes accrued interest and penalties of $0.8 million, $1.1 million and $1.2 million at December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Amount presented is net of state net operating losses of $0.3 million, $0.6 million and $0.8 million at December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
Approximately $3.3 million and $2.6 million of the unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, would ultimately affect the income tax rate if recognized. Included in the December 31, 2016 recorded liability is approximately $0.9 million related to interest and penalties which Sonic has estimated may be paid as a result of its tax positions. Sonic does not anticipate any significant changes in its unrecognized tax benefit liability within the next twelve months.
Sonic and its subsidiaries are subject to U.S. federal income tax as well as income tax of multiple state jurisdictions. Sonic’s 2013 through 2016 U.S. federal income tax returns remain open to examination by the Internal Revenue Service. Sonic and its subsidiaries’ state income tax returns remain open to examination by state taxing authorities for years ranging from 2006 to 2016.
8. Related Parties
Certain of Sonic’s dealerships purchase the zMAX micro-lubricant from Oil-Chem Research Corporation (“Oil-Chem”), a subsidiary of Speedway Motorsports, Inc. (“SMI”), for resale to Fixed Operations customers of Sonic’s dealerships in the ordinary course of business. Sonic’s Executive Chairman, Mr. O. Bruton Smith, is also the Executive Chairman of SMI, and Mr. Smith’s son, Mr. Marcus G. Smith, a greater than 10% beneficial owner of Sonic, is the Chief Executive Officer and President of SMI. Total purchases from Oil-Chem by Sonic dealerships were approximately $2.1 million in each of the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014. Sonic also engaged in other transactions with various SMI subsidiaries in the year ended December 31, 2016, consisting primarily of (i) merchandise and apparel purchases from SMISC Holdings, Inc. (d/b/a SMI Properties), for a net amount of
F-24
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
approximately $0.9 million, and (ii) vehicle sales to various SMI subsidiaries, for a net amount of approximately $0.2 million. Because Messrs. O. Bruton Smith, B. Scott Smith, David Bruton Smith and Marcus G. Smith and Sonic Financial Corporation (“SFC”), an entity jointly controlled by Messrs. O. Bruton Smith, B. Scott Smith, David Bruton Smith and Marcus G. Smith, own collectively approximately 70% of SMI, under applicable SEC rules, the amount of Messrs. O. Bruton Smith’s, B. Scott Smith’s, David Bruton Smith’s and Marcus G. Smith’s interest in these transactions may be deemed to be approximately $1.5 million, $0.6 million and $0.1 million, respectively.
Sonic participates in various aircraft-related transactions with SFC. Such transactions include, but are not limited to, the use of aircraft owned by SFC for business-related travel by Sonic executives, a management agreement with SFC for storage and maintenance of aircraft leased by Sonic from unrelated third parties, and the use of Sonic’s aircraft for business-related travel by certain affiliates of SFC. Sonic incurred net expenses of approximately $0.5 million, $0.6 million and $0.5 million in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, in aircraft-related transactions with these related parties.
Sonic incurred net expenses of approximately $0.8 million, $0.8 million and $0.6 million in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, related to other transactions with various SMI subsidiaries, consisting primarily of merchandise and apparel purchases.
9. Capital Structure and Per Share Data
Preferred Stock - Sonic has 3,000,000 shares of “blank check” preferred stock authorized with such designations, rights and preferences as may be determined from time to time by the Board of Directors. The Board of Directors has designated 300,000 shares of preferred stock as Class A convertible preferred stock, par value $0.10 per share (the “Preferred Stock”), which is divided into 100,000 shares of Series I Preferred Stock, 100,000 shares of Series II Preferred Stock, and 100,000 shares of Series III Preferred Stock. There were no shares of Preferred Stock issued or outstanding at December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Common Stock - Sonic has two classes of common stock. Sonic has authorized 100,000,000 shares of Class A common stock at a par value of $0.01 per share. Class A common stock entitles its holder to one vote per share. Sonic has also authorized 30,000,000 shares of Class B common stock at a par value of $0.01 per share. Class B common stock entitles its holder to ten votes per share, except in certain circumstances. Each share of Class B common stock is convertible into one share of Class A common stock either upon voluntary conversion at the option of the holder, or automatically upon the occurrence of certain events, as provided in Sonic’s charter. The two classes of common stock share equally in dividends and in the event of liquidation.
Share Repurchases - Prior to December 31, 2016, Sonic’s Board of Directors had authorized Sonic to expend up to $595.0 million to repurchase shares of its Class A common stock. As of December 31, 2016, Sonic had repurchased a total of approximately 30.3 million shares of Class A common stock at an average price per share of approximately $17.72 and had redeemed 13,801.5 shares of Class A convertible preferred stock at an average price of $1,000 per share. As of December 31, 2016, Sonic had approximately $45.0 million remaining under the Board’s authorization. Please refer to Note 15, “Subsequent Events,” to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further discussion of the Board’s authorization.
F-25
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
Per Share Data - The calculation of diluted earnings per share considers the potential dilutive effect of stock options and shares under Sonic’s stock compensation plans and Class A common stock purchase warrants. Certain of Sonic’s non-vested restricted stock and restricted stock units contain rights to receive non-forfeitable dividends and, thus, are considered participating securities and are included in the two-class method of computing earnings per share. The following table illustrates the dilutive effect of such items on earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
|
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
From Continuing |
|
|
From Discontinued |
|
|
Net |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operations |
|
|
Operations |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
||||
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
||||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per share amounts) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
45,637 |
|
|
$ |
94,516 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
(1,323 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
93,193 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of participating securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-vested restricted stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(52 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(52 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
45,637 |
|
|
$ |
94,464 |
|
|
$ |
2.07 |
|
|
$ |
(1,323 |
) |
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
$ |
93,141 |
|
|
$ |
2.04 |
|
|
Effect of dilutive securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock compensation plans |
|
|
311 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
45,948 |
|
|
$ |
94,464 |
|
|
$ |
2.06 |
|
|
$ |
(1,323 |
) |
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
$ |
93,141 |
|
|
$ |
2.03 |
|
|
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, 2015 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
From Continuing |
|
|
From Discontinued |
|
|
Net |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operations |
|
|
Operations |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
||||
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
||||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per share amounts) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
50,489 |
|
|
$ |
88,091 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
(1,780 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
86,311 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of participating securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-vested restricted stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(36 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(36 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
50,489 |
|
|
$ |
88,055 |
|
|
$ |
1.74 |
|
|
$ |
(1,780 |
) |
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
$ |
86,275 |
|
|
$ |
1.71 |
|
|
Effect of dilutive securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock compensation plans |
|
|
394 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
50,883 |
|
|
$ |
88,055 |
|
|
$ |
1.73 |
|
|
$ |
(1,780 |
) |
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
$ |
86,275 |
|
|
$ |
1.70 |
|
|
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31, 2014 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
From Continuing |
|
|
From Discontinued |
|
|
|
|
Net |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operations |
|
|
Operations |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Per |
|
||||
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share |
|
||||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Amount |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per share amounts) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
52,065 |
|
|
$ |
98,559 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
(1,342 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
97,217 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of participating securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-vested restricted stock and restricted stock units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(311 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(311 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
52,065 |
|
|
$ |
98,248 |
|
|
$ |
1.89 |
|
|
$ |
(1,342 |
) |
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
$ |
96,906 |
|
|
$ |
1.86 |
|
|
Effect of dilutive securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock compensation plans |
|
|
498 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted earnings (loss) and shares |
|
|
52,563 |
|
|
$ |
98,248 |
|
|
$ |
1.87 |
|
|
$ |
(1,342 |
) |
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
$ |
96,906 |
|
|
$ |
1.84 |
|
In addition to the stock options included in the tables above, options to purchase approximately 0.2 million, 0.4 million and 0.4 million shares of Class A common stock were outstanding during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, but were not included in the computation of diluted net income per share because the options were not dilutive.
F-26
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
10. Employee Benefit Plans
Substantially all of the employees of Sonic are eligible to participate in a 401(k) plan. Contributions by Sonic to the 401(k) plan were approximately $8.0 million, $7.7 million and $7.4 million in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Stock Compensation Plans
Sonic currently has three active stock compensation plans: the Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2004 Stock Incentive Plan (the “2004 Plan”), the Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Stock Incentive Plan (the “2012 Plan”), and the Sonic Automotive, Inc. 2012 Formula Restricted Stock Plan for Non-Employee Directors (the “2012 Formula Plan”). Effective February 19, 2014, new grants of equity awards under the 2004 Plan were no longer permitted. Stock options outstanding, non-vested restricted stock awards and restricted stock units previously granted under the 2004 Plan were unaffected by this change in plan status. Sonic has one additional terminated plan with outstanding grants as of December 31, 2016: the Sonic Automotive, Inc. 1997 Stock Option Plan. Collectively, these plans are referred to as the “Stock Plans.” During the second quarter of 2012, Sonic’s stockholders voted to approve the 2012 Plan and the 2012 Formula Plan, with authorization for issuance of 2,000,000 shares of Class A common stock and 300,000 shares of Class A common stock, respectively. During the second quarter of 2015, Sonic’s stockholders voted to increase the number of shares of Class A common stock authorized for issuance under the 2012 Plan from 2,000,000 shares to 4,000,000 shares.
The Stock Plans were adopted by the Board of Directors in order to attract and retain key personnel. Under the 2012 Plan and the 2004 Plan, options to purchase shares of Class A common stock may be granted to key employees of Sonic and its subsidiaries and to officers, directors, consultants and other individuals providing services to Sonic. The options are granted at the fair market value of Sonic’s Class A common stock at the date of grant, typically vest over a period ranging from six months to three years, are exercisable upon vesting and typically expire ten years from the date of grant. The 2012 Plan and the 2004 Plan also authorized the issuance of restricted stock awards and restricted stock units. Restricted stock award and restricted stock unit grants under the 2012 Plan and the 2004 Plan typically vest over a period ranging from one to three years, but may be longer in certain cases. The 2012 Formula Plan provides for grants of restricted stock awards to non-employee directors and restrictions on those shares expire on the earlier of the first anniversary of the grant date or the day before the next annual meeting of Sonic’s stockholders. Individuals holding non-vested restricted stock awards under the 2012 Plan, the 2012 Formula Plan and the 2004 Plan have voting rights and certain grants may receive dividends on non-vested shares. Individuals holding restricted stock units as of December 31, 2016 granted under the 2012 Plan and the 2004 Plan do not have voting or dividend rights. Sonic issues new shares of Class A common stock to employees and directors to satisfy its option exercise and stock grant obligations. To offset the effects of these transactions, Sonic has historically repurchased its shares of Class A common stock after considering cash flow, market conditions and other factors.
A summary of the status of the stock options related to the Stock Plans is presented below:
|
|
|
Options Outstanding |
|
|
Exercise Price Per Share (Low - High) |
|
Weighted Average Exercise Price Per Share |
|
|
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term |
|
|
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per share data, term in years) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
|
714 |
|
|
$ |
1.81 |
|
- |
30.07 |
|
$ |
17.56 |
|
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
$ |
5,605 |
|
|
Exercised |
|
|
(15 |
) |
|
$ |
1.81 |
|
- |
1.81 |
|
$ |
1.81 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
(260 |
) |
|
$ |
23.30 |
|
- |
26.42 |
|
$ |
25.44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
439 |
|
|
$ |
1.81 |
|
- |
30.07 |
|
$ |
13.42 |
|
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
$ |
5,327 |
|
|
Exercisable |
|
|
439 |
|
|
$ |
1.81 |
|
- |
30.07 |
|
$ |
13.42 |
|
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
$ |
5,327 |
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per option data) |
|
|||||||||
|
Intrinsic value of stock options exercised |
|
$ |
250 |
|
|
$ |
2,511 |
|
|
$ |
1,187 |
|
F-27
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
Sonic recognizes compensation expense within selling, general and administrative expenses related to the stock options in the Stock Plans. No stock option compensation expense was recognized during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 or 2014 as all previous stock option grants were completely vested prior to December 31, 2012.
A summary of the status of non-vested restricted stock award and restricted stock unit grants related to the Stock Plans is presented below:
|
|
|
Non-vested Restricted Stock Awards and Restricted Stock Units |
|
|
Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value per Share |
|
||
|
|
|
(Shares in thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
|
1,831 |
|
|
$ |
23.33 |
|
|
Granted |
|
|
750 |
|
|
$ |
16.30 |
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
(40 |
) |
|
$ |
25.32 |
|
|
Vested |
|
|
(361 |
) |
|
$ |
23.40 |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
2,180 |
|
|
$ |
20.86 |
|
During the year ended December 31, 2016, approximately 725,000 restricted stock units were awarded to Sonic’s executive officers and other key associates under the 2012 Plan. These awards were made in connection with establishing the objective performance criteria for the year ended December 31, 2016 incentive compensation and vest over three years. The majority of the restricted stock units awarded to executive officers and other key associates are subject to forfeiture, in whole or in part, based upon specified measures of Sonic’s earnings per share performance for the year ended December 31, 2016, continuation of employment and compliance with any restrictive covenants contained in an agreement between Sonic and the respective officer or other key associate. Also in the year ended December 31, 2016, approximately 25,000 non-vested restricted stock awards were granted to Sonic’s Board of Directors pursuant to the 2012 Formula Plan and vest on the earlier of the first anniversary of the grant date or the day before the next annual meeting of Sonic’s stockholders. Sonic recognized compensation expense within selling, general and administrative expenses related to restricted stock awards and restricted stock units of approximately $11.2 million, $9.8 million and $7.7 million in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Tax benefits recognized related to restricted stock awards and restricted stock units compensation expense were approximately $4.2 million, $3.7 million and $2.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Total compensation cost related to non-vested restricted stock awards and restricted stock units not yet recognized at December 31, 2016 was approximately $34.7 million and is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 8.5 years.
Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan
On December 7, 2009, the Compensation Committee of Sonic’s Board of Directors approved and adopted the Sonic Automotive, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (the “SERP”) to be effective as of January 1, 2010. The SERP is a nonqualified deferred compensation plan that is unfunded for federal tax purposes. The SERP included 12 active or former members of senior management at December 31, 2016. The purpose of the SERP is to attract and retain key members of management by providing a retirement benefit in addition to the benefits provided by Sonic’s tax-qualified and other nonqualified deferred compensation plans.
The following table sets forth the status of the SERP:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Change in projected benefit obligation: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Obligation at January 1, 2016 |
|
$ |
9,234 |
|
|
$ |
7,976 |
|
|
Service cost |
|
|
1,590 |
|
|
|
1,950 |
|
|
Interest cost |
|
|
383 |
|
|
|
307 |
|
|
Actuarial loss (gain) |
|
|
295 |
|
|
|
(737 |
) |
|
Amendments/settlements/curtailments loss (gain) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Benefits paid |
|
|
(269 |
) |
|
|
(262 |
) |
|
Obligation at December 31, 2016 (1) |
|
$ |
11,233 |
|
|
$ |
9,234 |
|
|
Accumulated benefit obligation |
|
$ |
8,557 |
|
|
$ |
7,115 |
|
F-28
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
|
(1) |
Approximately $11.0 million is included in other long-term liabilities and approximately $0.3 million is included in other accrued liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. |
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Change in fair value of plan assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plan assets at January 1, 2016 |
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
Actual return on plan assets |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Employer contributions |
|
|
269 |
|
|
|
262 |
|
|
Benefits paid |
|
|
(269 |
) |
|
|
(262 |
) |
|
Plan assets at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Funded status recognized |
|
$ |
(11,233 |
) |
|
$ |
(9,234 |
) |
The following table provides the cost components of the SERP:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Service cost |
|
$ |
1,590 |
|
|
$ |
1,950 |
|
|
Interest cost |
|
|
383 |
|
|
|
307 |
|
|
Net pension expense (benefit) |
|
$ |
1,973 |
|
|
$ |
2,257 |
|
The weighted average assumptions used to determine the benefit obligation and net periodic benefit costs consist of:
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
Discount rate |
|
|
4.04 |
% |
|
|
4.21 |
% |
|
Rate of compensation increase |
|
|
3.00 |
% |
|
|
3.00 |
% |
The estimated future benefit payments expected to be paid for each of the next five years and the sum of the payments expected for the next five years thereafter are:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Estimated Future Benefit Payments |
|
|
|
Year Ending December 31, |
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
$ |
265 |
|
|
2018 |
|
$ |
265 |
|
|
2019 |
|
$ |
265 |
|
|
2020 |
|
$ |
364 |
|
|
2021 |
|
$ |
364 |
|
|
2022 - 2026 |
|
$ |
1,820 |
|
Multiemployer Benefit Plan
Six of Sonic’s dealership subsidiaries currently make fixed-dollar contributions to the Automotive Industries Pension Plan (the “AI Pension Plan”) pursuant to collective bargaining agreements between Sonic’s subsidiaries and the International Association of Machinists (the “IAM”) and the International Brotherhood of Teamsters (the “IBT”). The AI Pension Plan is a “multiemployer plan” as defined under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended, and Sonic’s six dealership subsidiaries are among approximately 149 employers that are obligated to make contributions to the AI Pension Plan pursuant to collective bargaining agreements with the IAM, the IBT and other unions. The risks of participating in this multiemployer pension plan are different from single-employer plans in the following aspects:
|
|
• |
assets contributed to the multiemployer pension plan by one employer may be used to provide benefits to employees of other participating employers; |
F-29
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
|
|
• |
if a participating employer stops contributing to the plan, the unfunded obligations of the plan may be borne by the remaining participating employers; and |
|
|
• |
if Sonic chooses to stop participating in the multiemployer pension plan, Sonic may be required to pay the plan an amount based on the underfunded status of the plan, referred to as a withdrawal liability. |
Sonic’s participation in the AI Pension Plan for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 is outlined in the table below. The “EIN/Pension Plan Number” column provides the Employee Identification Number (the “EIN”). Unless otherwise noted, the most recent Pension Protection Act of 2006 (the “PPA”) zone status available in the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 is for the plan’s year-end at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The zone status is based on information that Sonic received from the AI Pension Plan. Among other factors, plans in the red zone are generally less than 65% funded (“Critical Status”), plans in the yellow zone are less than 80% funded, and plans in the green zone are at least 80% funded. The “FIP/RP Status Pending/Implemented” column indicates plans for which a Financial Improvement Plan (the “FIP”) or a Rehabilitation Plan (the “RP”) is either pending or has been implemented. The last column lists the expiration dates of the collective bargaining agreements to which the plan is subject. The number of employees covered by Sonic’s multiemployer pension plans increased 4.8% from December 31, 2014 to December 31, 2015 and increased 2.6% from December 31, 2015 to December 31, 2016, affecting the period-to-period comparability of the contributions for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014.
|
|
|
|
|
Pension Protection Act Zone Status |
|
FIP/RP Status |
|
Sonic Contributions |
|
|
|
|
Collective Bargaining |
|||||||||||
|
Pension |
|
EIN/Pension |
|
|
|
|
|
Pending / |
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
Surcharge |
|
Agreement |
|||||||||
|
Fund |
|
Plan Number |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
Implemented |
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
Imposed |
|
Expiration Date (1) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
AI Pension Plan |
|
94-1133245 |
|
Red |
|
Red |
|
RP Implemented |
|
$ |
150 |
|
|
$ |
140 |
|
|
$ |
148 |
|
|
Yes |
|
Between August 31, 2014 and November 29, 2017 |
|
(1) |
Collective bargaining agreement expiration dates vary by union and dealership. Dates shown represent the range of the earliest and latest stated expirations for Sonic’s union employees, noting certain of Sonic’s collective bargaining agreements are expired as of December 31, 2016 and are currently under negotiation. |
Sonic’s participating dealership subsidiaries were not listed in the AI Pension Plan’s Form 5500 as providing more than 5% of the total contributions for the plan years ended December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014. In June 2006, Sonic received information that the AI Pension Plan was substantially underfunded as of December 31, 2005. In July 2007, Sonic received updated information that the AI Pension Plan continued to be substantially underfunded as of December 31, 2006, with the amount of such underfunding increasing versus year end 2005. In March 2008, the Board of Trustees of the AI Pension Plan notified participants, participating employers and local unions that the AI Pension Plan’s actuary, in accordance with the requirements of the PPA, had issued a certification that the AI Pension Plan was in Critical Status effective with the plan year commencing January 1, 2008. In conjunction with the AI Pension Plan’s Critical Status, the Board of Trustees of the AI Pension Plan adopted a rehabilitation plan that implements reductions or eliminations of certain adjustable benefits that were previously available under the AI Pension Plan (including some forms of early retirement benefits, and disability and death benefits, among other items), and also implemented a requirement on all participating employers to increase employer contributions to the AI Pension Plan for a seven-year period which commenced in 2013. As of April 2015, the AI Pension Plan’s actuary certified that the AI Pension Plan remained in Critical Status for the plan year commencing January 1, 2015. According to publicly available information, in September 2016, the AI Pension Plan made a formal application for approval of suspension of benefits with the U.S. Treasury Department, which, if approved by the Treasury Department, would implement a benefit reduction effective July 1, 2017 for participants in the AI Pension Plan. The filing included an Actuarial Certification of Plan Status as of January 1, 2016 that the AI Pension Plan previously filed with the U.S. Internal Revenue Service on March 30, 2016, which reported that the AI Pension Plan was in critical and declining status as of January 1, 2016 and further notified that the AI Pension Plan is making the scheduled progress in meeting the requirements of the plan’s previously-adopted Rehabilitation Plan. The September 2016 filing with the Treasury Department also included an Actuarial Certification of Plan Solvency as of July 1, 2016 with the actuarial firm’s projection that the proposed suspensions of benefits are reasonably estimated to enable the AI Pension Plan to avoid insolvency assuming the proposed suspensions of benefits continue indefinitely and the benefit accrual reduction becomes effective upon the proposed July 1, 2017 suspension effective date. Under applicable federal law, any employer contributing to a multiemployer pension plan that completely ceases participating in the plan while the plan is underfunded is subject to payment of such employer’s assessed share of the aggregate unfunded vested benefits of the plan. In certain circumstances, an employer can be assessed withdrawal liability for a partial withdrawal from a multiemployer pension plan. In addition, if the financial condition of the
F-30
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
AI Pension Plan were to continue to deteriorate to the point that the AI Pension Plan is forced to terminate and be administered by the Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (the “PBGC”), the participating employers could be subject to assessments by the PBGC to cover the participating employers’ assessed share of the unfunded vested benefits. If any of these adverse events were to occur in the future, it could result in a substantial withdrawal liability assessment to Sonic.
11. Fair Value Measurements
In determining fair value, Sonic uses various valuation approaches including market, income and/or cost approaches. “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures” in the ASC establishes a hierarchy for inputs used in measuring fair value that maximizes the use of observable inputs and minimizes the use of unobservable inputs by requiring that the most observable inputs be used when available. Observable inputs are inputs that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability developed based on market data obtained from sources independent of Sonic. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect Sonic’s assumptions about the assumptions market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability developed based on the best information available in the circumstances. The hierarchy is broken down into three levels based on the reliability of inputs as follows:
Level 1 – Valuations based on quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that Sonic has the ability to access. Assets utilizing Level 1 inputs include marketable securities that are actively traded including the value of Sonic’s stock or public bonds.
Level 2 – Valuations based on quoted prices in markets that are not active or for which all significant inputs are observable, either directly or indirectly. Assets and liabilities utilizing Level 2 inputs include cash flow swap instruments and deferred compensation plan balances.
Level 3 – Valuations based on inputs that are unobservable and significant to the overall fair value measurement. Asset and liability measurements utilizing Level 3 inputs include those used in estimating fair value of non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities in purchase acquisitions, those used in assessing impairment of property, plant and equipment and other intangibles and those used in the reporting unit valuation in the annual goodwill impairment evaluation.
The availability of observable inputs can vary and is affected by a wide variety of factors. To the extent that valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment required by Sonic in determining fair value is greatest for assets and liabilities categorized in Level 3. In certain cases, the inputs used to measure fair value may fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy. In such cases, for disclosure purposes, the level in the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value measurement is disclosed is determined based on the lowest level input (Level 3 being the lowest level) that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Fair value is a market-based measure considered from the perspective of a market participant who holds the asset or owes the liability rather than an entity-specific measure. Therefore, even when market assumptions are not readily available, Sonic’s own assumptions are set to reflect those that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability at the measurement date. Sonic uses inputs that are current as of the measurement date, including during periods when the market may be abnormally high or abnormally low. Accordingly, fair value measurements can be volatile based on various factors that may or may not be within Sonic’s control.
F-31
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
Assets or liabilities recorded at fair value in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
|
|
|
Fair Value Based on Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash surrender value of life insurance policies (1) |
|
$ |
31,475 |
|
|
$ |
29,055 |
|
|
|
Cash flow swaps designated as hedges (1) |
|
|
2,772 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
34,247 |
|
|
$ |
29,055 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flow swaps designated as hedges (2) |
|
$ |
6,135 |
|
|
$ |
9,094 |
|
|
|
Cash flow swaps not designated as hedges (3) |
|
|
346 |
|
|
|
913 |
|
|
|
Deferred compensation plan (4) |
|
|
14,824 |
|
|
|
13,551 |
|
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
$ |
21,305 |
|
|
$ |
23,558 |
|
|
|
(1) |
Included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. |
As of December 31, 2016, approximately $3.7 million and $2.4 million were included in other accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
|
(2) |
As of December 31, 2016, approximately $0.3 million was included in other accrued liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2015, approximately $4.6 million and $4.5 million were included in other accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. |
|
(3) |
As of December 31, 2015, approximately $0.5 million and $0.4 million were included in other accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. |
|
(4) |
Included in other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. |
The carrying value of assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis but not completely adjusted to fair value in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2016, are included in the table below. Certain components of long-lived assets held and used have been adjusted to fair value through impairment charges as discussed in Note 4, “Property and Equipment” and Note 5, “Intangible Assets and Goodwill.”
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Significant |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unobservable |
|
|
Total Gains / |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inputs |
|
|
(Losses) for the |
|
||
|
|
|
Balance as of |
|
|
(Level 3) as of |
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Long-lived assets held and used (1) |
|
$ |
1,010,380 |
|
|
$ |
1,010,380 |
|
|
$ |
(8,063 |
) |
|
Goodwill (2) |
|
$ |
472,437 |
|
|
$ |
472,437 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
Franchise assets (2) |
|
$ |
74,900 |
|
|
$ |
74,900 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
(1) |
See Notes 1 and 4 for discussion. |
|
(2) |
See Notes 1 and 5 for discussion. |
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the fair values of Sonic’s financial instruments, including receivables, notes receivable from finance contracts, notes payable - floor plan, trade accounts payable, borrowings under the revolving credit facilities and certain mortgage notes, approximate their carrying values due either to length of maturity or existence of variable interest rates that approximate prevailing market rates.
F-32
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
The fair value and carrying value of Sonic’s fixed rate long-term debt were as follows:
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Fair Value |
|
|
Carrying Value |
|
|
Fair Value |
|
|
Carrying Value |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
7.0% Notes (1) |
|
$ |
211,000 |
|
|
$ |
198,871 |
|
|
$ |
211,000 |
|
|
$ |
198,708 |
|
|
5.0% Notes (1) |
|
$ |
284,934 |
|
|
$ |
289,273 |
|
|
$ |
284,250 |
|
|
$ |
300,000 |
|
|
Mortgage Notes (2) |
|
$ |
185,979 |
|
|
$ |
176,369 |
|
|
$ |
174,007 |
|
|
$ |
168,410 |
|
|
Other (2) |
|
$ |
4,057 |
|
|
$ |
4,280 |
|
|
$ |
5,192 |
|
|
$ |
5,457 |
|
|
(1) |
As determined by market quotations as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively (Level 1). |
|
(2) |
As determined by discounted cash flows (Level 3). |
12. Commitments and Contingencies
Facility and Equipment Leases
For the year ended December 31, 2016, Sonic recognized approximately $1.4 million of lease exit expense, which consists of $1.0 million of interest expense and $0.4 million related to adjustments to lease exit accruals recorded in previous years for the present value of the lease payments, net of estimated sublease rentals, for the remaining life of the operating leases and other accruals necessary to satisfy the lease commitment to the landlord. A summary of the activity of these operating lease accruals consists of the following:
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
14,527 |
|
|
Lease exit expense (1) |
|
|
1,386 |
|
|
Payments (2) |
|
|
(6,123 |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
9,790 |
|
|
(1) |
Expense of approximately $0.1 million is recorded in interest expense, other, net and expense of approximately $0.3 million is recorded in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. In addition, expense of approximately $1.0 million is recorded in income (loss) from discontinued operations in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. |
|
(2) |
Amount is recorded as an offset to rent expense in selling, general and administrative expenses, with approximately $0.7 million in continuing operations and $5.4 million in income (loss) from discontinued operations in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. |
Sonic leases facilities for the majority of its dealership operations under operating lease arrangements. These facility lease arrangements normally have fifteen- to twenty-year terms with one or two five- to ten-year renewal options and do not contain provisions for contingent rent related to the dealership’s operations. Many of the leases are subject to the provisions of a guaranty and subordination agreement that contains financial and affirmative covenants. Sonic was in compliance with these covenants at December 31, 2016. Approximately 10% of these facility leases have payments that may vary based on interest rates.
Minimum future lease payments for facility leases and future receipts from subleases as required under non-cancelable operating leases for both continuing and discontinued operations based on current interest rates in effect are as follows:
|
|
|
Future Minimum Lease Payments, Net |
|
|
Receipts from Future Subleases |
|
||
|
Year Ending December 31, |
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
2017 |
|
$ |
87,663 |
|
|
$ |
(10,363 |
) |
|
2018 |
|
$ |
79,585 |
|
|
$ |
(8,486 |
) |
|
2019 |
|
$ |
64,550 |
|
|
$ |
(7,373 |
) |
|
2020 |
|
$ |
41,319 |
|
|
$ |
(6,912 |
) |
|
2021 |
|
$ |
32,217 |
|
|
$ |
(5,541 |
) |
|
Thereafter |
|
$ |
96,657 |
|
|
$ |
(15,419 |
) |
F-33
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
Total lease expense for continuing operations for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 was approximately $94.6 million, $98.2 million and $106.0 million, respectively. Total lease expense for discontinued operations for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 was approximately $0.9 million and $1.4 million, respectively. Total lease income for discontinued operations for the year ended December 31, 2014 was approximately $0.9 million. Total lease expense or income for discontinued operations includes the effects of lease exit accrual adjustments for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, including a benefit of approximately $1.4 million related to a lease exit accrual adjustment for the extension of a sublease during the year ended December 31, 2014. The total net contingent rent benefit related to a decrease in interest rates since the underlying leases commenced was approximately $1.8 million and $0.1 million for continuing and discontinued operations, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2016, and was approximately $2.0 million and $0.1 million for continuing and discontinued operations, respectively, for each of the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014.
Many of Sonic’s facility operating leases are subject to affirmative and financial covenant provisions related to a subordination and guaranty agreement executed with the landlord of many of its facility properties. The required financial covenants related to certain lease agreements are as follows:
|
|
|
Covenant |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
Minimum Consolidated Liquidity Ratio |
|
|
Minimum Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio |
|
|
Maximum Consolidated Total Lease Adjusted Leverage Ratio |
|
|
Minimum EBTDAR to Rent Ratio |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Required ratio |
|
|
1.05 |
|
|
|
1.20 |
|
|
|
5.75 |
|
|
|
1.50 |
|
|
December 31, 2016 actual |
|
|
1.17 |
|
|
|
1.92 |
|
|
|
4.08 |
|
|
|
4.01 |
|
Guarantees and Indemnifications
In accordance with the terms of Sonic’s operating lease agreements, Sonic’s dealership subsidiaries, acting as lessees, generally agree to indemnify the lessor from certain exposure arising as a result of the use of the leased premises, including environmental exposure and repairs to leased property upon termination of the lease. In addition, Sonic has generally agreed to indemnify the lessor in the event of a breach of the lease by the lessee.
In connection with dealership dispositions and facility relocations, certain of Sonic’s subsidiaries have assigned or sublet to the buyer its interests in real property leases associated with such dealerships. In general, the subsidiaries retain responsibility for the performance of certain obligations under such leases, including rent payments, and repairs to leased property upon termination of the lease, to the extent that the assignee or sublessee does not perform. These obligations are included within the future minimum lease payments, net, in the table above. In the event the sublessees do not perform their obligations, Sonic remains liable for the lease payments. As of December 31, 2016, the total amount relating to this risk was approximately $54.1 million, which is the total of the receipts from future subleases in the table above under the heading “Facility and Equipment Leases.” However, there are situations where Sonic has assigned a lease to the buyer and Sonic was not able to obtain a release from the landlord. In these situations, although Sonic is no longer the primary obligor, Sonic is contingently liable if the buyer does not perform under the lease terms. The total estimated minimum lease payments remaining related to these leases totaled approximately $1.0 million at December 31, 2016. However, in accordance with the terms of the assignment and sublease agreements, the assignees and sublessees have generally agreed to indemnify Sonic and its subsidiaries in the event of non-performance. Additionally, in connection with certain dispositions, Sonic has obtained indemnifications from the parent company or owners of these assignees and sublessees in the event of non-performance.
F-34
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
In accordance with the terms of agreements entered into for the sale of Sonic’s dealerships, Sonic generally agrees to indemnify the buyer from certain liabilities and costs arising subsequent to the date of sale, including environmental exposure and exposure resulting from the breach of representations or warranties made in accordance with the agreement. While Sonic’s exposure with respect to environmental remediation and repairs is difficult to quantify, Sonic’s maximum exposure associated with these general indemnifications was approximately $0.5 million at December 31, 2016. These indemnifications expire within a period of one to three years following the date of sale. The estimated fair value of these indemnifications was not material and the amount recorded for this contingency was not significant at December 31, 2016.
Sonic also guarantees the floor plan commitments of its 50%-owned joint venture, the amount of which was approximately $2.8 million at December 31, 2016.
Legal Matters
Sonic is involved, and expects to continue to be involved, in numerous legal and administrative proceedings arising out of the conduct of its business, including regulatory investigations and private civil actions brought by plaintiffs purporting to represent a potential class or for which a class has been certified. Although Sonic vigorously defends itself in all legal and administrative proceedings, the outcomes of pending and future proceedings arising out of the conduct of Sonic’s business, including litigation with customers, employment-related lawsuits, contractual disputes, class actions, purported class actions and actions brought by governmental authorities, cannot be predicted with certainty. An unfavorable resolution of one or more of these matters could have a material adverse effect on Sonic’s business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows or prospects.
Included in other accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities at December 31, 2016 was approximately $0.3 million and $0.2 million, respectively, in reserves that Sonic was holding for pending proceedings. Included in other accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities at December 31, 2015 was approximately $0.3 million and $0.2 million, respectively, for such reserves. Except as reflected in such reserves, Sonic is currently unable to estimate a range of reasonably possible loss, or a range of reasonably possible loss in excess of the amount accrued, for pending proceedings.
13. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The changes in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) for the year ended December 31, 2016 are as follows:
|
|
|
Gains and Losses on Cash Flow Hedges |
|
|
Defined Benefit Pension Plan |
|
|
Total Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
(5,638 |
) |
|
$ |
6 |
|
|
$ |
(5,632 |
) |
|
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications (1) |
|
|
95 |
|
|
|
(183 |
) |
|
|
(88 |
) |
|
|
Amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (2) |
|
|
3,458 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
3,458 |
|
|
|
Net current-period other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
3,553 |
|
|
|
(183 |
) |
|
|
3,370 |
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
(2,085 |
) |
|
$ |
(177 |
) |
|
$ |
(2,262 |
) |
|
|
(1) |
Net of tax expense of $59 related to gains and losses on cash flow hedges, and tax benefit of $112 related to the defined benefit pension plan. |
|
(2) |
Net of tax expense of $2,119. |
See the heading “Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities” in Note 6, “Long-Term Debt,” for further discussion of Sonic’s cash flow hedges. For further discussion of Sonic’s defined benefit pension plan, see Note 10, “Employee Benefit Plans.”
14. Segment Information
As of December 31, 2016, Sonic had two operating segments: Franchised Dealerships and EchoPark®. The Franchised Dealerships segment is comprised of retail automotive franchises that sell new vehicles and buy and sell used vehicles, sell replacement parts, perform vehicle repair and maintenance services, and arrange finance and insurance products. The EchoPark® segment is comprised of stand-alone specialty retail locations that provide customers an opportunity to search, buy, service, finance and sell pre-owned vehicles.
F-35
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
The operating segments identified above are the business activities of Sonic for which discrete financial information is available and for which operating results are regularly reviewed by Sonic’s chief operating decision maker to assess operating performance and allocate resources. Sonic’s chief operating decision maker is a group of three individuals consisting of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and President, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, and Executive Vice President of Operations. The Company has determined that its operating segments also represent its reportable segments.
Reportable segment revenue, segment income, floor plan interest expense, depreciation and amortization, capital expenditures and total assets are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
9,602,562 |
|
|
$ |
9,547,236 |
|
|
$ |
9,191,661 |
|
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
129,217 |
|
|
|
77,063 |
|
|
|
5,438 |
|
|
Total consolidated revenues |
|
$ |
9,731,779 |
|
|
$ |
9,624,299 |
|
|
$ |
9,197,099 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Segment income (loss) (1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
217,306 |
|
|
$ |
213,224 |
|
|
$ |
230,733 |
|
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
(12,113 |
) |
|
|
(17,257 |
) |
|
|
(15,913 |
) |
|
Total segment income (loss) |
|
|
205,193 |
|
|
|
195,967 |
|
|
|
214,820 |
|
|
Interest expense, other, net |
|
|
(50,106 |
) |
|
|
(50,910 |
) |
|
|
(53,190 |
) |
|
Other income (expense), net |
|
|
125 |
|
|
|
99 |
|
|
|
97 |
|
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations before taxes |
|
$ |
155,212 |
|
|
$ |
145,156 |
|
|
$ |
161,727 |
|
|
(1) Segment income (loss) for each segment is defined as operating income less floor plan interest expense. |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Floor plan interest expense: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
26,777 |
|
|
$ |
20,727 |
|
|
$ |
18,727 |
|
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
939 |
|
|
|
599 |
|
|
|
66 |
|
|
Total floor plan interest expense |
|
$ |
27,716 |
|
|
$ |
21,326 |
|
|
$ |
18,793 |
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
73,635 |
|
|
$ |
65,766 |
|
|
$ |
58,001 |
|
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
3,811 |
|
|
|
3,033 |
|
|
|
259 |
|
|
Total depreciation and amortization |
|
$ |
77,446 |
|
|
$ |
68,799 |
|
|
$ |
58,260 |
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Capital expenditures: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
$ |
170,876 |
|
|
$ |
148,593 |
|
|
$ |
117,129 |
|
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
35,356 |
|
|
|
24,656 |
|
|
|
29,303 |
|
|
Total capital expenditures |
|
$ |
206,232 |
|
|
$ |
173,249 |
|
|
$ |
146,432 |
|
F-36
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Franchised Dealerships |
|
|
|
$ |
2,095,777 |
|
|
$ |
2,211,232 |
|
|
EchoPark® |
|
|
|
|
128,125 |
|
|
|
76,808 |
|
|
Corporate and other: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and Cash Equivalents |
|
|
|
|
3,108 |
|
|
|
3,625 |
|
|
Goodwill, Net |
|
|
|
|
472,437 |
|
|
|
471,493 |
|
|
Other Intangible Assets, Net |
|
|
|
|
80,233 |
|
|
|
80,876 |
|
|
Other Corporate and other assets |
|
|
|
|
859,656 |
|
|
|
718,347 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
|
|
$ |
3,639,336 |
|
|
$ |
3,562,381 |
|
15. Subsequent Events
Subsequent to December 31, 2016, Sonic’s Board of Directors authorized an additional $100.0 million to repurchase shares of Sonic’s Class A common stock, increasing Sonic’s remaining repurchase authorization to approximately $145.0 million before including the effect of any share repurchases subsequent to December 31, 2016.
16. Summary of Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
The following table summarizes Sonic’s results of operations as presented in the accompanying consolidated statements of income by quarter for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015:
|
|
|
First Quarter |
|
|
Second Quarter |
|
|
Third Quarter |
|
|
Fourth Quarter |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per share data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total revenues (1) |
|
$ |
2,234,626 |
|
|
$ |
2,382,312 |
|
|
$ |
2,557,928 |
|
|
$ |
2,556,913 |
|
|
Gross profit (1) |
|
$ |
345,150 |
|
|
$ |
353,305 |
|
|
$ |
359,085 |
|
|
$ |
371,734 |
|
|
Net income (loss) (2) |
|
$ |
14,624 |
|
|
$ |
22,822 |
|
|
$ |
18,111 |
|
|
$ |
37,636 |
|
|
Earnings (loss) per common share - Basic (2) (3) |
|
$ |
0.31 |
|
|
$ |
0.50 |
|
|
$ |
0.40 |
|
|
$ |
0.84 |
|
|
Earnings (loss) per common share - Diluted (2) (3) |
|
$ |
0.31 |
|
|
$ |
0.50 |
|
|
$ |
0.40 |
|
|
$ |
0.83 |
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total revenues (1) |
|
$ |
2,235,516 |
|
|
$ |
2,423,740 |
|
|
$ |
2,494,408 |
|
|
$ |
2,470,635 |
|
|
Gross profit (1) |
|
$ |
334,959 |
|
|
$ |
355,554 |
|
|
$ |
360,251 |
|
|
$ |
363,848 |
|
|
Net income (loss) (2) |
|
$ |
13,967 |
|
|
$ |
14,781 |
|
|
$ |
26,505 |
|
|
$ |
31,058 |
|
|
Earnings (loss) per common share - Basic (2) (3) |
|
$ |
0.27 |
|
|
$ |
0.29 |
|
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
|
$ |
0.62 |
|
|
Earnings (loss) per common share - Diluted (2) (3) |
|
$ |
0.27 |
|
|
$ |
0.29 |
|
|
$ |
0.52 |
|
|
$ |
0.62 |
|
|
(1) |
Results are for continuing operations. |
|
(2) |
Results include both continuing operations and discontinued operations. |
|
(3) |
The sum of net income per common share for the quarters may not equal the full year amount due to weighted average common shares being calculated on a quarterly versus annual basis. |
Operations are subject to seasonal variations. The first quarter generally contributes less operating profits than the second, third and fourth quarters. Parts and service demand remains more stable throughout the year.
Net income for the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2016 includes a pre-tax benefit of approximately $14.8 million related to an original equipment manufacturer emissions-related settlement and a pre-tax benefit of approximately $0.4 million related to lease exit and storm damage accrual adjustments, offset partially by pre-tax impairment charges of approximately $1.8 million primarily
F-37
SONIC AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
related to the write-off of certain construction project costs and pre-tax charges of approximately $0.5 million related to lease exit accrual adjustments.
Net income for the third quarter ended September 30, 2016 includes approximately $6.1 million of pre-tax impairment charges related to dealership facility construction projects, pre-tax charges of approximately $2.3 million related to storm damage and legal accrual adjustments and pre-tax charges of $1.0 million related to lease exit accrual adjustments.
Net income for the first quarter ended March 31, 2016 includes pre-tax charges of approximately $6.0 million related to storm damage, offset partially by a pre-tax benefit of approximately $0.5 million related to lease exit accrual adjustments.
Net income for the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2015 includes approximately $2.3 of pre-tax gain from the sale of dealership franchises, offset partially by approximately $1.3 million of pre-tax impairment charges.
Net income for the second quarter ended June 30, 2015 includes a pre-tax gain of approximately $1.1 million from the sale of dealership franchises, offset by approximately $10.5 million of pre-tax impairment charges and approximately $4.2 million of pre-tax charges related to storm damage and legal settlements.
Net income for the first quarter ended March 31, 2015 includes approximately $6.2 million of pre-tax impairment charges and approximately $0.9 million of pre-tax severance expense.
F-38